במאמר הזה מוסבר איך Fleet Engine מאבטח את חילופי המידע בין שלושת הסביבות העיקריות של מערכת Fleet Engine: שרת הקצה העורפי, שרת Fleet Engine והאפליקציות והאתרים של הלקוח.
Fleet Engine מנהל את האבטחה בשתי דרכים בסיסיות, על סמך העיקרון של הרשאות מינימליות:
Application Default Credentials (ADC): לסביבות עם הרשאות גבוהות, כמו תקשורת בין שרתים. השימוש הוא כששרת הקצה העורפי יוצר כלי רכב ונסיעות ומנהל אותם ב-Fleet Engine. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר בנושא Application Default Credentials.
אסימוני JWT (JSON Web Tokens): לסביבות עם רמת אמון נמוכה, כמו אפליקציות לקוח שפועלות בסמארטפונים ובדפדפנים. הם משמשים לביצוע פעולות עם פחות הרשאות, כמו עדכון המיקום של כלי רכב ב-Fleet Engine.
סביבות עם רמת אמון נמוכה דורשות שימוש ב-JWT, שנוצרים ומונפקים על ידי שרת הקצה העורפי כדי להגן על מפתחות סודיים של חשבונות שירות, וכוללים טענות נוספות שספציפיות ל-Fleet Engine. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר בנושא אסימוני אינטרנט מסוג JSON.
לדוגמה, אם יש לכם אפליקציית נהגים, הנהגים ניגשים לנתונים מ-Fleet Engine דרך האפליקציה. האימות של האפליקציה מתבצע באמצעות אסימוני JWT שהיא מקבלת משרת הקצה העורפי שלכם. התביעות שכלולות ב-JWT, יחד עם התפקיד של חשבון השירות, קובעות לאילו חלקים במערכת יש לאפליקציית הנהג גישה, ולאילו פעולות היא יכולה לבצע. הגישה מוגבלת רק לנתונים שנדרשים להשלמת משימות הנהיגה.
Fleet Engine משתמש בגישות האבטחה האלה כדי לספק את הדברים הבאים:
אימות מאמת את הזהות של הגורם ששולח את הבקשה. Fleet Engine משתמש ב-ADC בסביבות עם רמת אמון גבוהה וב-JWT בסביבות עם רמת אמון נמוכה.
הרשאה מציינת לאילו משאבים יש לישות מאומתת גישה. Fleet Engine משתמש בחשבונות שירות עם תפקידי IAM ב-Google Cloud, בתוספת טענות JWT שמבטיחות לישויות מאומתות הרשאות לראות או לשנות את הנתונים שהן מבקשות.
הגדרת אבטחה של השרת והלקוח
כדי להפעיל אבטחה ב-Fleet Engine, צריך להגדיר את החשבונות הנדרשים ואת האבטחה בשרת הקצה העורפי ובאפליקציות ובאתרים של הלקוח.
בתרשים הבא מוצג סקירה כללית של השלבים להגדרת אבטחה בשרת העורפי ובאפליקציות הלקוח.
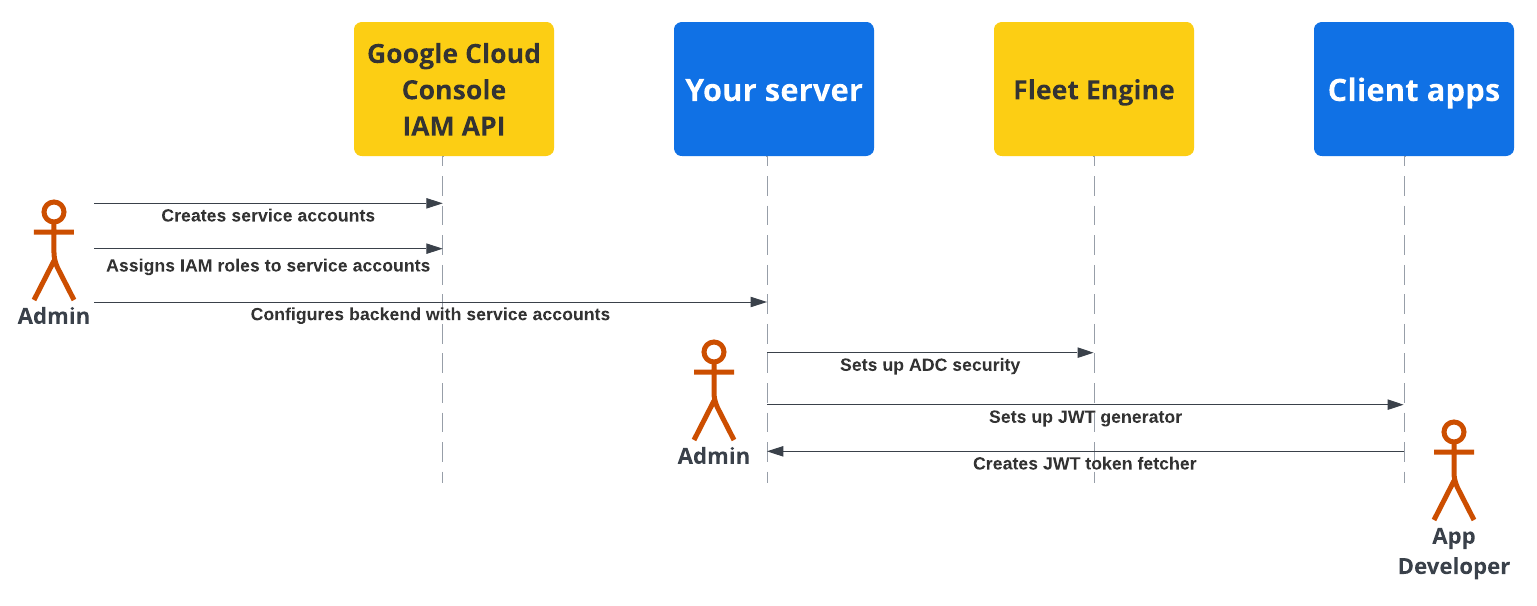
בסעיפים הבאים יש מידע נוסף בנושא.
