Questo documento spiega in che modo Fleet Engine protegge lo scambio di informazioni tra i tre ambienti principali del sistema Fleet Engine: il server di backend, il server Fleet Engine e le applicazioni e i siti web client.
Fleet Engine gestisce la sicurezza in due modi fondamentali, utilizzando il principio del privilegio minimo:
Credenziali predefinite dell'applicazione (ADC): per ambienti con privilegi elevati, come le comunicazioni da server a server. Utilizzato quando il server di backend crea veicoli e viaggi e li gestisce in Fleet Engine. Per maggiori dettagli, vedi Credenziali predefinite dell'applicazione.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): per ambienti a bassa attendibilità come le applicazioni client in esecuzione su smartphone e browser. Utilizzato per eseguire operazioni con privilegi inferiori, ad esempio l'aggiornamento della posizione del veicolo in Fleet Engine.
I JWT richiesti dagli ambienti a bassa attendibilità vengono generati ed emessi dal server di backend per proteggere le chiavi segrete del service account e includono rivendicazioni aggiuntive specifiche di Fleet Engine. Per maggiori dettagli, consulta la sezione Token web JSON.
Ad esempio, se hai un'app per i conducenti, questi accedono ai dati di Fleet Engine tramite l'app. L'app viene autenticata utilizzando i JWT che riceve dal tuo server di backend. Le rivendicazioni JWT incluse, insieme al ruolo dell'account di servizio, determinano a quali parti del sistema ha accesso l'app per i conducenti e cosa può fare. Questo approccio limita l'accesso solo ai dati necessari per completare gli incarichi di guida.
Fleet Engine utilizza questi approcci alla sicurezza per fornire quanto segue:
L'autenticazione verifica l'identità dell'entità che effettua la richiesta. Fleet Engine utilizza ADC per gli ambienti ad alta affidabilità e JWT per gli ambienti a bassa affidabilità.
L'autorizzazione specifica a quali risorse ha accesso un'entità autenticata. Fleet Engine utilizza service account con ruoli Google Cloud IAM, oltre a rivendicazioni JWT che garantiscono che le entità autenticate dispongano delle autorizzazioni per visualizzare o modificare i dati che richiedono.
Configurazione della sicurezza del server e del client
Per attivare la sicurezza con Fleet Engine, configura gli account e la sicurezza richiesti sul server di backend e sui siti web e sulle applicazioni client.
Il seguente diagramma mostra una panoramica dei passaggi per configurare la sicurezza sul server di backend e sulle applicazioni client.
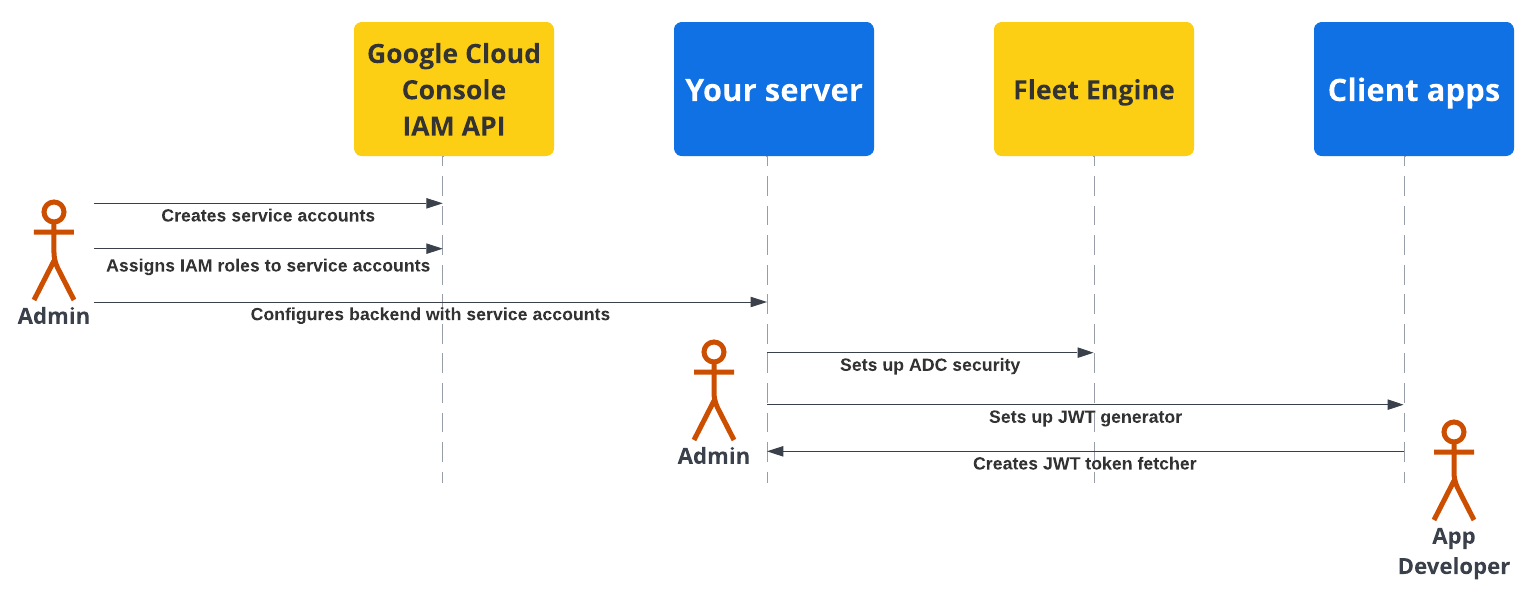
Per maggiori dettagli, consulta le sezioni seguenti.
