במסמך הזה מוסבר איך לשלוח את הבקשה הראשונה אל Route Optimization API באמצעות תרחיש שימוש מהעולם האמיתי.
לצורך פשטות, בדוגמה נעשה שימוש ב-HTTP וב-JSON כדי להדגים את REST API. עם זאת, בסביבת הייצור, מומלץ להשתמש ב-gRPC כדי ליהנות מיתרונות הביצועים שלו. עם זאת, צריך להתקין את gRPC. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר ספריות הלקוח של Route Optimization API.
תרחיש
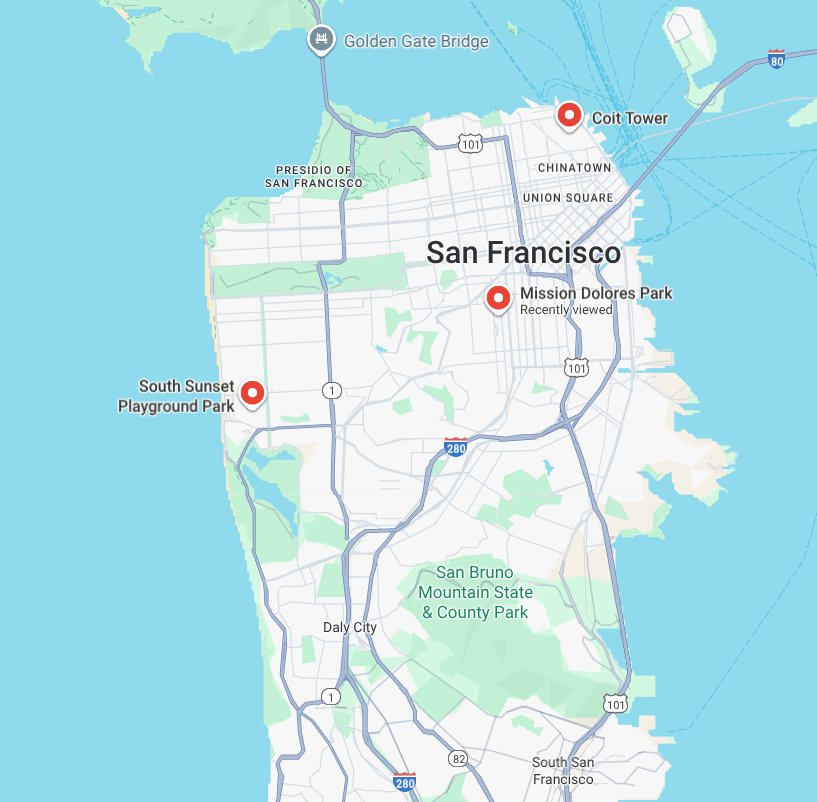
אתם מפעילים שירות של משחקייה לכלבים מ-7:00 עד 19:00 בתל אביב. הבוקר, עליך לאסוף שני כלבים ממיקומים שונים בעיר. שני בעלי הכלבים נתנו לך חלון איסוף בין 7:30 ל-9:30.
יש לכם טנדר אחד לעבודה, ואתם משלמים לנהג 27 דולר לשעה. הנהג והוואן מתחילים את היום במרכז הטיפול בילדים בשעה 7:00 בבוקר, והם צריכים לחזור מאיסופי הבוקר עד השעה 12:00 בצהריים להפסקת צהריים.
היום הוא 13 בפברואר 2024, ולנהג יש את המשימות הבאות:
- אוספים את כלב הברנר זננהונד ליד מגדל קויט.
- תאסוף את הצ'יוואווה בפארק South Sunset Playground.
- מורידים את שני הכלבים במרכז לטיפול ביום לכלבים בפארק מישן דולורס.
אתם צריכים מסלול שיצמצם את הזמן שהכלבים ישהו בוואן, וגם יעמוד בדרישות האיסוף וההורדה.
לפני שמתחילים
כדי להריץ את הקוד בתרחיש לדוגמה הזה, צריך קודם לבצע את ההוראות במאמר הגדרת Route Optimization API.
1. בחירת הגישה לאופטימיזציה של מסלולים
ל-Route Optimization API יש כמה שיטות שתוכלו לבחור מתוכן, בהתאם למורכבות של בעיית האופטימיזציה שלכם.