הגדרת אבטחה של שרת קצה עורפי
אדמין של צי רכבים צריך לפעול לפי השלבים הבאים:
יצירה והגדרה של חשבונות שירות:
יוצרים חשבונות שירות במסוף Google Cloud.
מקצים לחשבונות השירות תפקידים ספציפיים ב-IAM.
מגדירים את שרת הקצה העורפי באמצעות חשבונות השירות שנוצרו. פרטים על תפקידים בחשבונות שירות
הגדרת תקשורת מאובטחת עם Fleet Engine (ADC): מגדירים את ה-Backend כך שיתקשר עם מופע Fleet Engine באמצעות Application Default Credentials עם חשבון השירות המתאים מסוג *Admin. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא Application Default Credentials.
הגדרת תקשורת מאובטחת עם אפליקציות לקוח (JWT): יוצרים מחולל JSON Web Token כדי ליצור אסימוני JWT עם טענות מתאימות לאפליקציות לקוח ולאתרים למעקב. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר בנושא הנפקת אסימוני JWT.
הגדרת אבטחת אפליקציות
מפתחי אפליקציות צריכים לכלול באפליקציות או באתרים שלהם דרך לאחזור אסימוני אינטרנט מסוג JSON שנוצרו על ידי שרת הקצה העורפי, ולהשתמש בהם כדי לתקשר בצורה מאובטחת עם Fleet Engine. פרטים נוספים זמינים בהוראות ההגדרה במסמכי חוויית הנהג או חוויית הצרכן של האפליקציות שאתם צריכים.
תהליך האבטחה של השרת ואפליקציית הלקוח
תרשים הרצף הבא מדגים את תהליך האימות וההרשאה של אפליקציית הלקוח והשרת עם Fleet Engine באמצעות ADC עם שרת הקצה העורפי, ואסימוני JWT עם אפליקציות הלקוח והאתרים.
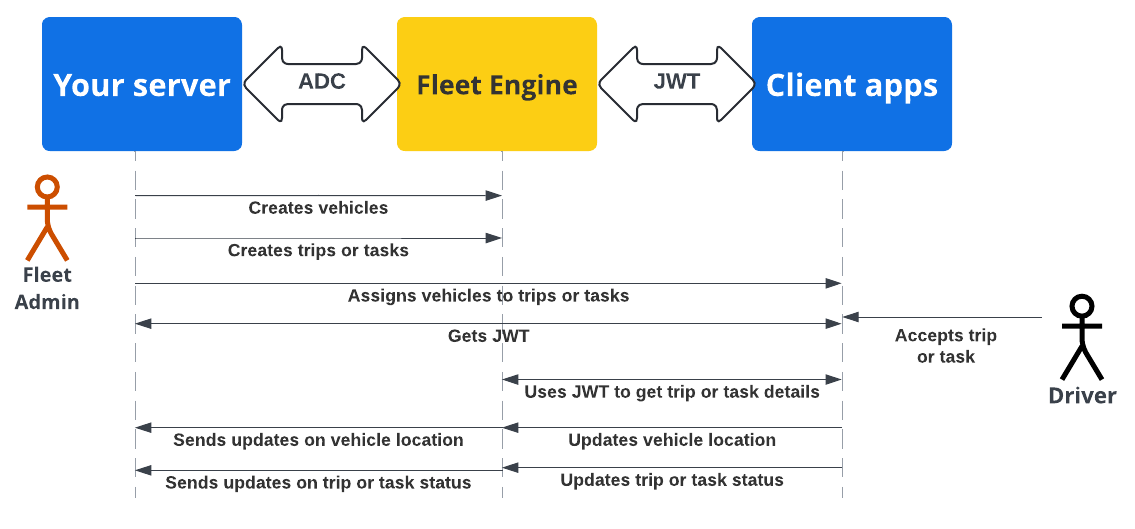
השרת העורפי שלכם יוצר רכבים, נסיעות או משימות ב-Fleet Engine.
השרת העורפי שלכם משייך נסיעה או משימה לרכב: אפליקציית הנהג, כשהיא פעילה, מאחזרת את השיוך.
השרת העורפי: חותם על JWT ומוציא אותו לחשבון השירות הרלוונטי עם תפקיד ה-IAM המתאים למשימה או לנסיעה שהוקצו.
אפליקציית הלקוח: אפליקציית הלקוח משתמשת ב-JWT שהתקבל כדי לשלוח עדכונים לגבי מיקום הרכב אל Fleet Engine.
המאמרים הבאים
- יוצרים פרויקט Fleet Engine.
- כך מנפיקים אסימוני אינטרנט מסוג JSON מהשרת.
- מידע נוסף על תפקידים בחשבונות שירות
- מידע נוסף על JWT

