ฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT จะแสดงผลค่าการนับเดียวของสถานที่ตามพื้นที่ค้นหาและตัวกรองการค้นหาที่ระบุ
คุณต้องระบุพื้นที่ค้นหาให้กับฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT และระบุพารามิเตอร์ตัวกรองเพิ่มเติมได้โดยไม่บังคับ เช่น ประเภทสถานที่ สถานะการดำเนินงาน ระดับราคา และอื่นๆ
เนื่องจากฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT แสดงผลค่าเดียว ให้เรียกใช้โดยใช้
คําสั่ง SELECT
พารามิเตอร์อินพุต
ต้องระบุ:
geographyพารามิเตอร์ตัวกรองที่ ระบุพื้นที่ค้นหา พารามิเตอร์geographyจะใช้ค่าที่กำหนด โดยประเภทข้อมูล BigQueryGEOGRAPHYซึ่งรองรับจุด เส้น และรูปหลายเหลี่ยมไม่บังคับ: พารามิเตอร์ตัวกรองเพิ่มเติมเพื่อปรับแต่งการค้นหา
ค่าที่ส่งคืน:
- ค่า
countเดียวเป็นINT64
- ค่า
ตัวอย่าง: คำนวณจำนวนสถานที่ในรัศมีการค้นหา
การเรียกฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT ที่ง่ายที่สุดจะแสดงผลจำนวนสถานที่ทั้งหมด
ในพื้นที่ทางภูมิศาสตร์ ในตัวอย่างนี้ คุณจะแสดงผลจำนวนสถานที่ที่เปิดให้บริการทั้งหมด
ภายในรัศมี 1, 000 เมตรจากตึกเอ็มไพร์สเตต
ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ฟังก์ชัน BigQuery
ST_GEOGPOINT
เพื่อแสดงค่า GEOGRAPHY จากจุด
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
การตอบกลับจะมีจำนวนเดียวดังนี้
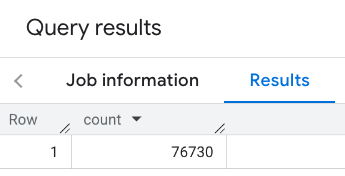
การเรียกที่พบบ่อยกว่าจะใช้ตัวกรองกับพื้นที่ค้นหา ตัวอย่างถัดไปใช้ ตัวกรองเพื่อจำกัดการค้นหาให้แสดงผลเฉพาะจำนวนต่อไปนี้
- สถานที่ประเภท
restaurantที่มีคะแนนขั้นต่ำ 3 - มีระดับราคาที่ไม่แพงหรือปานกลาง
- ใช้งานได้ในปัจจุบัน
- นำสุนัขเข้าได้
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
คำตอบที่กรองแล้ว

โปรดทราบว่าการค้นหาชุดข้อมูลสถานที่บังคับใช้เกณฑ์จำนวนขั้นต่ำที่ 5 ข้อดีอย่างหนึ่งของฟังก์ชันการนับสถานที่คือ ฟังก์ชันนี้จะแสดงผลการนับใดก็ได้ รวมถึง 0 ตัวอย่างเช่น การเรียกต่อไปนี้ จะแสดงผลการนับเป็น 1
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
ตัวอย่าง: คำนวณจำนวนร้านอาหารโดยใช้รูปหลายเหลี่ยม
คุณใช้รูปหลายเหลี่ยมเพื่อระบุพื้นที่ค้นหาได้ เมื่อใช้รูปหลายเหลี่ยม จุดของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมต้องกำหนดลูปปิด โดยจุดแรกใน รูปหลายเหลี่ยมต้องเหมือนกับจุดสุดท้าย
ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ฟังก์ชัน BigQuery
ST_GEOGFROMTEXT
เพื่อแสดงผลค่า GEOGRAPHY จากรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
การตอบกลับสำหรับวิวพอร์ต
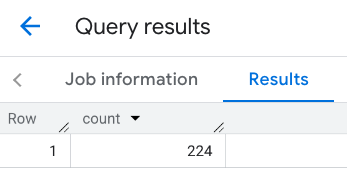
ตัวอย่าง: คำนวณจำนวนร้านอาหารโดยใช้เส้น
ในตัวอย่างถัดไป คุณจะกำหนดพื้นที่ค้นหาโดยใช้เส้นของจุดที่เชื่อมต่อกัน โดยมีรัศมีการค้นหา 100 เมตรรอบเส้น เส้นทางนี้คล้ายกับเส้นทางการเดินทางที่คำนวณโดย Routes API เส้นทางอาจเป็นเส้นทางสำหรับยานพาหนะ จักรยาน หรือคนเดินเท้า
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
คำตอบสำหรับบรรทัดนี้
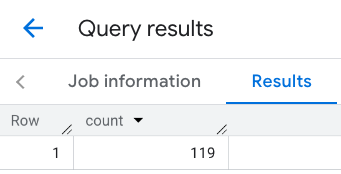
ตัวอย่าง: รวมผลลัพธ์ของการเรียกหลายครั้ง
คุณรวมผลลัพธ์ของการเรียกใช้หลายครั้งเข้ากับฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT ได้
เช่น คุณต้องการผลการค้นหาเดียวที่แสดงจำนวนร้านอาหารสำหรับระดับราคาต่อไปนี้ภายในพื้นที่ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
ในตัวอย่างนี้ คุณจะสร้างลูปเพื่อเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน PLACES_COUNT สำหรับแต่ละ
ระดับราคา และแทรกผลลัพธ์ของการเรียกใช้แต่ละครั้งลงในตารางชั่วคราว จากนั้นคุณจะ
ค้นหาตารางชั่วคราวเพื่อแสดงผลลัพธ์ได้โดยทำดังนี้
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
คำตอบที่รวมกัน
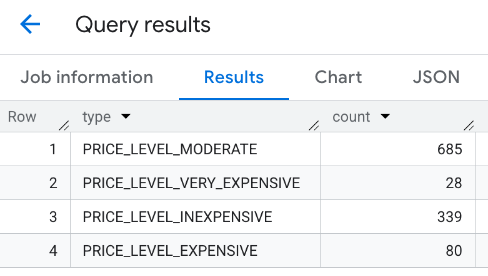
อีกตัวเลือกหนึ่งคือการใช้คำสั่ง UNION ALL เพื่อรวมผลลัพธ์ของคำสั่ง SELECT หลายรายการ ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงผลลัพธ์เดียวกันกับ
ตัวอย่างก่อนหน้า
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