מכיוון שהתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים הוא בקשה קטנה ופשוטה, כדאי להשתמש בשיטה חוסמת, כמו optimizeTours, שמספקת תוצאות במהירות לבקשות קטנות. מידע נוסף על השיטות של Route Optimization API זמין במאמר בנושא נקודות קצה סינכרוניות ואסינכרוניות.
כדי לשלוח בקשת HTTP POST לשיטה optimizeTours, משתמשים בכתובת ה-URL הבאה:
https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_OR_ID:optimizeTours
כדאי גם להגדיר את הגדרות הזמן הקצוב לתפוגה והמועד האחרון לזמנים קצרים כדי לצמצם את זמן ההמתנה המיותר. בתרחיש הזה של גן לכלבים, הכלי לא צריך הרבה זמן כדי להגיב לבקשה שלכם, ולכן אפשר להשתמש בהגדרות הבאות:
- מגדירים את הפרמטר
timeoutל-2 שניות. - משאירים את הגדרות הדדליין בערך ברירת המחדל, שהוא 60 שניות לבקשות REST.
2. יצירת גוף ההודעה של הבקשה
אחרי שבוחרים את שיטת החסימה optimizeTours ומגדירים את הזמן הקצוב לתפוגה ואת תאריך היעד, השלב הבא הוא ליצור את גוף הודעת הבקשה.
בתרחיש הזה, הבקשה היא הודעת OptimizeToursRequest שמקודדת כ-JSON ב-REST API.
כדי ליצור את הודעת הבקשה, פועלים לפי השלבים הבאים:
מתחילים במבנה הבסיסי של הבקשה, שהוא כזה:
{ "timeout": ..., "model": { "shipments": [...], "vehicles": [...], "globalStartTime": "...", "globalEndTime": "..." } }מידע נוסף על המבנה זמין במדריך למושגי מפתח בנושא מבנה בסיסי (ShipmentModel, Shipment ו-Vehicle).
הגדרת משלוחים בשדה
shipments, מוסיפים הודעהShipmentלכל כלב שצריך לאסוף בבוקר ולהחזיר בערב. כאן מגדירים את המיקום והשעות המועדפים על בעלי הכלבים לאיסוף הכלבים, ואת המיקום והשעות של מרכז הטיפול להורדת הכלבים.לכל כלב, יוצרים
VisitRequestלאיסוף ועוד אחד למשלוח, שבמקרה הזה נקרא 'הורדה למעון'.במאפיין 'איסוף' [pickups], מגדירים את
arrivalWaypointלמיקום האיסוף של הכלב (Coit Tower לכלב ברניז או South Sunset Playground Park לצ'יוואווה) ואתtimeWindowsלשעת האיסוף שהבעלים ביקשו (7:30 עד 9:30).בקטע 'משלוחים', מגדירים את
arrivalWaypointלמרכז הטיפול ואתtimeWindowsלשעת המסירה הנדרשת (9:30 עד 11:30).
מידע נוסף על חלונות זמן זמין במאמר חלונות זמן.
אתם יכולים להשתמש בשדה
labelכדי להוסיף מזהה לכל משלוח, כמו "כלב הרים ברני" ו"צ'יוואווה". כך תוכלו לזהות את המשלוחים בתשובה.
מידע נוסף על הגדרת משלוחים זמין במאמר משלוח.
הגדרת כלי רכב בשדה
vehicles, מוסיפים הודעה לגבי הטנדר האחד עם מרכז הטיפול היומי כנקודת ההתחלה והסיום, עלות שכר הנהג ושעות הפעילות של הטנדר.Vehicleמגדירים את
startWaypointואתendWaypointשל הטנדר למיקומי ההתחלה והסיום של היום, כלומר למעון היום ליד פארק מישן דולורס.כדי לצמצם את עלויות התפעול, צריך להגדיר את מגבלות העלויות של העסק. מגדירים את פרמטר העלות
costPerHourל-27, שזה הסכום שמשלמים לנהג על הנסיעה בוואן של המעון לכלבים. מידע נוסף על פרמטרים של עלויות זמין במאמר בנושא מודל עלויות.כדי לוודא שהכלי לאופטימיזציה ייצור מסלול בתוך שעות הפעילות של הטנדר, צריך להגדיר את
startTimeWindowsלטווח המקובל שבו הנהג יכול להתחיל להפעיל את הטנדר, ואתendTimeWindowsלטווח המקובל שבו הנהג צריך לחזור למרכז הטיפול. מידע נוסף על חלונות זמן זמין במאמר חלונות זמן.