Configurazione della sicurezza del server di backend
Un amministratore del parco auto deve procedere come segue:
Crea e configura gli account di servizio:
Nella console Google Cloud, crea service account.
Assegna ruoli IAM specifici ai service account.
Configura il server di backend con i service account creati. Per i dettagli, consulta Ruoli degli account di servizio.
Configura la comunicazione sicura con Fleet Engine (ADC): configura il backend per comunicare con l'istanza di Fleet Engine utilizzando le credenziali predefinite dell'applicazione con il service account *Admin appropriato. Per i dettagli, consulta Credenziali predefinite dell'applicazione.
Configura la comunicazione sicura con le app client (JWT): crea un generatore di token web JSON per creare JWT con attestazioni appropriate per le applicazioni client e i siti web di monitoraggio. Per maggiori dettagli, consulta Emettere token web JSON.
Configurazione della sicurezza delle applicazioni
Gli sviluppatori di applicazioni devono includere un modo per recuperare i token web JSON generati dal server di backend nelle app o nei siti web client e utilizzarli per comunicare in modo sicuro con Fleet Engine. Per maggiori dettagli, consulta le istruzioni di configurazione nella documentazione relativa all'esperienza del conducente o all'esperienza del consumatore per le applicazioni che ti servono.
Flusso di sicurezza dell'app server e client
Il seguente diagramma di sequenza mostra il flusso di autenticazione e autorizzazione dell'app server e client con Fleet Engine utilizzando ADC con il server di backend e JWT con le applicazioni client e i siti web.
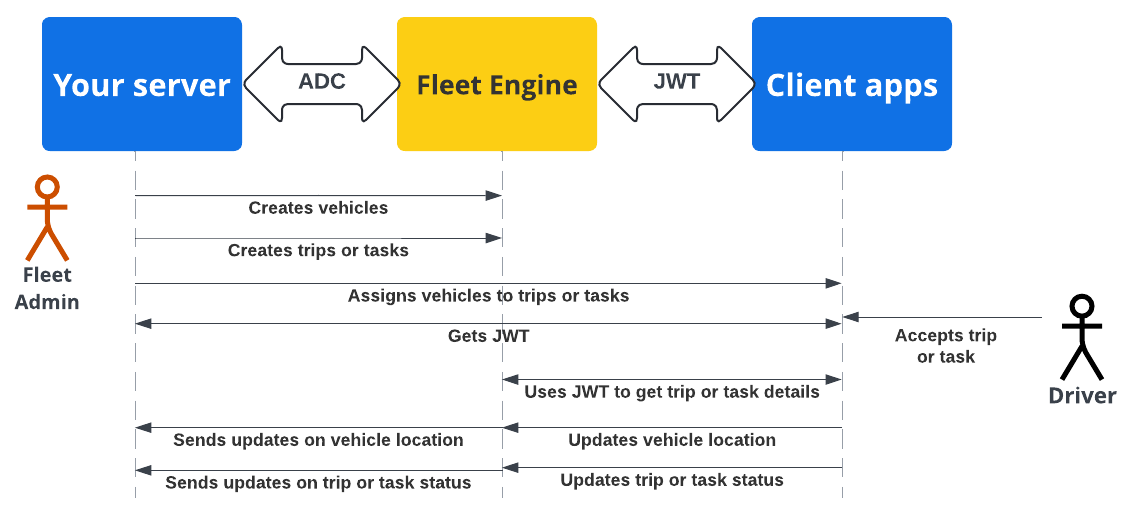
Il server di backend crea veicoli e viaggi o attività in Fleet Engine.
Il tuo server di backend assegna un viaggio o un'attività a un veicolo: L'app per i conducenti, quando è attiva, recupera l'assegnazione.
Il tuo server di backend: firma ed emette un JWT per il rispettivo service account con il ruolo IAM appropriato per l'attività o il viaggio assegnato.
L'app client: l'app client utilizza il JWT ricevuto per inviare aggiornamenti della posizione del veicolo a Fleet Engine.
Passaggi successivi
- Crea il tuo progetto Fleet Engine.
- Scopri come emettere token web JSON dal tuo server.
- Scopri di più sui ruoli del service account.
- Scopri di più sui JWT.

