Một trong những tính năng độc đáo của ứng dụng dành cho thiết bị di động là nhận biết vị trí. Người dùng mang theo thiết bị di động ở mọi nơi, do vậy việc thêm tính năng nhận biết vị trí vào ứng dụng giúp người dùng có được trải nghiệm phù hợp với bối cảnh hơn.
Mã mẫu
Kho lưu trữ ApiDemos trên GitHub có các mẫu minh hoạ cách sử dụng vị trí trên bản đồ:
Kotlin
- MyLocationDemoActivity: Sử dụng lớp Vị trí của tôi, bao gồm cả các quyền trong thời gian chạy
- LocationSourceDemoActivity: Sử dụng
LocationSourcetuỳ chỉnh - CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap: Tìm vị trí hiện tại của một thiết bị Android và hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm (doanh nghiệp hoặc điểm tham quan khác) tại vị trí đó. Xem hướng dẫn về cách hiện thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm hiện tại trên bản đồ.
Java
- MyLocationDemoActivity: Sử dụng lớp Vị trí của tôi, bao gồm cả các quyền trong thời gian chạy
- LocationSourceDemoActivity: Sử dụng
LocationSourcetuỳ chỉnh - CurrentPlaceDetailsOnMap: Tìm vị trí hiện tại của một thiết bị Android và hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm (doanh nghiệp hoặc điểm tham quan khác) tại vị trí đó. Xem hướng dẫn về cách hiện thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm hiện tại trên bản đồ.
Làm việc với dữ liệu vị trí
Dữ liệu vị trí mà thiết bị Android có thể truy cập bao gồm vị trí hiện tại của thiết bị (được xác định chính xác bằng cách kết hợp nhiều công nghệ), hướng và phương thức di chuyển, cũng như việc thiết bị có di chuyển qua ranh giới địa lý (hay còn gọi là hàng rào địa lý) được xác định trước hay không. Tuỳ thuộc vào nhu cầu của ứng dụng, bạn có thể chọn một trong số các cách làm việc với dữ liệu vị trí:
- Lớp Vị trí của tôi là một cách đơn giản để hiển thị vị trí của thiết bị trên bản đồ. Báo cáo này không cung cấp dữ liệu.
- Bạn nên dùng Location API của Dịch vụ Google Play cho tất cả các yêu cầu theo chương trình về dữ liệu vị trí.
- Giao diện
LocationSourcecho phép bạn cung cấp một nhà cung cấp vị trí tuỳ chỉnh.
Quyền truy cập thông tin vị trí
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn cần truy cập vào vị trí của người dùng, bạn phải yêu cầu cấp quyền bằng cách thêm quyền truy cập thông tin vị trí có liên quan trên Android vào ứng dụng của mình.
Android cung cấp 2 quyền truy cập thông tin vị trí: ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION và ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. Quyền mà bạn chọn sẽ xác định độ chính xác của vị trí do API trả về.
android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION– Cho phép API trả về thông tin vị trí gần đúng của thiết bị. Quyền này cung cấp thông tin ước đoán về vị trí thiết bị từ các dịch vụ vị trí, như mô tả trong tài liệu về độ chính xác của vị trí ước chừng.android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION– Cho phép API xác định vị trí chính xác nhất có thể từ các trình cung cấp vị trí hiện có, bao gồm Hệ thống định vị toàn cầu (GPS) cũng như dữ liệu Wi-Fi và mạng di động.
Thêm các quyền vào tệp kê khai ứng dụng
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn chỉ cần thông tin vị trí ước chừng để hoạt động, hãy thêm quyền ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION vào tệp kê khai của ứng dụng:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myapp" > ... <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/> ... </manifest>
Tuy nhiên, nếu cần thông tin vị trí chính xác, hãy thêm cả quyền ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION và ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION vào tệp kê khai của ứng dụng:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myapp" > ... <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/> ... </manifest>
Yêu cầu quyền khi bắt đầu chạy
Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) giới thiệu một mô hình mới để xử lý các quyền, giúp đơn giản hoá quy trình cho người dùng khi họ cài đặt và nâng cấp ứng dụng. Nếu ứng dụng của bạn nhắm đến API cấp 23 trở lên, bạn có thể sử dụng mô hình quyền mới.