מידע נוסף על הגדרת כלי רכב זמין במאמר כלי רכב.
הגדרת חלון זמן גלובלי חלון הזמן הגלובלי מייצג את מסגרת הזמן שבה הטנדר יכול לבצע איסופים והחזרות של ילדים למעון במהלך היום. בתרחיש הזה, מגדירים את
globalStartTimeל-7:00 ואתglobalEndTimeל-19:00 ל-13 בפברואר 2024, שעות הפעילות של המעון לכלבים.
3. שליחת הבקשה
הבקשה הבאה מסוג curl היא פשוטה ומתבססת על התרחיש של מעון היום לכלבים. היא משתמשת בשיטת החסימה optimizeTours.
לפני ששולחים את הבקשה, מחליפים את PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID בקוד לדוגמה במזהה הפרויקט ב-Google Cloud.
curl -X POST 'https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID:optimizeTours' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)" \
--data @- << EOM
{
"timeout": "2s",
"model": {
"shipments": [
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.802395,
"longitude": -122.405822
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Bernese mountain dog"
},
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.738067,
"longitude": -122.498593
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Chihuahua"
}
],
"vehicles": [
{
"startWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"endWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"costPerHour": 27,
"startTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T07:15:00Z"
}
],
"endTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T11:45:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T12:00:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"globalStartTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"globalEndTime": "2024-02-13T19:00:00Z"
}
}
EOM
פרמטרים של בקשה שנעשה בהם שימוש בבקשה
בטבלה הבאה מפורטים פרמטרים של הבקשה שמשמשים בגוף הבקשה בתרחיש לדוגמה. אפשר לסנן את התוכן לפי הורה או לפי חיפוש טקסט.
| הורה | פרמטר | סוג הנכס | תיאור |
|---|---|---|---|
OptimizeToursRequest |
model |
אובייקט (ShipmentModel) |
זהו עיקר הבקשה שלך. זהו אובייקט יחיד שבו מגדירים את כל הבעיה, כולל כל הכלבים שצריך לאסוף ולהוריד (shipments) ואת הטנדר בצי הרכבים (vehicles). אפשר לחשוב על זה כעל תוכנית העבודה המלאה לבעיה שצריך לבצע אופטימיזציה שלה. |
timeout |
משך | הפרמטר הזה מציין את משך הזמן המקסימלי שהשרת עובד על בקשה לפני שהוא מחזיר תשובה. השתמשו בפרמטר הזה כדי לקצר את זמן ההמתנה. עבור בקשות קטנות ומהירות, כמו התרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, מגדירים את הערך הזה ל-2 שניות. | |
ShipmentModel |
shipments[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (Shipment) |
זהו מערך של אובייקטים, כאשר כל אובייקט מייצג כלב שצריך לאסוף או להוריד. |
vehicles[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (Vehicle) |
זהו מערך של אובייקטים, שכל אחד מהם מגדיר רכב בצי שלכם. כאן מתארים את המשאבים, למשל את הטנדר שמבצע את האיסופים והמשלוחים. כדי לקבל מסלול אופטימלי, צריך להגדיר לפחות רכב אחד. | |
globalStartTime |
חותמת זמן | זהו הזמן המוקדם ביותר שבו יכול להתרחש אירוע כלשהו במודל כולו. הפרמטר הזה מצמצם את בעיית האופטימיזציה בזמן, וזה חיוני לחישובים מדויקים של תנועת הגולשים והניתוב. בתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, מגדירים את השעה המוקדמת ביותר שבה הנהג יכול להפעיל את הטנדר באותו יום, שהיא 7:00 בבוקר ב-13 בפברואר 2024. | |
