این سند به شما نشان میدهد که چگونه اولین درخواست خود را با استفاده از یک سناریوی کاربردی در دنیای واقعی به API بهینهسازی مسیر ارسال کنید.
برای سادگی، این مثال از HTTP و JSON برای نمایش REST API استفاده میکند. با این حال، برای محیط عملیاتی شما، توصیه کلی این است که از gRPC به دلیل مزایای عملکردی آن استفاده کنید . با این حال، gRPC نیاز به نصب دارد. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به کتابخانههای کلاینت API بهینهسازی مسیر مراجعه کنید.
سناریو
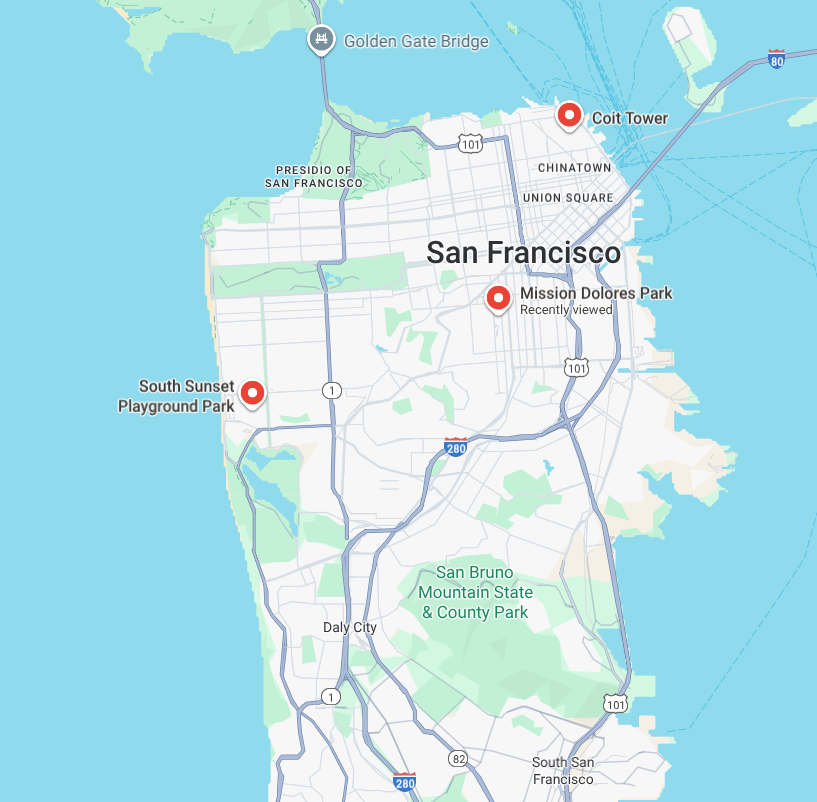
شما یک سرویس مراقبت روزانه از سگها را از ساعت ۷ صبح تا ۷ بعد از ظهر در سانفرانسیسکو اداره میکنید. امروز صبح، باید دو سگ را از مکانهای مختلف شهر تحویل بگیرید. هر دو صاحب سگ به شما یک بازه زمانی بین ساعت ۷:۳۰ تا ۹:۳۰ صبح برای تحویل دادن سگها داده بودند.
شما یک ون برای این کار دارید و به راننده ساعتی ۲۷ دلار میدهید. راننده و ون، روز کاری خود را ساعت ۷ صبح در مهدکودک شما شروع میکنند و باید تا ساعت ۱۲ ظهر برای استراحت ناهار از محل تحویل صبحگاهی برگردند.
امروز ۱۳ فوریه ۲۰۲۴ است و راننده وظایف زیر را بر عهده دارد:
- سگ کوهی برنی را از نزدیکی برج کویت بردارید.
- چیواوا را از پارک ساوت سانست پلیگراند تحویل بگیرید.
- هر دو سگ را در مرکز نگهداری روزانه سگها در پارک میشن دولورس بگذارید.
شما به مسیری نیاز دارید که زمان حضور سگها در ون را به حداقل برساند، در عین حال که الزامات جمعآوری و تحویل را نیز برآورده کند.
قبل از اینکه شروع کنی
برای اجرای کد در این سناریوی مثالی، ابتدا باید دستورالعملهای موجود در Setup the Route Optimization API را تکمیل کنید.