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn hỗ trợ mô hình quyền mới và thiết bị đang chạy Android 6.0 (Marshmallow) trở lên, thì người dùng không phải cấp bất kỳ quyền nào khi cài đặt hoặc nâng cấp ứng dụng. Ứng dụng phải kiểm tra để xem có quyền cần thiết hay không khi bắt đầu chạy và yêu cầu quyền nếu không có. Hệ thống sẽ hiển thị một hộp thoại cho người dùng để yêu cầu cấp quyền.
Để mang lại trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người dùng, bạn cần yêu cầu cấp quyền theo bối cảnh. Nếu thông tin vị trí là yếu tố thiết yếu để ứng dụng của bạn hoạt động, thì bạn nên yêu cầu quyền truy cập thông tin vị trí khi khởi động ứng dụng. Một cách hay để thực hiện việc này là sử dụng màn hình chào mừng hoặc trình hướng dẫn giúp người dùng hiểu rõ lý do cần có quyền.
Nếu ứng dụng chỉ yêu cầu quyền này cho một phần chức năng, thì bạn nên yêu cầu quyền truy cập thông tin vị trí vào thời điểm ứng dụng thực hiện hành động yêu cầu quyền này.
Ứng dụng phải xử lý một cách thích hợp trường hợp người dùng không cấp quyền. Ví dụ: nếu cần có quyền cho một tính năng cụ thể, thì ứng dụng có thể tắt tính năng đó. Nếu quyền này là cần thiết để ứng dụng hoạt động, thì ứng dụng có thể tắt tất cả chức năng và thông báo cho người dùng rằng họ cần cấp quyền.
Mã mẫu sau đây kiểm tra quyền bằng cách sử dụng thư viện AndroidX trước khi bật lớp Vị trí của tôi. Sau đó, ứng dụng sẽ xử lý kết quả của yêu cầu cấp quyền bằng cách triển khai ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback từ Thư viện hỗ trợ:
Kotlin
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.kotlindemos import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat import com.example.common_ui.R import com.example.kotlindemos.PermissionUtils.PermissionDeniedDialog.Companion.newInstance import com.example.kotlindemos.PermissionUtils.isPermissionGranted import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment /** * This demo shows how GMS Location can be used to check for changes to the users location. The * "My Location" button uses GMS Location to set the blue dot representing the users location. * Permission for [Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] and [Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] * are requested at run time. If either permission is not granted, the Activity is finished with an error message. */ class MyLocationDemoActivity : SamplesBaseActivity(), OnMyLocationButtonClickListener, OnMyLocationClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback, OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback { /** * Flag indicating whether a requested permission has been denied after returning in * [.onRequestPermissionsResult]. */ private var permissionDenied = false private lateinit var map: GoogleMap override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.my_location_demo) val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) applyInsets(findViewById<View?>(R.id.map_container)) } override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { map = googleMap googleMap.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this) googleMap.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this) enableMyLocation() } /** * Enables the My Location layer if the fine location permission has been granted. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun enableMyLocation() { // 1. Check if permissions are granted, if so, enable the my location layer if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED ) { map.isMyLocationEnabled = true return } // 2. If if a permission rationale dialog should be shown if (ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) || ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) { PermissionUtils.RationaleDialog.newInstance( LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE, true ).show(supportFragmentManager, "dialog") return } // 3. Otherwise, request permission ActivityCompat.requestPermissions( this, arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ), LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE ) } override fun onMyLocationButtonClick(): Boolean { Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT) .show() // Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs // (the camera animates to the user's current position). return false } override fun onMyLocationClick(location: Location) { Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n$location", Toast.LENGTH_LONG) .show() } override fun onRequestPermissionsResult( requestCode: Int, permissions: Array<String>, grantResults: IntArray ) { if (requestCode != LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE) { super.onRequestPermissionsResult( requestCode, permissions, grantResults ) return } if (isPermissionGranted( permissions, grantResults, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) || isPermissionGranted( permissions, grantResults, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) { // Enable the my location layer if the permission has been granted. enableMyLocation() } else { // Permission was denied. Display an error message // Display the missing permission error dialog when the fragments resume. permissionDenied = true } } override fun onResumeFragments() { super.onResumeFragments() if (permissionDenied) { // Permission was not granted, display error dialog. showMissingPermissionError() permissionDenied = false } } /** * Displays a dialog with error message explaining that the location permission is missing. */ private fun showMissingPermissionError() { newInstance(true).show(supportFragmentManager, "dialog") } companion object { /** * Request code for location permission request. * * @see .onRequestPermissionsResult */ private const val LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE = 1 } }
