이 문서에서는 Fleet Engine 시스템의 세 가지 기본 환경(백엔드 서버, Fleet Engine 서버, 클라이언트 애플리케이션 및 웹사이트) 간 정보 교환을 Fleet Engine이 보호하는 방법을 설명합니다.
Fleet Engine은 최소 권한의 원칙을 사용하여 두 가지 기본 방식으로 보안을 관리합니다.
애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보 (ADC): 서버 간 통신과 같은 높은 권한이 있는 환경에 사용됩니다. 백엔드 서버가 차량과 여정을 생성하고 Fleet Engine에서 관리할 때 사용됩니다. 자세한 내용은 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 참고하세요.
JSON 웹 토큰 (JWT): 스마트폰 및 브라우저에서 실행되는 클라이언트 애플리케이션과 같은 신뢰도가 낮은 환경에 적합합니다. Fleet Engine에서 차량 위치를 업데이트하는 등 권한이 낮은 작업을 실행하는 데 사용됩니다.
신뢰 수준이 낮은 환경에 필요한 JWT는 서비스 계정 보안 비밀 키를 보호하기 위해 백엔드 서버에서 생성 및 발급되며 Fleet Engine에 특정한 추가 클레임이 포함됩니다. 자세한 내용은 JSON 웹 토큰을 참고하세요.
예를 들어 운전자 앱이 있는 경우 운전자는 앱을 통해 Fleet Engine의 데이터에 액세스합니다. 앱은 백엔드 서버에서 가져온 JWT를 사용하여 인증됩니다. 포함된 JWT 클레임은 서비스 계정 역할과 함께 드라이버 앱이 액세스할 수 있는 시스템 부분과 드라이버 앱이 할 수 있는 작업을 결정합니다. 이 접근 방식을 사용하면 운전 과제를 완료하는 데 필요한 데이터에만 액세스할 수 있습니다.
Fleet Engine은 이러한 보안 접근 방식을 사용하여 다음을 제공합니다.
인증은 요청을 하는 항목의 ID를 확인합니다. Fleet Engine은 신뢰도가 높은 환경에는 ADC를 사용하고 신뢰도가 낮은 환경에는 JWT를 사용합니다.
승인은 인증된 주체가 액세스할 수 있는 리소스를 지정합니다. Fleet Engine은 Google Cloud IAM 역할이 있는 서비스 계정과 인증된 엔티티가 요청하는 데이터를 보거나 변경할 권한이 있음을 보장하는 JWT 클레임을 사용합니다.
서버 및 클라이언트 보안 설정
Fleet Engine으로 보안을 사용 설정하려면 백엔드 서버와 클라이언트 애플리케이션 및 웹사이트에서 필요한 계정과 보안을 설정하세요.
다음 다이어그램은 백엔드 서버와 클라이언트 애플리케이션에서 보안을 설정하는 단계의 개요를 보여줍니다.
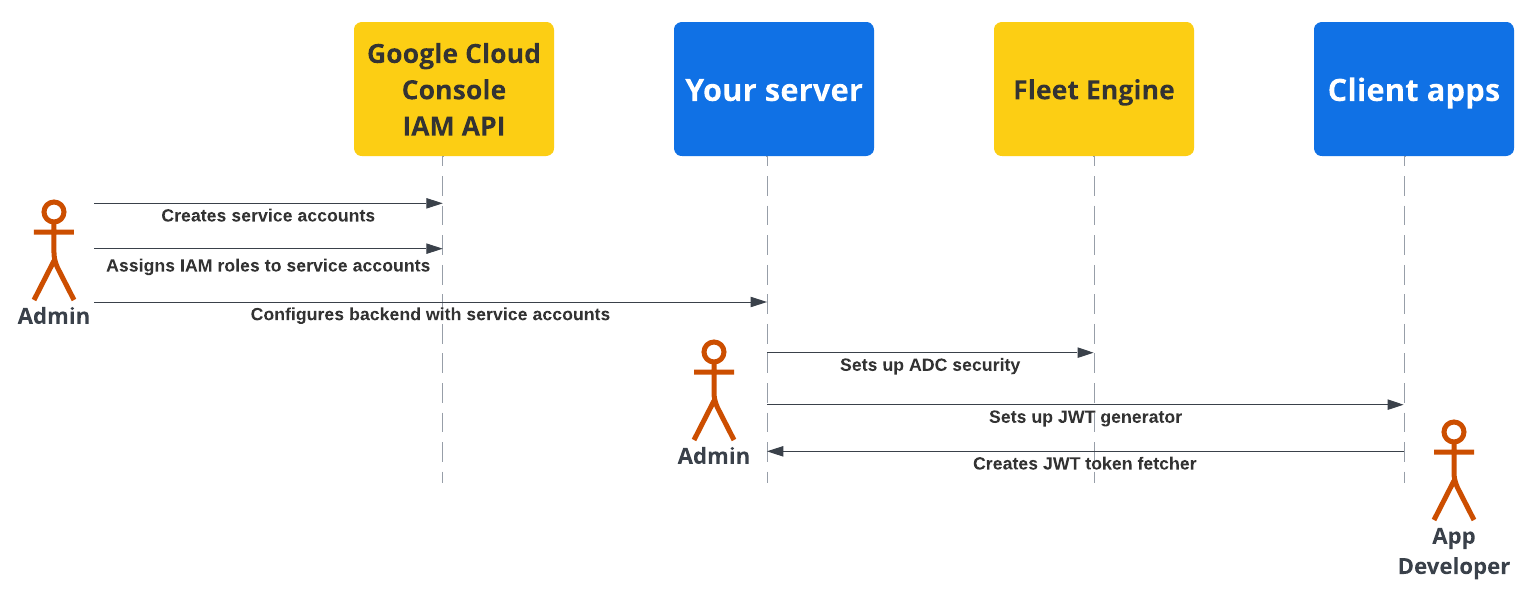
자세한 내용은 다음 섹션을 참고하세요.
