Neste tutorial, mostramos como adicionar um mapa do Google ao seu app Android, incluindo um marcador (também chamado de alfinete), para indicar um local específico.
Siga o tutorial e crie um app Android usando o SDK do Maps para Android. O ambiente recomendado para desenvolvedores é o Android Studio.
Acessar o código
Clone ou faça o download do repositório de exemplos da API Google Maps para Android v2 do GitHub (em inglês).
Confira a versão Java da atividade:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker; import android.os.Bundle; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } /** * Manipulates the map when it's available. * The API invokes this callback when the map is ready to be used. * This is where we can add markers or lines, add listeners or move the camera. In this case, * we just add a marker near Sydney, Australia. * If Google Play services is not installed on the device, the user receives a prompt to install * Play services inside the SupportMapFragment. The API invokes this method after the user has * installed Google Play services and returned to the app. */ @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { // Add a marker in Sydney, Australia, // and move the map's camera to the same location. LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)); } }
Confira a versão em Kotlin da atividade:
// Copyright 2020 Google LLC // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); // you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. // You may obtain a copy of the License at // // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 // // Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software // distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, // WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. // See the License for the specific language governing permissions and // limitations under the License. package com.example.mapwithmarker import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions /** * An activity that displays a Google map with a marker (pin) to indicate a particular location. */ class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) } override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney)) } }
Configurar seu projeto de desenvolvimento
Siga estas etapas para criar o projeto de tutorial no Android Studio.
- Faça o download e instale o Android Studio.
- Adicione o pacote Google Play Services ao Android Studio.
- Clone ou faça o download do repositório de exemplos da API Google Maps Android v2 (link em inglês), caso não tenha feito isso no início do tutorial.
Importe o projeto do tutorial:
- No Android Studio, selecione File > New > Import Project.
- Acesse o local onde você salvou o repositório de exemplos da API Google Maps Android v2 após fazer o download.
- Encontre o projeto MapWithMarker neste local:
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/java/MapWithMarker(Java) ou
PATH-TO-SAVED-REPO/android-samples/tutorials/kotlin/MapWithMarker(Kotlin) - Selecione o diretório do projeto e clique em Open. O Android Studio vai criar seu projeto usando a ferramenta Gradle.
Ativar as APIs necessárias e gerar uma chave de API
Para concluir este tutorial, você precisa de um projeto do Google Cloud com as APIs necessárias ativadas e uma chave de API que possa usar o SDK do Maps para Android. Confira mais detalhes em:
Adicionar a chave de API ao seu app
- Abra o arquivo
local.propertiesdo projeto. Adicione a string a seguir e substitua
YOUR_API_KEYpelo valor da sua chave de API:MAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYQuando você cria o app, o plug-in Secrets Gradle para Android (link em inglês) copia a chave de API e a disponibiliza como uma variante de build no manifesto do Android, como explicado abaixo.
Criar e executar o app
Para criar e executar o app, faça o seguinte:
Conecte um dispositivo Android ao computador. Siga as instruções se você quiser ativar as opções para desenvolvedores no seu dispositivo Android e permitir que o sistema detecte o aparelho.
Também é possível usar o AVD Manager para configurar um dispositivo virtual. Ao escolher um emulador, selecione uma imagem que inclua as APIs do Google. Para mais detalhes, consulte o artigo Configurar um projeto do Android Studio.
No Android Studio, clique na opção de menu Run ou no ícone do botão de reprodução. Escolha um dispositivo quando solicitado.