Java
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapdemo; import android.Manifest.permission; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import android.Manifest; import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android.location.Location; import android.os.Bundle; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat; import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat; import android.widget.Toast; /** * This demo shows how GMS Location can be used to check for changes to the users location. The "My * Location" button uses GMS Location to set the blue dot representing the users location. * Permission for {@link android.Manifest.permission#ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION} and {@link * android.Manifest.permission#ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION} are requested at run time. If either * permission is not granted, the Activity is finished with an error message. */ public class MyLocationDemoActivity extends SamplesBaseActivity implements OnMyLocationButtonClickListener, OnMyLocationClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback, ActivityCompat.OnRequestPermissionsResultCallback { /** * Request code for location permission request. * * @see #onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[]) */ private static final int LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE = 1; /** * Flag indicating whether a requested permission has been denied after returning in {@link * #onRequestPermissionsResult(int, String[], int[])}. */ private boolean permissionDenied = false; private GoogleMap map; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(com.example.common_ui.R.layout.my_location_demo); SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); applyInsets(findViewById(com.example.common_ui.R.id.map_container)); } @Override public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) { map = googleMap; map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this); map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this); enableMyLocation(); } /** * Enables the My Location layer if the fine location permission has been granted. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private void enableMyLocation() { // 1. Check if permissions are granted, if so, enable the my location layer if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); return; } // 2. Otherwise, request location permissions from the user. PermissionUtils.requestLocationPermissions(this, LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE, true); } @Override public boolean onMyLocationButtonClick() { Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); // Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs // (the camera animates to the user's current position). return false; } @Override public void onMyLocationClick(@NonNull Location location) { Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n" + location, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } @Override public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) { if (requestCode != LOCATION_PERMISSION_REQUEST_CODE) { super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults); return; } if (PermissionUtils.isPermissionGranted(permissions, grantResults, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) || PermissionUtils .isPermissionGranted(permissions, grantResults, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)) { // Enable the my location layer if the permission has been granted. enableMyLocation(); } else { // Permission was denied. Display an error message // Display the missing permission error dialog when the fragments resume. permissionDenied = true; } } @Override protected void onResumeFragments() { super.onResumeFragments(); if (permissionDenied) { // Permission was not granted, display error dialog. showMissingPermissionError(); permissionDenied = false; } } /** * Displays a dialog with error message explaining that the location permission is missing. */ private void showMissingPermissionError() { PermissionUtils.PermissionDeniedDialog .newInstance(true).show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "dialog"); } }
Lớp Vị trí của tôi
Bạn có thể dùng lớp Vị trí của tôi và nút Vị trí của tôi để cho người dùng thấy vị trí hiện tại của họ trên bản đồ. Gọi mMap.setMyLocationEnabled() để bật lớp Vị trí của tôi trên bản đồ.