۱. رویکرد بهینهسازی مسیر خود را انتخاب کنید
API بهینهسازی مسیر، بسته به پیچیدگی مسئله بهینهسازی شما، روشهای متعددی برای انتخاب دارد.
از آنجا که این سناریوی مهدکودک سگی یک درخواست کوچک و سرراست است، از یک روش مسدودکننده مانند optimizeTours استفاده کنید که به سرعت نتایج را برای درخواستهای کوچک ارائه میدهد. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد روشهای API بهینهسازی مسیر، به نقاط پایانی همگام و ناهمگام مراجعه کنید.
از URL زیر برای ارسال یک درخواست HTTP POST به متد optimizeTours استفاده کنید:
https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_OR_ID:optimizeTours
همچنین باید تنظیمات زمان انتظار و مهلت را کوتاه تنظیم کنید تا زمان انتظار غیرضروری کاهش یابد. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، بهینهساز به زمان زیادی برای پاسخ به درخواست شما نیاز ندارد، بنابراین از تنظیمات زیر استفاده کنید:
- پارامتر
timeoutرا روی ۲ ثانیه تنظیم کنید. - تنظیمات مهلت را به صورت پیشفرض، که برای درخواستهای REST، 60 ثانیه است، باقی بگذارید.
۲. ساخت بدنه پیام درخواست
پس از انتخاب متد مسدودکننده optimizeTours و تعریف تنظیمات timeout و deadline، گام بعدی شما ساخت بدنه پیام درخواست است.
برای این سناریو، درخواست یک پیام OptimizeToursRequest است که به صورت JSON در REST API کدگذاری شده است.
برای ساخت پیام درخواست، مراحل زیر را دنبال کنید:
با ساختار درخواست اولیه شروع کنید که به شرح زیر است:
{ "timeout": ..., "model": { "shipments": [...], "vehicles": [...], "globalStartTime": "...", "globalEndTime": "..." } }برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد ساختار، به راهنمای مفاهیم کلیدی برای ساختار پایه (مدل حمل و نقل، محموله و وسیله نقلیه) مراجعه کنید.
تعریف محمولهها. در فیلد
shipments، برای هر سگی که باید صبح تحویل گرفته و تحویل داده شود، یک پیامShipmentاضافه کنید. در اینجا میتوانید مکان و زمان ترجیحی تحویل گرفتن سگ توسط صاحب سگ و مکان و زمان تحویل سگها توسط مهدکودک را تعریف کنید.برای هر سگ، یک
VisitRequestبرای بردن سگ و یک درخواست دیگر برای تحویل سگ ایجاد کنید که در این سناریو، به آن تحویل سگ به مهدکودک گفته میشود.در قسمت تحویل سگ،
arrivalWaypointرا روی محل تحویل سگ (برج کویت برای سگهای کوهی برنیز یا پارک بازی South Sunset برای چیواوا) وtimeWindowsرا روی زمان تحویل درخواستی صاحب سگ (۷:۳۰ صبح تا ۹:۳۰ صبح) تنظیم کنید.در قسمت تحویلها،
arrivalWaypointروی مرکز مراقبت روزانه وtimeWindowsبرای زمان تحویل مورد نیاز (۹:۳۰ صبح تا ۱۱:۳۰ صبح) تنظیم کنید.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد پنجرههای زمانی، به پنجرههای زمانی مراجعه کنید.
شما میتوانید از فیلد
labelبرای اضافه کردن یک شناسه برای هر محموله، مانند «سگ کوهستانی برنیز» و «چیواوا» استفاده کنید. این میتواند به شما در شناسایی محمولهها در پاسخ کمک کند.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد تعریف محمولهها، به بخش «محموله» مراجعه کنید.
