Cloud Search를 사용하면 직원이 내부 데이터 저장소에서 내부 문서, 데이터베이스 필드, CRM 데이터와 같은 정보를 검색할 수 있습니다.
아키텍처 개요
그림 1은 Cloud Search 구현의 주요 구성요소를 보여줍니다.
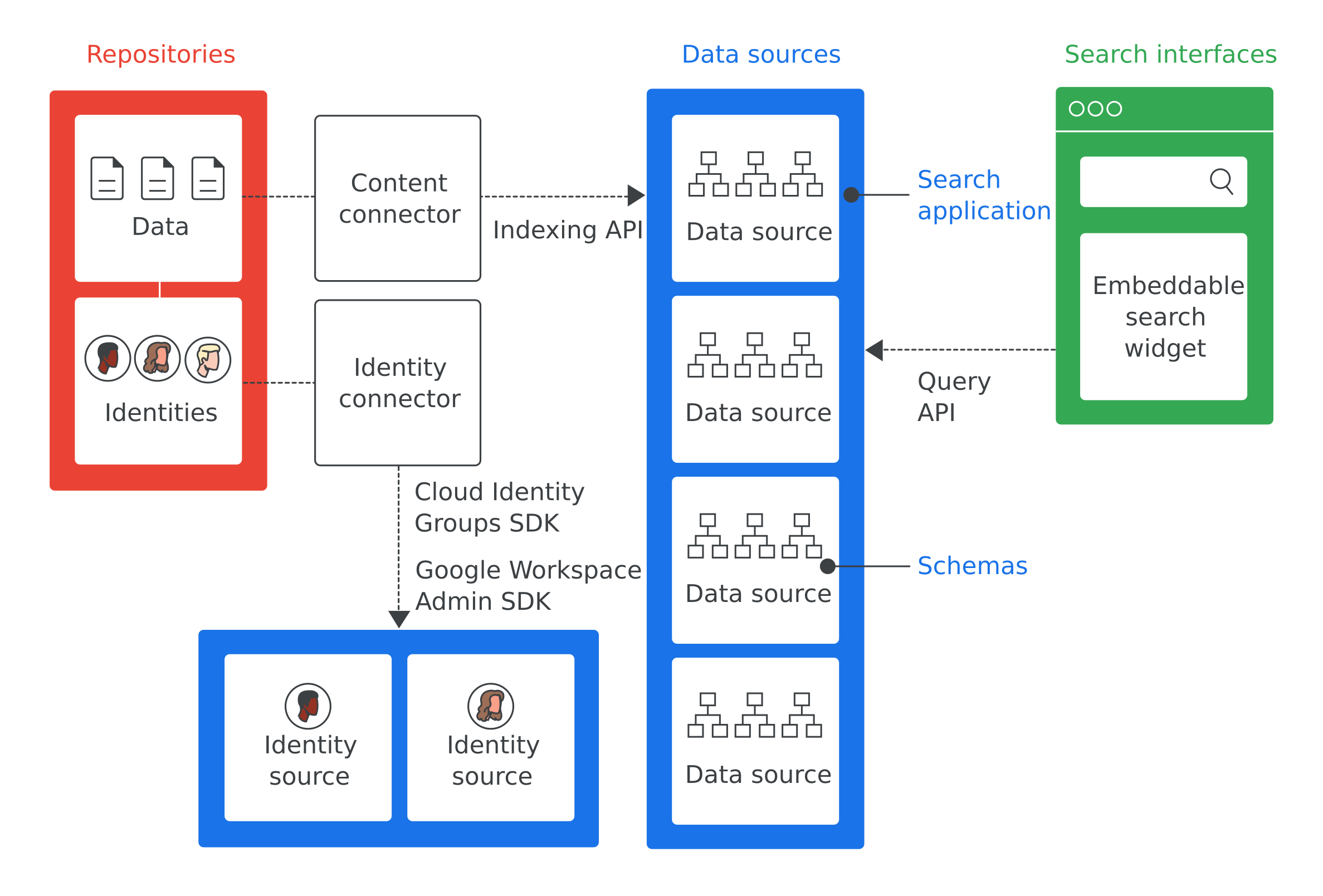
그림 1에서 가장 중요한 용어의 정의는 다음과 같습니다.
- 저장소
- 기업에서 데이터를 저장하는 데 사용하는 소프트웨어(예: 직원 정보를 저장하는 데 사용되는 데이터베이스)
- 데이터 소스
- Cloud Search에서 색인을 생성하고 저장하는 저장소의 데이터
- 검색 인터페이스
- 직원이 데이터 소스를 검색하는 데 사용하는 사용자 인터페이스입니다. 휴대전화나 데스크톱 컴퓨터와 같은 모든 기기용 검색 인터페이스를 개발할 수 있습니다. Google에서 제공하는 검색 위젯을 배포하여 내부 웹사이트 내에서 검색할 수도 있습니다. 각 검색에는 고객 서비스 도구 내와 같은 검색 컨텍스트를 식별하는 검색 애플리케이션 ID가 포함됩니다. cloudsearch.google.com 사이트에 검색 인터페이스가 있습니다.