Mẫu sau đây minh hoạ cách sử dụng đơn giản của lớp Vị trí của tôi:
Kotlin
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.google.maps.example.kotlin import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.maps.example.R internal class MyLocationLayerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMyLocationButtonClickListener, OnMyLocationClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_location) val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment mapFragment.getMapAsync(this) } @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { // TODO: Before enabling the My Location layer, you must request // location permission from the user. This sample does not include // a request for location permission. map.isMyLocationEnabled = true map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this) map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this) } override fun onMyLocationClick(location: Location) { Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n$location", Toast.LENGTH_LONG) .show() } override fun onMyLocationButtonClick(): Boolean { Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT) .show() // Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs // (the camera animates to the user's current position). return false } }
Java
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.google.maps.example; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.location.Location; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; class MyLocationLayerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements GoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener, GoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_location); SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { // TODO: Before enabling the My Location layer, you must request // location permission from the user. This sample does not include // a request for location permission. map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); map.setOnMyLocationButtonClickListener(this); map.setOnMyLocationClickListener(this); } @Override public void onMyLocationClick(@NonNull Location location) { Toast.makeText(this, "Current location:\n" + location, Toast.LENGTH_LONG) .show(); } @Override public boolean onMyLocationButtonClick() { Toast.makeText(this, "MyLocation button clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT) .show(); // Return false so that we don't consume the event and the default behavior still occurs // (the camera animates to the user's current position). return false; } }
Khi lớp Vị trí của tôi được bật, nút Vị trí của tôi sẽ xuất hiện ở góc trên cùng bên phải của bản đồ. Khi người dùng nhấp vào nút này, máy ảnh sẽ đặt bản đồ vào vị trí hiện tại của thiết bị (nếu có). Vị trí được biểu thị trên bản đồ bằng một chấm màu xanh dương nhỏ nếu thiết bị đang đứng yên hoặc bằng một hình chữ V nếu thiết bị đang di chuyển.
Ảnh chụp màn hình sau đây cho thấy nút Vị trí của tôi ở trên cùng bên phải và chấm màu xanh dương Vị trí của tôi ở giữa bản đồ:
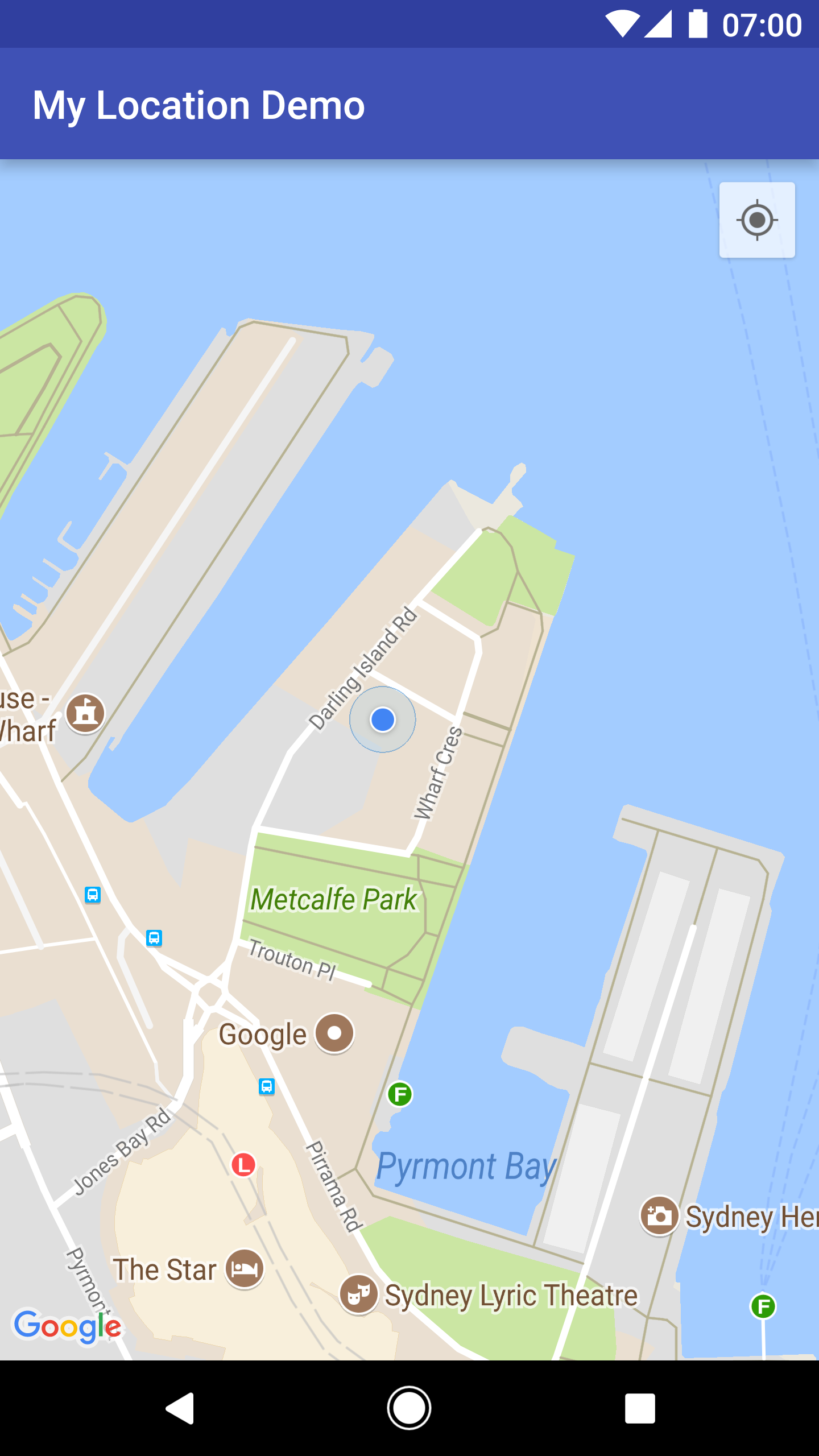
Bạn có thể ngăn nút Vị trí của tôi xuất hiện bằng cách gọi UiSettings.setMyLocationButtonEnabled(false).
Ứng dụng của bạn có thể phản hồi các sự kiện sau:
- Nếu người dùng nhấp vào nút Vị trí của tôi, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ nhận được một lệnh gọi lại
onMyLocationButtonClick()từGoogleMap.OnMyLocationButtonClickListener. - Nếu người dùng nhấp vào dấu chấm màu xanh dương Vị trí của tôi, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ nhận được lệnh gọi lại
onMyLocationClick()từGoogleMap.OnMyLocationClickListener.
Location API của Dịch vụ Google Play
Location API của Dịch vụ Google Play là phương thức ưu tiên để thêm tính năng nhận biết vị trí vào ứng dụng Android của bạn. Công cụ này có chức năng cho phép bạn:
- Xác định vị trí của thiết bị.
- Lắng nghe các thay đổi về vị trí.
- Xác định phương tiện giao thông nếu thiết bị đang di chuyển.
- Tạo và giám sát các khu vực địa lý được xác định trước, còn gọi là hàng rào địa lý.
API vị trí giúp bạn dễ dàng tạo các ứng dụng tiết kiệm pin và nhận biết vị trí. Giống như Maps SDK dành cho Android, Location API được phân phối trong SDK Dịch vụ Google Play. Để biết thêm thông tin về Location API, vui lòng tham khảo lớp học Android Giúp ứng dụng của bạn nhận biết được vị trí hoặc Tài liệu tham khảo về Location API. Các ví dụ về mã được đưa vào SDK Dịch vụ Google Play.
