تابع PLACES_COUNT یک مقدار تعداد مکان ها را بر اساس ناحیه جستجوی مشخص شده و فیلترهای جستجو برمی گرداند. شما باید ناحیه جستجو را برای تابع PLACES_COUNT مشخص کنید و می توانید به صورت اختیاری پارامترهای فیلتر اضافی مانند نوع مکان، وضعیت عملیاتی، سطح قیمت و موارد دیگر را مشخص کنید.
از آنجایی که تابع PLACES_COUNT یک مقدار واحد را برمی گرداند، آن را با استفاده از یک عبارت SELECT فراخوانی کنید.
پارامترهای ورودی:
مورد نیاز : پارامتر فیلتر
geographyکه ناحیه جستجو را مشخص می کند. پارامترgeographyمقداری را می گیرد که توسط نوع داده BigQueryGEOGRAPHYتعریف شده است که از نقاط، رشته های خطی و چند ضلعی ها پشتیبانی می کند.اختیاری : پارامترهای فیلتر اضافی برای اصلاح جستجوی شما.
برمی گرداند:
- یک مقدار
countواحد به عنوان یکINT64.
- یک مقدار
مثال: تعداد مکان ها را در شعاع جستجو محاسبه کنید
سادهترین فراخوانی تابع PLACES_COUNT تعداد واحدی از همه مکانها در یک منطقه جغرافیایی را برمیگرداند. در این مثال، شمارش تمام مکانهای عملیاتی در 1000 متری ساختمان امپایر استیت را برمیگردانید.
این مثال از تابع BigQuery ST_GEOGPOINT برای برگرداندن یک مقدار GEOGRAPHY از یک نقطه استفاده می کند.
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
پاسخ شامل یک تعداد واحد است:
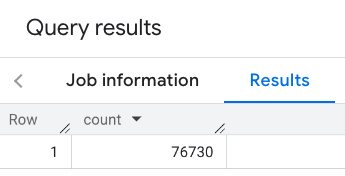
یک تماس معمولی تر، فیلترهایی را در ناحیه جستجو اعمال می کند. مثال بعدی از فیلترها استفاده می کند تا جستجو را محدود کند تا فقط تعدادی از موارد زیر را برگرداند:
- مکان هایی از نوع
restaurantبا حداقل امتیاز 3 - سطح قیمت ارزان یا متوسط
- در حال حاضر عملیاتی است
- به سگ ها اجازه می دهد
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
پاسخ فیلتر شده:

به یاد داشته باشید که پرس و جوهای مجموعه داده مکان حداقل آستانه شمارش 5 را اعمال می کنند. یکی از مزایای توابع شمارش مکان این است که آنها می توانند هر تعداد از جمله 0 را برگردانند. به عنوان مثال، فراخوانی زیر تعداد 1 را برمی گرداند:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
مثال: تعداد رستوران ها را با استفاده از چند ضلعی محاسبه کنید
می توانید از یک چند ضلعی برای تعیین ناحیه جستجو استفاده کنید. هنگام استفاده از چند ضلعی، نقاط چند ضلعی باید یک حلقه بسته را تعریف کنند که اولین نقطه در چند ضلعی همان نقطه آخر باشد.
این مثال از تابع BigQuery ST_GEOGFROMTEXT برای برگرداندن مقدار GEOGRAPHY از یک چند ضلعی استفاده می کند.
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
پاسخ برای viewport:
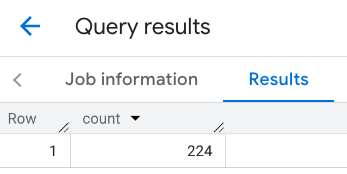
مثال: تعداد رستوران ها را با استفاده از یک خط محاسبه کنید
در مثال بعدی، منطقه جستجو را با استفاده از خطی از نقاط متصل با شعاع جستجو 100 متر در اطراف خط تعریف می کنید. این خط شبیه به مسیر سفر محاسبه شده توسط Routes API است. مسیر ممکن است برای یک وسیله نقلیه، یک دوچرخه یا برای یک عابر پیاده باشد:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
پاسخ خط:
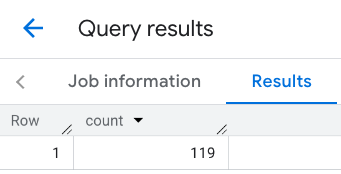
مثال: نتایج چند تماس را ترکیب کنید
می توانید نتایج تماس های متعدد را با تابع PLACES_COUNT ترکیب کنید. به عنوان مثال، شما یک نتیجه واحد می خواهید که تعداد رستوران ها را برای سطوح قیمت زیر در یک منطقه خاص نشان دهد:
-
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE -
PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE -
PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE -
PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
در این مثال، شما یک حلقه برای فراخوانی تابع PLACES_COUNT برای هر سطح قیمت ایجاد میکنید و نتایج هر تماس را در یک جدول موقت درج میکنید. سپس جدول موقت را برای نمایش نتایج پرس و جو کنید:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
پاسخ ترکیبی:
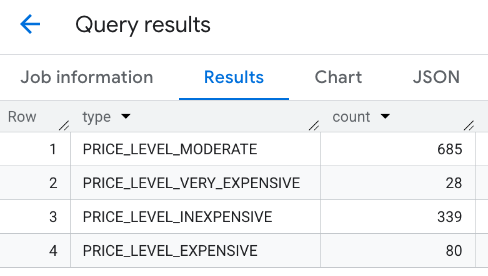
گزینه دیگر استفاده از دستور UNION ALL برای ترکیب نتایج چند عبارت SELECT . مثال زیر همان نتایج مثال قبلی را نشان می دهد:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count