تعریف وسایل نقلیه. در فیلد
vehicles، یک پیامVehicleبرای ون خود اضافه کنید که در آن مهدکودک به عنوان نقاط شروع و پایان، هزینه دستمزد راننده و ساعات کاری ون ذکر شده باشد.startWaypointوendWaypointون را روی مکانهای شروع و پایان روز تنظیم کنید، که همان مهدکودک نزدیک پارک میشن دولورس است.برای به حداقل رساندن هزینههای عملیاتی، باید محدودیتهای هزینه کسب و کار خود را تعریف کنید. پارامتر هزینه
costPerHourرا روی ۲۷ تنظیم کنید، که نشان میدهد شما برای رانندگی ون مخصوص مهدکودک چقدر به راننده پرداخت میکنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد پارامترهای هزینه، به مدل هزینه مراجعه کنید.برای اطمینان از اینکه بهینهساز مسیری را در محدوده ساعات کاری ون ایجاد میکند،
startTimeWindowsرا روی محدوده قابل قبول برای راننده جهت شروع به کار ون وendTimeWindowsرا روی محدوده قابل قبول برای زمانی که راننده باید به مهدکودک برگردد، تعریف کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد پنجرههای زمانی، به پنجرههای زمانی مراجعه کنید.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد تعریف وسایل نقلیه، به بخش وسایل نقلیه مراجعه کنید.
یک پنجره زمانی جهانی تنظیم کنید. پنجره زمانی جهانی نشان دهنده بازه زمانی است که ون میتواند در طول روز، کودکان را برای مهدکودک شما سوار و پیاده کند. برای این سناریو،
globalStartTimeبرای ۱۳ فوریه ۲۰۲۴ روی ۷:۰۰ صبح وglobalEndTimeرا روی ۷:۰۰ بعد از ظهر تنظیم کنید که نشان دهنده ساعات کاری مهدکودک شما است.
۳. درخواست را ارسال کنید
در ادامه یک درخواست curl ساده بر اساس سناریوی مهدکودک سگی آمده است و از متد optimizeTours مسدودکننده استفاده میکند.
قبل از ارسال درخواست، PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID در کد نمونه با شناسه پروژه Google Cloud خود جایگزین کنید.
curl -X POST 'https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID:optimizeTours' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)" \
--data @- << EOM
{
"timeout": "2s",
"model": {
"shipments": [
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.802395,
"longitude": -122.405822
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Bernese mountain dog"
},
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.738067,
"longitude": -122.498593
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Chihuahua"
}
],
"vehicles": [
{
"startWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"endWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"costPerHour": 27,
"startTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T07:15:00Z"
}
],
"endTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T11:45:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T12:00:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"globalStartTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"globalEndTime": "2024-02-13T19:00:00Z"
}
}
EOM
پارامترهای درخواست استفاده شده در درخواست
جدول زیر پارامترهای درخواست مورد استفاده در بدنه درخواست سناریوی مثال را شرح میدهد. میتوانید محتویات را بر اساس والد یا جستجوی متن فیلتر کنید.
| والدین | پارامتر | نوع ملک | توضیحات |
|---|---|---|---|
OptimizeToursRequest | model | شیء ( ShipmentModel ) | این هسته درخواست شماست. این یک شیء واحد است که در آن کل مسئله خود را تعریف میکنید، از جمله تمام سگهایی که برای سوار و پیاده کردن ( shipments ) و ون موجود در ناوگان خود ( vehicles ). آن را به عنوان طرح کلی مسئلهای که باید بهینه کنید، در نظر بگیرید. |
timeout | مدت زمان | این پارامتر حداکثر زمانی را که سرور قبل از بازگرداندن پاسخ، روی یک درخواست کار میکند، مشخص میکند. از این پارامتر برای کوتاه کردن زمان انتظار خود استفاده کنید. برای درخواستهای کوچک و سریع، مانند این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، این مقدار را روی ۲ ثانیه تنظیم کنید. | |
ShipmentModel | shipments[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( Shipment ) | این آرایهای از اشیاء است که هر شیء نشاندهندهی یک سگ است که باید برداشته یا رها شود. |
vehicles[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( Vehicle ) | این آرایهای از اشیاء است که در آن هر شیء یک وسیله نقلیه را در ناوگان شما تعریف میکند. در اینجا منابع خود را توصیف میکنید، مانند ونی که کار جمعآوری و تحویل را انجام میدهد. برای رسیدن به یک مسیر بهینه، باید حداقل یک وسیله نقلیه تعریف کنید. | |
