Dokumen ini menjelaskan cara Fleet Engine mengamankan pertukaran informasi antara tiga lingkungan utama sistem Fleet Engine Anda: server backend Anda, server Fleet Engine, dan aplikasi serta situs klien Anda.
Fleet Engine mengelola keamanan dalam dua cara mendasar, menggunakan prinsip hak istimewa terendah:
Kredensial Default Aplikasi (ADC): Untuk lingkungan dengan hak istimewa tinggi seperti komunikasi server ke server. Digunakan saat server backend Anda membuat kendaraan dan perjalanan serta mengelolanya di Fleet Engine. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat Kredensial Default Aplikasi.
Token Web JSON (JWT): Untuk lingkungan dengan tingkat kepercayaan rendah seperti aplikasi klien yang berjalan di smartphone dan browser. Digunakan untuk menyelesaikan operasi dengan hak istimewa yang lebih rendah, seperti memperbarui lokasi kendaraan di Fleet Engine.
JWT yang diperlukan oleh lingkungan dengan tingkat kepercayaan rendah dibuat dan dikeluarkan oleh server backend Anda untuk mengamankan kunci rahasia akun layanan, dan menyertakan klaim tambahan khusus untuk Fleet Engine. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat Token Web JSON.
Misalnya, jika Anda memiliki aplikasi pengemudi, pengemudi mengakses data dari Fleet Engine melalui aplikasi. Aplikasi diautentikasi menggunakan JWT yang didapat dari server backend Anda. Klaim JWT yang disertakan, beserta peran akun layanan, menentukan bagian sistem Anda yang dapat diakses oleh aplikasi pengemudi dan apa yang dapat dilakukannya. Pendekatan ini membatasi akses hanya ke data yang diperlukan untuk menyelesaikan tugas mengemudi.
Fleet Engine menggunakan pendekatan keamanan ini untuk menyediakan hal berikut:
Otentikasi memverifikasi identitas entitas yang membuat permintaan. Fleet Engine menggunakan ADC untuk lingkungan dengan tingkat kepercayaan tinggi dan JWT untuk lingkungan dengan tingkat kepercayaan rendah.
Otorisasi menentukan resource mana yang dapat diakses oleh entitas terautentikasi. Fleet Engine menggunakan akun layanan dengan peran IAM Google Cloud, ditambah klaim JWT yang memastikan entitas yang diautentikasi memiliki izin untuk melihat atau mengubah data yang mereka minta.
Penyiapan keamanan server dan klien
Untuk mengaktifkan keamanan dengan Fleet Engine, siapkan akun dan keamanan yang diperlukan di server backend serta di aplikasi dan situs klien Anda.
Diagram berikut menunjukkan ringkasan langkah-langkah untuk menyiapkan keamanan di server backend dan aplikasi klien Anda.
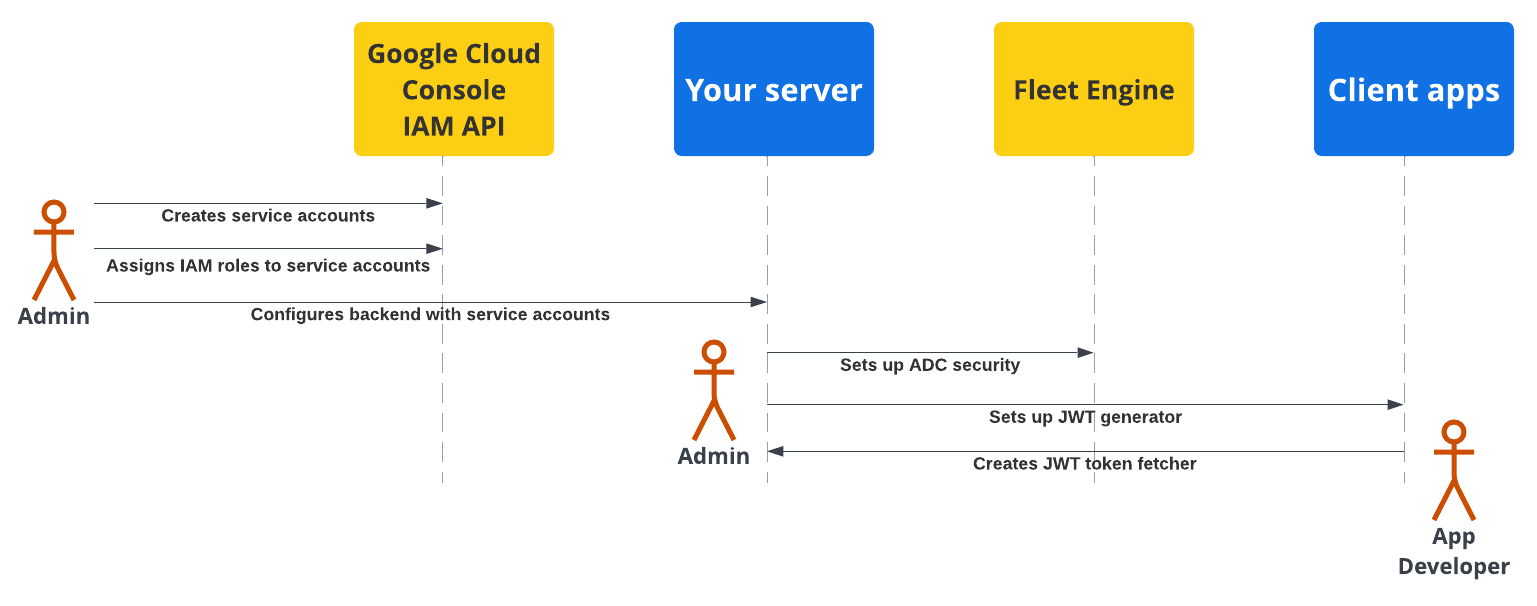
Untuk detail selengkapnya, lihat bagian berikut.