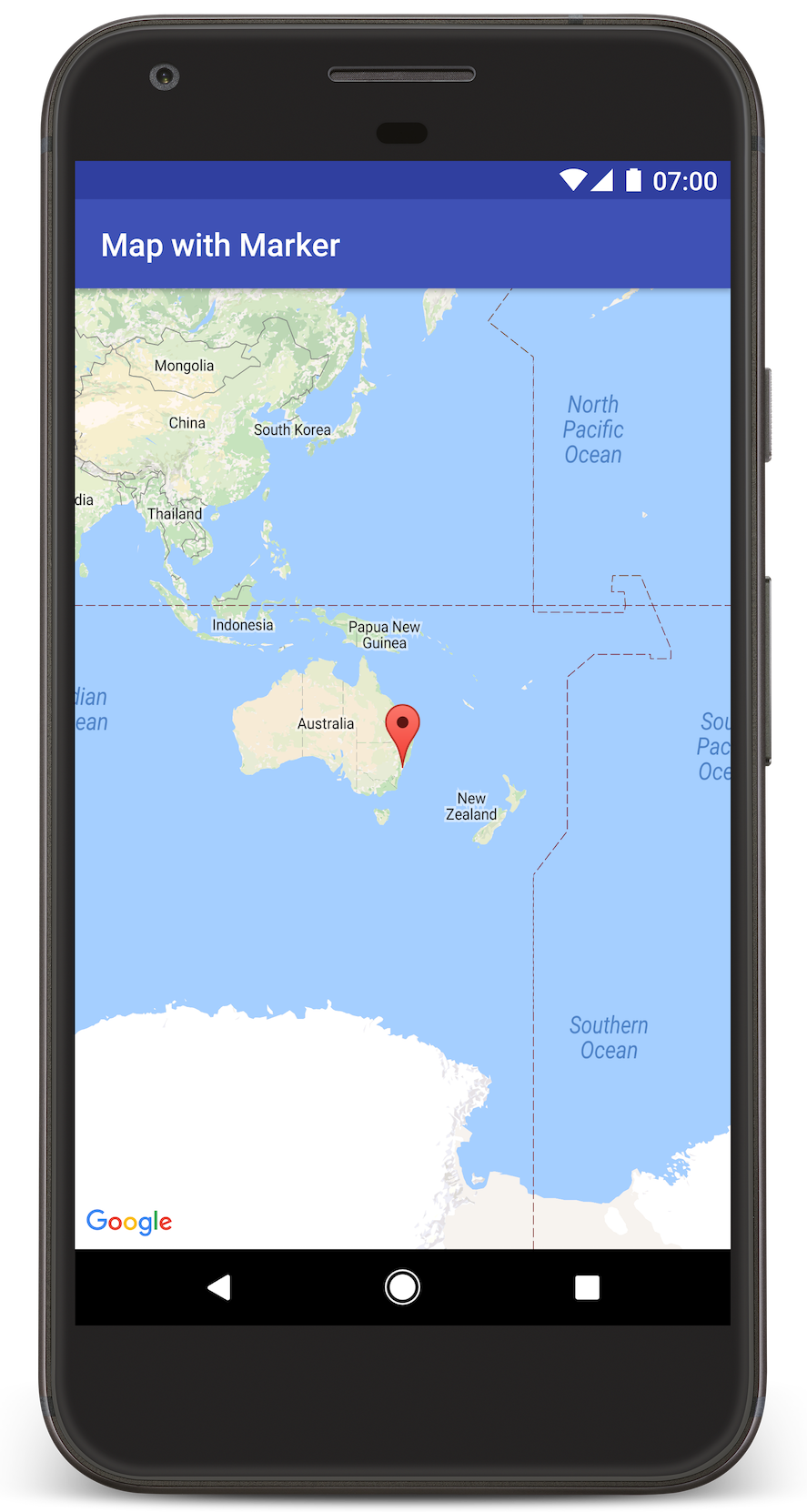
O Android Studio invoca o Gradle para criar o app e, em seguida, executa o aplicativo no aparelho ou no emulador. Será mostrado um mapa com um marcador apontando para Sydney, na costa leste da Austrália, semelhante à imagem desta página.
Solução de problemas:
- Se o mapa não aparecer, confirme se você recebeu uma chave de API e a incluiu no app, como descrito acima. Verifique se há mensagens de erro sobre essa chave no registro do Android Monitor do Android Studio.
- Use as ferramentas de depuração do Android Studio para conferir os registros e depurar o app.
Entender o código
Nesta seção do tutorial, explicamos as partes mais importantes do app MapWithMarker para ajudar a criar um aplicativo semelhante.
Verificar o manifesto do Android
Observe os seguintes elementos no arquivo AndroidManifest.xml do seu app:
Adicione um elemento
meta-datapara incorporar a versão do Google Play Services com que o app foi compilado.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />Inclua um elemento
meta-dataque especifique sua chave de API. O exemplo neste tutorial mapeia o valor da chave de API para uma variante de build correspondente ao nome da chave definida antes,MAPS_API_KEY. Quando você cria o app, o plug-in de secrets do Gradle para Android disponibiliza as chaves no seu arquivolocal.propertiescomo variantes de build no manifesto.<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" />No arquivo
build.gradle, a linha a seguir transmite sua chave de API ao manifesto do Android.id 'com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.secrets-gradle-plugin'
Confira o exemplo de um manifesto completo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> <!-- The API key for Google Maps-based APIs. --> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="${MAPS_API_KEY}" /> <activity android:name=".MapsMarkerActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps" android:exported="true"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
Adicionar um mapa
Mostre mapas usando o SDK do Maps para Android.
Adicione um elemento
<fragment>ao arquivo de layout da sua atividade,activity_maps.xml. Esse elemento define umSupportMapFragmentpara atuar como um contêiner do mapa e conceder acesso ao objetoGoogleMap. Neste tutorial, usamos a versão do fragmento de mapa da Biblioteca de Suporte do Android para oferecer compatibilidade com versões anteriores do framework Android.<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/map" android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.mapwithmarker.MapsMarkerActivity" />
No método
onCreate()da atividade, defina o arquivo de layout como a visualização de conteúdo. Gere um handle para o fragmento de mapa chamandoFragmentManager.findFragmentById(). Depois, usegetMapAsync()para registrar o callback do mapa:Java
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps); // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); }
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Retrieve the content view that renders the map. setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps) // Get the SupportMapFragment and request notification when the map is ready to be used. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as? SupportMapFragment mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) }
Implemente a interface
OnMapReadyCallbacke modifique o métodoonMapReady()para configurar o mapa quando o objetoGoogleMapestiver disponível:Java
public class MapsMarkerActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { // ... @Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap googleMap) { LatLng sydney = new LatLng(-33.852, 151.211); googleMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney")); } }
Kotlin
class MapsMarkerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback { // ... override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { val sydney = LatLng(-33.852, 151.211) googleMap.addMarker( MarkerOptions() .position(sydney) .title("Marker in Sydney") ) } }
Por padrão, o SDK do Maps para Android mostra o conteúdo da janela de informações quando o usuário toca em um marcador. Não é preciso adicionar um listener de clique ao marcador se o comportamento padrão atende às suas expectativas.
Próximas etapas
Saiba mais sobre o map object e o que você pode fazer com os marcadores.

