PLACES_COUNT 関数は、指定された検索エリアと検索フィルタに基づいて、場所の単一のカウント値を返します。PLACES_COUNT 関数に検索エリアを指定する必要があります。必要に応じて、場所のタイプ、営業状況、価格帯などの追加のフィルタ パラメータを指定できます。
PLACES_COUNT 関数は単一の値を返すため、SELECT 句を使用して呼び出します。
入力パラメータ:
必須: 検索エリアを指定する
geographyフィルタ パラメータ。geographyパラメータは、BigQuery のGEOGRAPHYデータ型で定義された値を受け取ります。このデータ型は、ポイント、ラインストリング、ポリゴンをサポートしています。省略可: 検索を絞り込むための追加のフィルタ パラメータ。
戻り値:
- 単一の
count値(INT64として)。
- 単一の
例: 検索半径内の場所の数を計算する
最もシンプルな PLACES_COUNT 関数呼び出しは、地理的エリア内のすべての場所の単一のカウントを返します。この例では、エンパイア ステート ビルディングから 1, 000 メートル以内のすべての営業所の数を返します。
この例では、BigQuery の ST_GEOGPOINT 関数を使用して、ポイントから GEOGRAPHY 値を返します。
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
レスポンスには 1 つのカウントが含まれます。
より一般的な呼び出しでは、検索範囲にフィルタが適用されます。次の例では、フィルタを使用して検索を制限し、次のカウントのみを返します。
- 評価が 3 以上の
restaurantタイプの場所 - 価格レベルが「安い」または「普通」
- 現在運用中
- 犬の同伴可能
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
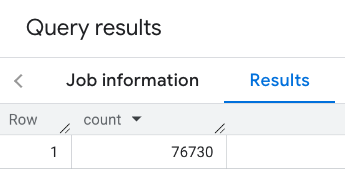
フィルタされたレスポンス:

プレイス データセットのクエリでは、最小カウントしきい値が 5 に設定されていることに注意してください。プレースカウント関数の利点の 1 つは、0 を含む任意のカウントを返すことができることです。たとえば、次の呼び出しは 1 を返します。
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
例: ポリゴンを使用してレストランの数を計算する
検索エリアを指定するには、ポリゴンを使用します。ポリゴンを使用する場合、ポリゴンの点は閉じたループを定義する必要があります。ポリゴンの最初の点は最後の点と同じです。
この例では、BigQuery の ST_GEOGFROMTEXT 関数を使用して、ポリゴンから GEOGRAPHY 値を返します。
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
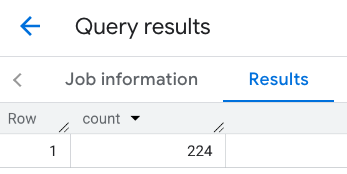
ビューポートのレスポンス:
例: 線を使用してレストランの数を計算する
次の例では、線を中心とした半径 100 メートルの検索範囲を、線で結ばれた一連のポイントを使用して定義します。この線は、Routes API で計算された移動ルートに似ています。ルートは、車両、自転車、歩行者のいずれかになります。
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
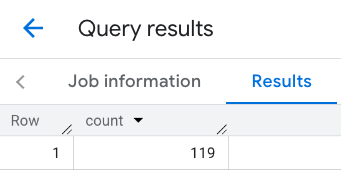
行のレスポンス:
例: 複数の呼び出しの結果を結合する
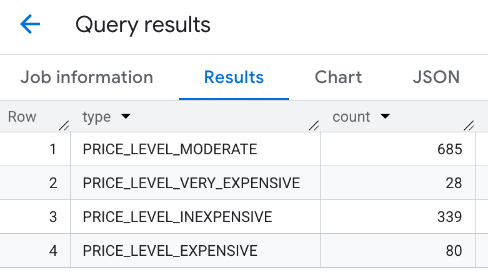
PLACES_COUNT 関数への複数の呼び出しの結果を組み合わせることができます。たとえば、特定のエリア内の次の価格帯のレストランの数を 1 つの結果で表示したいとします。
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
この例では、価格レベルごとに PLACES_COUNT 関数を呼び出すループを作成し、各呼び出しの結果を一時テーブルに挿入します。次に、一時テーブルに対してクエリを実行して結果を表示します。
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
結合されたレスポンス:
別の方法として、UNION ALL コマンドを使用して複数の SELECT ステートメントの結果を結合することもできます。次の例は、前の例と同じ結果を示しています。
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