백엔드 서버 보안 설정
차량 관리자는 다음 단계를 따라야 합니다.
서비스 계정 만들기 및 구성:
Google Cloud 콘솔에서 서비스 계정을 만듭니다.
서비스 계정에 특정 IAM 역할을 할당합니다.
생성된 서비스 계정으로 백엔드 서버를 구성합니다. 자세한 내용은 서비스 계정 역할을 참고하세요.
Fleet Engine과의 보안 통신 구성 (ADC): 적절한 *관리 서비스 계정으로 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 사용하여 Fleet Engine 인스턴스와 통신하도록 백엔드를 구성합니다. 자세한 내용은 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 참고하세요.
클라이언트 앱과의 보안 통신 구성 (JWT): 클라이언트 애플리케이션 및 모니터링 웹사이트에 적합한 클레임이 있는 JWT를 생성하는 JSON 웹 토큰 생성기를 만듭니다. 자세한 내용은 JSON 웹 토큰 발급을 참고하세요.
애플리케이션 보안 설정
애플리케이션 개발자는 클라이언트 앱이나 웹사이트에 백엔드 서버에서 생성된 JSON 웹 토큰을 가져오는 방법을 포함하고 이를 사용하여 Fleet Engine과 안전하게 통신해야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 필요한 애플리케이션의 운전자 환경 또는 소비자 환경 문서에 있는 설정 안내를 참고하세요.
서버 및 클라이언트 앱 보안 흐름
다음 시퀀스 다이어그램은 백엔드 서버와 함께 ADC를 사용하고 클라이언트 애플리케이션 및 웹사이트와 함께 JWT를 사용하는 Fleet Engine의 서버 및 클라이언트 앱 인증 및 승인 흐름을 보여줍니다.
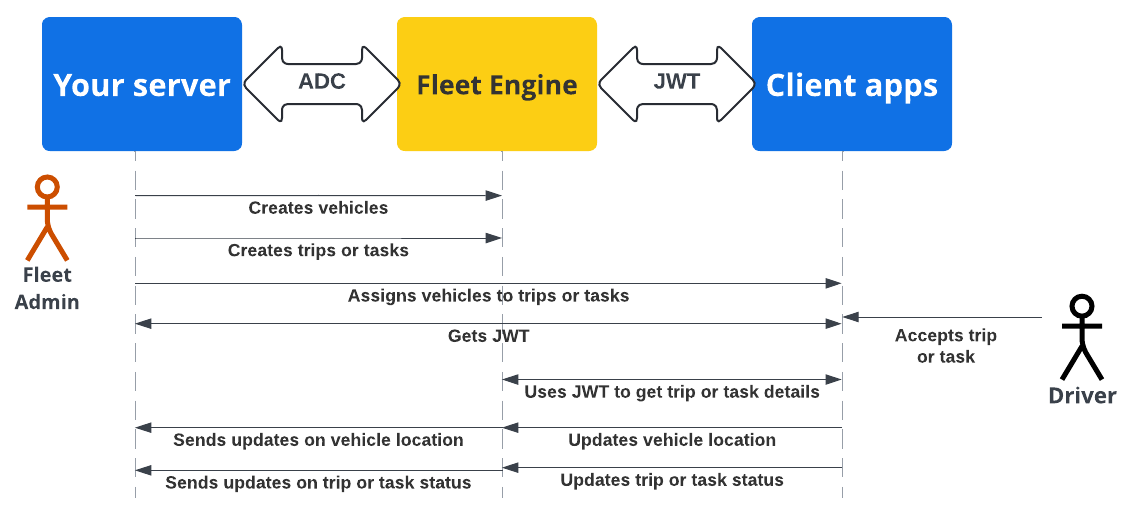
백엔드 서버가 Fleet Engine에서 차량, 여정 또는 작업을 만듭니다.
백엔드 서버에서 차량에 여정 또는 작업 할당: 활성 상태인 경우 운전자 앱이 할당을 가져옵니다.
백엔드 서버: 할당된 작업 또는 여정에 적합한 IAM 역할이 있는 해당 서비스 계정의 JWT에 서명하고 발급합니다.
클라이언트 앱: 클라이언트 앱은 수신된 JWT를 사용하여 차량 위치 업데이트를 Fleet Engine에 전송합니다.
다음 단계
- Fleet Engine 프로젝트를 만듭니다.
- 서버에서 JSON 웹 토큰을 발급하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
- 서비스 계정 역할에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
- JWT에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