Penyiapan keamanan server backend
Administrator armada harus mengikuti langkah-langkah berikut:
Membuat dan mengonfigurasi akun layanan:
Di Konsol Google Cloud, buat akun layanan.
Tetapkan peran IAM tertentu ke akun layanan.
Konfigurasi server backend Anda dengan akun layanan yang dibuat. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat Peran akun layanan.
Mengonfigurasi komunikasi yang aman dengan Fleet Engine (ADC): Konfigurasi backend Anda untuk berkomunikasi dengan instance Fleet Engine menggunakan Kredensial Default Aplikasi dengan akun layanan *Admin yang sesuai. Untuk detailnya, lihat Kredensial Default Aplikasi.
Mengonfigurasi komunikasi yang aman dengan aplikasi klien (JWT): Buat generator Token Web JSON untuk membuat JWT dengan klaim yang sesuai untuk aplikasi klien dan situs pemantauan. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat Menerbitkan Token Web JSON.
Penyiapan keamanan aplikasi
Developer aplikasi harus menyertakan cara untuk mengambil Token Web JSON yang dibuat oleh server backend Anda di aplikasi atau situs klien, dan menggunakannya untuk berkomunikasi dengan Fleet Engine secara aman. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat petunjuk penyiapan dalam dokumentasi Pengalaman Pengemudi atau Pengalaman Konsumen untuk aplikasi yang Anda butuhkan.
Alur keamanan aplikasi server dan klien
Diagram urutan berikut menunjukkan alur autentikasi dan otorisasi aplikasi server dan klien dengan Fleet Engine menggunakan ADC dengan server backend dan JWT dengan aplikasi dan situs klien.
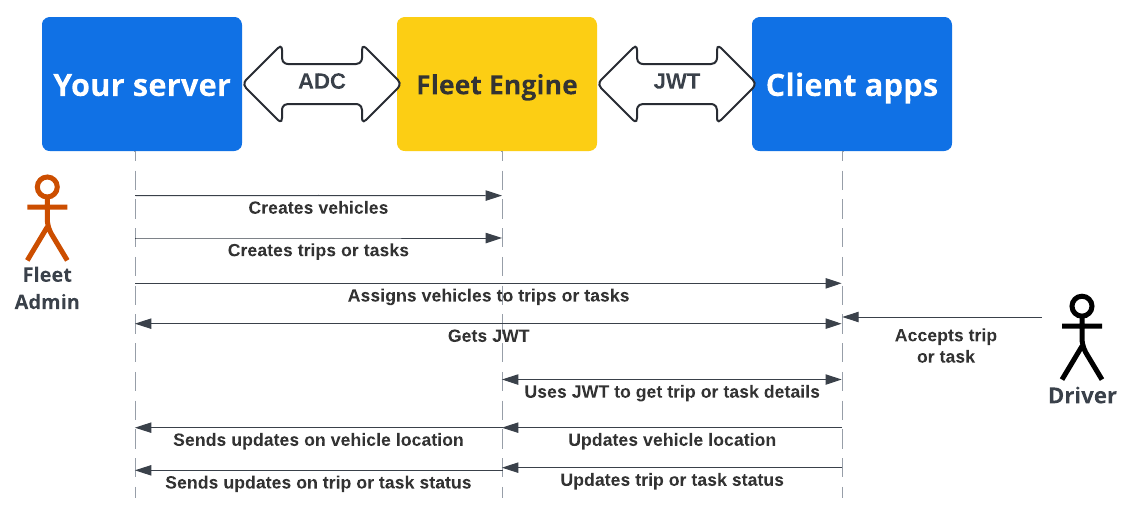
Server backend Anda membuat kendaraan dan perjalanan atau tugas di Fleet Engine.
Server backend Anda mengirimkan perjalanan atau tugas ke kendaraan: Aplikasi pengemudi, saat aktif, akan mengambil tugas.
Server backend Anda: Menandatangani dan menerbitkan JWT untuk akun layanan terkait dengan peran IAM yang sesuai untuk tugas atau perjalanan yang ditetapkan.
Aplikasi klien: Aplikasi klien menggunakan JWT yang diterima untuk mengirim update lokasi kendaraan ke Fleet Engine.
Langkah berikutnya
- Buat project Fleet Engine Anda.
- Pelajari cara Menerbitkan Token Web JSON dari server Anda.
- Pelajari lebih lanjut Peran akun layanan.
- Pelajari JWT lebih lanjut.