globalEndTime |
חותמת זמן | זהו הזמן המאוחר ביותר האפשרי להתרחשות של אירוע כלשהו במודל כולו. בתרחיש הזה של גן הכלבים, צריך להגדיר את השעה שבה הטנדר צפוי לסיים את הפעילות שלו, כלומר 19:00 ב-13 בפברואר 2024. | |
Shipment |
pickups[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (VisitRequest) |
זו רשימה של כל אפשרויות האיסוף האפשריות של המשלוח. הכלי לאופטימיזציה בוחר את הפתרון הטוב ביותר לבעיה שלכם. בתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, תציין את מיקומי האיסוף ואת חלונות הזמן שכל בעלים סיפק לכל כלב. |
deliveries[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (VisitRequest) |
זו רשימה של כל האפשרויות האפשריות למסירת המשלוח. הכלי לאופטימיזציה בוחר את הפתרון הטוב ביותר לבעיה שלכם. במקרה של הטיפול היומי בכלבים, צריך לציין את המיקום של המקום לטיפול בכלבים ואת חלון הזמן שבו הנהג צריך לחזור לארוחת צהריים לכל כלב. | |
label |
מחרוזת | זהו מזהה של משלוח ספציפי בבקשה. אפשר לציין תוויות בבקשה כדי שיהיה קל יותר לקרוא את התשובה. בתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, אפשר להשתמש במחרוזת תיאורית כמו 'צ'יוואווה', 'כלב הרים ברני' או שם הכלב כדי להתאים את הפתרון לקלט כשמקבלים את תגובת ה-API. | |
VisitRequest |
arrivalWaypoint[] |
אובייקט (Waypoint) |
זהו המיקום של ביקור ספציפי במסלול. אפשר להגדיר את זה באמצעות קואורדינטות של קו אורך וקו רוחב, מזהה מקום או כיוון. בתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, צריך להגדיר את המיקום שבעל הכלב סיפק עבור pickups ואת הכתובת של מעון היום עבור deliveries. |
timeWindows[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (TimeWindow) |
מערך של אובייקטים שמגדירים את מגבלות הזמן לאיסוף או למשלוח. במקרה הזה, צריך להשתמש בנתונים האלה כדי להגדיר את חלון האיסוף של כל אחד מהכלבים ואת חלון הזמן שבו אפשר להוריד את הכלבים במרכז לטיפול ביום. | |
Vehicle |
startWaypoint[] |
אובייקט (Waypoint) |
זהו מיקום ההתחלה של מסלול הנסיעה של הרכב, שמוגדר באמצעות קואורדינטות של קו רוחב וקו אורך או מזהה מקום. הפרמטר הזה מציין לכלי האופטימיזציה את נקודת ההתחלה של המסלול. אם לא מגדירים את נקודת הביניים הזו, הכלי לאופטימיזציה בוחר אחת מנקודות האיסוף או המסירה כמיקום ההתחלה. בתרחיש הזה של המטפלת ביום, הנהג מתחיל את היום במתקן של המטפלת, ולכן צריך להשתמש בקואורדינטות של פארק מישן דולורס. |
endWaypoint[] |
אובייקט (Waypoint) |
זהו היעד הסופי של מסלול הרכב, שמוגדר באמצעות קואורדינטות של קו רוחב וקו אורך או מזהה מקום. הפרמטר הזה מציין לכלי האופטימיזציה איפה הרכב צריך לסיים את המסלול. אם לא מגדירים את נקודת הדרך הזו, האופטימיזציה בוחרת אחת מהעצירות לאיסוף או למסירה כסוף המסלול. בתרחיש הזה של מעון יום לכלבים, הנהג צריך לסיים את היום במעון, ולכן משתמשים בקואורדינטות של פארק מיסיון דולורס. | |
costPerHour |
number | העלות הזו היא העלות שנוצרת על כל שעה שבה נעשה שימוש ברכב, בלי קשר אם הוא נוסע או לא. בתרחיש הזה של גן כלבים, אפשר להשתמש בנתונים הבאים כדי ליצור מודל של שכר שעתי של נהג. | |
startTimeWindows[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (TimeWindow) |
זהו חלון הזמנים המקובל שבו הנהג יכול להתחיל לנהוג בוואן כדי לאסוף את הכלבים בבוקר. | |
endTimeWindows[] |
מערך של אובייקטים (TimeWindow) |
זהו חלון הזמנים המקובל לנהג לסיים את הנסיעה בוואן ולחנות בחזרה במרכז לטיפול ביום לכלבים. |

