تعرض الدالة PLACES_COUNT قيمة عددية واحدة للأماكن استنادًا إلى
منطقة البحث وفلاتر البحث المحدّدة. يجب تحديد مساحة البحث للدالة PLACES_COUNT، ويمكنك اختياريًا تحديد مَعلمات فلترة إضافية، مثل نوع المكان وحالة التشغيل ومستوى السعر وغير ذلك.
بما أنّ الدالة PLACES_COUNT تعرض قيمة واحدة، استدعِها باستخدام عبارة SELECT.
مَعلمات الإدخال:
مطلوبة:
geographyمَعلمة الفلترة التي تحدّد مساحة البحث. تأخذ المَعلمةgeographyقيمة محدّدة حسب نوع البياناتGEOGRAPHYفي BigQuery، والذي يتيح استخدام النقاط والخطوط المتعددة الأجزاء والمضلّعات.اختياري: مَعلمات الفلتر الإضافية لتحسين البحث.
المرتجعات:
- قيمة
countواحدة كـINT64
- قيمة
مثال: احتساب عدد الأماكن ضمن نطاق بحث
يعرض أبسط استدعاء للدالة PLACES_COUNT عددًا واحدًا لجميع الأماكن في منطقة جغرافية. في هذا المثال، يتم عرض عدد جميع الأماكن المتاحة للعمل ضمن مسافة 1, 000 متر من مبنى إمباير ستيت.
يستخدم هذا المثال الدالة BigQuery
ST_GEOGPOINT
لعرض قيمة GEOGRAPHY من نقطة.
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
تحتوي الاستجابة على عدد واحد:
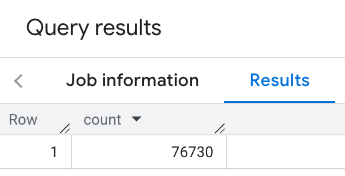
تطبِّق المكالمة الأكثر شيوعًا فلاتر على منطقة البحث. يستخدم المثال التالي فلاتر لحصر البحث على عرض عدد فقط من:
- أماكن من النوع
restaurantمع حد أدنى للتقييم يبلغ 3 - مستوى سعر منخفض أو متوسط
- مفتوح حاليًا
- يسمح المكان باصطحاب الكلاب
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
الردّ الذي تمت فلترته:

يُرجى العِلم أنّ طلبات البحث في مجموعة بيانات الأماكن تفرض حدًا أدنى للعدد يبلغ 5. من مزايا دوال احتساب الأماكن أنّها يمكن أن تعرض أي أعداد، بما في ذلك 0. على سبيل المثال، يعرض الطلب التالي العدد 1:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
مثال: احتساب عدد المطاعم باستخدام مضلّع
يمكنك استخدام مضلّع لتحديد مساحة البحث. عند استخدام مضلّع، يجب أن تحدّد نقاط المضلّع حلقة مغلقة تكون فيها النقطة الأولى في المضلّع هي نفسها النقطة الأخيرة.
يستخدم هذا المثال الدالة BigQuery
ST_GEOGFROMTEXT
لعرض قيمة GEOGRAPHY من مضلّع.
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
الردّ على إطار العرض:
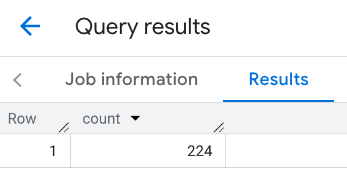
مثال: احتساب عدد المطاعم باستخدام خط
في المثال التالي، يتم تحديد مساحة البحث باستخدام خط من النقاط المتصلة بنصف قطر بحث يبلغ 100 متر حول الخط. يشبه الخط مسار رحلة يتم احتسابه بواسطة Routes API. قد يكون المسار مخصّصًا لمركبة أو دراجة هوائية أو للمشاة:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
الردّ على السطر:
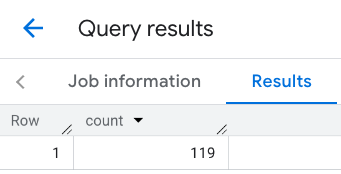
مثال: دمج نتائج مكالمات متعددة
يمكنك دمج نتائج طلبات متعددة إلى الدالة PLACES_COUNT.
على سبيل المثال، تريد الحصول على نتيجة واحدة تعرض عدد المطاعم
التي تندرج ضمن مستويات الأسعار التالية في منطقة معيّنة:
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
في هذا المثال، يمكنك إنشاء حلقة لاستدعاء الدالة PLACES_COUNT لكل مستوى سعر، وإدراج نتائج كل استدعاء في جدول مؤقت. بعد ذلك، يمكنك الاستعلام من الجدول المؤقت لعرض النتائج:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
الردّ المجمّع:
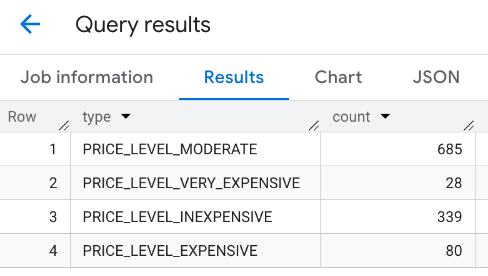
هناك خيار آخر وهو استخدام الأمر UNION ALL لدمج نتائج عبارات SELECT متعددة. يعرض المثال التالي النتائج نفسها كما في المثال السابق:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count