- 검색 애플리케이션
- 설정 그룹이 검색 인터페이스와 연결된 경우 검색에 관한 컨텍스트 정보가 제공됩니다. 컨텍스트 정보에는 검색에 사용되는 데이터 소스 및 검색 순위가 포함됩니다. 검색 애플리케이션에는 결과 필터링 메커니즘도 포함되어 있으며, 특정 기간 동안 수행된 쿼리 수와 같은 데이터 소스에 대한 보고 기능을 지원합니다.
- 스키마
- Cloud Search를 위해 엔터프라이즈 저장소에서 데이터를 표현하는 방법을 간략히 보여주는 데이터 구조. 스키마는 사용자가 데이터를 필터링하고 보는 방식과 같은 직원의 Cloud Search 환경을 정의합니다.
- 콘텐츠 커넥터
- 엔터프라이즈 저장소의 데이터를 순회하고 데이터 소스를 채우는 소프트웨어 프로그램입니다.
- ID 커넥터
- 기업 ID (사용자 및 그룹)를 Cloud Search에 필요한 ID에 동기화하는 소프트웨어 프로그램입니다.
Cloud Search 사용 사례
Cloud Search의 사용 사례 예:
- 직원이 다른 직원이 작성한 회사 정책, 문서, 콘텐츠를 검색해야 하는 경우
- 고객 서비스 팀원이 관련 문제해결 문서를 찾아 고객에게 보내야 하는 경우
- 직원이 회사 프로젝트에 관한 내부 정보를 검색해야 하는 경우
- 영업 담당자가 특정 고객의 모든 지원 문제 상태를 보고 싶어 하는 경우
- 직원들이 회사 관련 용어의 정의를 알고 싶어 하는 경우
Cloud Search를 구현하는 첫 번째 단계는 관련 사용 사례를 파악하는 것입니다.
Cloud Search 구현
기본적으로 Cloud Search는 Google 문서 및 스프레드시트와 같은 Google Workspace 데이터의 색인을 생성합니다. Google Workspace 데이터용 Cloud Search를 구현할 필요가 없습니다. 하지만 타사 데이터베이스에 저장된 데이터, Windows 파일 공유, OneDrive 같은 파일 시스템 또는 SharePoint 같은 인트라넷 포털과 같은 Google Workspace 이외 데이터용 Cloud Search를 구현해야 합니다. 다음 단계에 따라 기업용 Cloud Search를 구현하세요.
- Cloud Search로 해결할 수 있는 사용 사례를 파악합니다.
- 사용 사례와 관련된 데이터가 들어 있는 저장소를 식별합니다.
- 각 저장소의 데이터에 대한 액세스를 관리하기 위해 회사에서 사용하는 ID 시스템을 식별합니다.
- Google Cloud Search API에 대한 액세스를 구성합니다.
- Cloud Search에 데이터 소스 추가하기
- 각 데이터 소스의 스키마를 만들고 등록합니다.
- 저장소에 사용할 수 있는 콘텐츠 커넥터가 있는지 확인합니다. 사전 제작된 커넥터 목록은 Cloud Search 커넥터 디렉터리를 참고하세요. 콘텐츠 커넥터를 사용할 수 있다면 9단계로 건너뜁니다.
- 콘텐츠 커넥터를 생성하여 각 저장소의 데이터에 액세스하고 Cloud Search 데이터 소스에 색인을 생성합니다.
- ID 커넥터가 필요한지 확인합니다. ID 커넥터가 필요 없다면 11단계로 건너뜁니다.
- ID 커넥터를 생성하여 저장소 또는 기업 ID를 Google ID에 매핑합니다.
- 검색 애플리케이션을 설정합니다.
- 검색 인터페이스를 생성하여 검색 쿼리를 수행합니다.
- 커넥터 및 검색 인터페이스를 배포합니다. 사전 제작된 커넥터를 사용한 경우 커넥터에 관한 안내를 따라 커넥터를 받고 배포하세요. 사용 가능한 커넥터는 Cloud Search 커넥터 디렉터리에 나열되어 있습니다.
다음 단계
- Cloud Search 시작하기 가이드를 시도해 봅니다.
- Cloud Search를 사용할 사용 사례를 파악합니다.
- 이러한 사용 사례와 관련된 저장소를 식별합니다.
- 저장소에서 사용하는 ID 시스템을 식별합니다.
- Cloud Search API에 대한 액세스 구성을 진행합니다.