globalStartTime | مهر زمانی | این زودترین زمان ممکن برای وقوع هر رویدادی در کل مدل شماست. این پارامتر، مسئله بهینهسازی را از نظر زمانی محدود میکند، که برای محاسبات دقیق ترافیک و مسیریابی بسیار مهم است. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، این را روی زودترین زمانی که راننده میتواند ون را در طول روز روشن کند، تنظیم کنید، که ساعت ۷ صبح برای ۱۳ فوریه ۲۰۲۴ است. | |
globalEndTime | مهر زمانی | این آخرین زمان ممکن برای وقوع هر رویدادی در کل مدل شماست. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، این را روی زمانی تنظیم کنید که انتظار میرود ون کار خود را تمام کند، که برای ۱۳ فوریه ۲۰۲۴ ساعت ۷ بعد از ظهر است. | |
Shipment | pickups[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( VisitRequest ) | این فهرستی از تمام گزینههای ممکن برای تحویل گرفتن محموله است. بهینهساز بهترین گزینه را برای حل مشکل شما انتخاب میکند. برای این سناریوی مراقبت از سگ، مکانهای تحویل گرفتن و بازههای زمانی که هر صاحب سگ برای هر سگ در نظر گرفته است را فهرست کنید. |
deliveries[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( VisitRequest ) | این فهرستی از تمام گزینههای ممکن برای تحویل محموله است. بهینهساز بهترین گزینه را برای حل مشکل شما انتخاب میکند. برای این سناریوی مراقبت از سگ، محل مرکز مراقبت از سگ و بازه زمانی لازم برای بازگشت راننده برای ناهار هر سگ را فهرست کنید. | |
label | رشته | این یک شناسه برای یک محموله خاص در درخواست شما است. میتوانید برچسبها را در درخواست خود مشخص کنید تا خواندن پاسخ آسانتر شود. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، از یک رشته توصیفی مانند "چیواوا"، "سگ کوهستانی برنیز" یا نام سگ استفاده کنید تا هنگام دریافت پاسخ API، راهحل با ورودی شما مطابقت داشته باشد. | |
VisitRequest | arrivalWaypoint[] | شیء ( Waypoint ) | این مکان یک بازدید خاص در مسیر است. میتوانید این را با استفاده از مختصات طول و عرض جغرافیایی، شناسه مکان یا عنوان تعریف کنید. در این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، این را روی مکانی که توسط مالک برای pickups ارائه شده و روی آدرس مهدکودک برای deliveries تنظیم کنید. |
timeWindows[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( TimeWindow ) | این آرایهای از اشیاء است که محدودیتهای زمانی برای برداشتن یا تحویل دادن سگها را تعریف میکند. برای این سناریو، از این برای تعریف بازه زمانی برداشتن هر سگ و بازه زمانی قابل قبول برای گذاشتن سگها در مهدکودک استفاده کنید. | |
Vehicle | startWaypoint[] | شیء ( Waypoint ) | این محل شروع مسیر وسیله نقلیه است که با مختصات طول و عرض جغرافیایی یا شناسه مکان تعریف میشود. این پارامتر به بهینهساز میگوید که وسیله نقلیه باید مسیر را از کجا شروع کند. اگر این نقطه مسیر را تعریف نکنید، بهینهساز یکی از محلهای تحویل یا تحویل را به عنوان محل شروع انتخاب میکند. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، از آنجا که راننده روز را در مهدکودک شروع میکند، از مختصات پارک میشن دولورس استفاده کنید. |
endWaypoint[] | شیء ( Waypoint ) | این مقصد نهایی مسیر وسیله نقلیه است که با مختصات طول و عرض جغرافیایی یا شناسه مکان تعریف میشود. این پارامتر به بهینهساز میگوید که وسیله نقلیه باید مسیر را در کجا به پایان برساند. اگر این نقطه مسیر را تعریف نکنید، بهینهساز یکی از محلهای تحویل یا تحویل را به عنوان انتهای مسیر انتخاب میکند. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، از آنجا که راننده باید روز را در مهدکودک به پایان برساند، از مختصات پارک میشن دولورس استفاده کنید. | |
costPerHour | شماره | این هزینهای است که برای هر ساعت استفاده از وسیله نقلیه، صرف نظر از اینکه در حال حرکت است یا متوقف، متحمل میشود. برای این سناریوی مهدکودک سگ، از این برای مدلسازی دستمزد ساعتی راننده استفاده کنید. | |
startTimeWindows[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( TimeWindow ) | این زمان، زمان قابل قبولی برای راننده است تا ون را برای بردن سگها در صبح شروع کند. | |
endTimeWindows[] | آرایهای از اشیاء ( TimeWindow ) | این زمان قابل قبول برای راننده است تا رانندگی ون را تمام کند و دوباره در مهدکودک سگها پارک کند. |

