कोरोप्लेथ मैप, एक तरह का थीमैटिक मैप होता है. इसमें प्रशासनिक इलाकों को डेटा वैल्यू के हिसाब से रंगा या शेड किया जाता है. स्टाइल फ़ैक्ट्री फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल करके, डेटा के आधार पर मैप को स्टाइल किया जा सकता है. इसमें हर प्रशासनिक क्षेत्र को संख्यात्मक वैल्यू की एक रेंज से जोड़ा जाता है. यहां दिए गए उदाहरण मैप में, अमेरिका के राज्यों के लिए कोरोप्लेथ मैप दिखाया गया है.
इस उदाहरण में, डेटा में राज्य का प्लेस आईडी शामिल है. style factory फ़ंक्शन, राज्य के लिए प्लेस आईडी की हैश की गई वैल्यू के आधार पर, हर राज्य को रंग देता है.
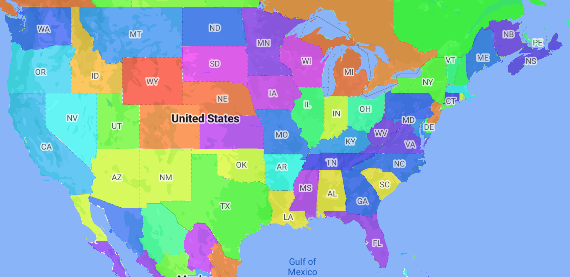
अगर आपने अब तक ऐसा नहीं किया है, तो नया मैप आईडी और मैप स्टाइल बनाने के लिए, शुरू करें में दिया गया तरीका अपनाएं. प्रशासनिक क्षेत्र का लेवल 1 फ़ीचर लेयर को चालू करना न भूलें.
मैप शुरू होने पर, एडमिनिस्ट्रेटिव एरिया लेवल 1 की फ़ीचर लेयर का रेफ़रंस पाएं. अमेरिका के लिए, ये प्रशासनिक लेवल अलग-अलग राज्यों के हिसाब से होते हैं.
Java
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }स्टाइल फ़ैक्ट्री फ़ंक्शन बनाएं और इसे एडमिनिस्ट्रेटिव एरिया लेवल 1 फ़ीचर लेयर पर लागू करें. यहां दिए गए उदाहरण में, अमेरिका के हर राज्य को दिखाने वाले पॉलीगॉन पर फ़ंक्शन लागू किया गया है.
Java
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }

