이 문서에서는 실제 사용 사례 시나리오를 사용하여 Route Optimization API에 첫 번째 요청을 보내는 방법을 보여줍니다.
이 예에서는 REST API를 보여주기 위해 HTTP와 JSON을 사용합니다. 하지만 프로덕션 환경에서는 성능상의 이점을 위해 gRPC를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다. 하지만 gRPC에는 설치가 필요합니다. 자세한 내용은 Route Optimization API 클라이언트 라이브러리를 참고하세요.
시나리오
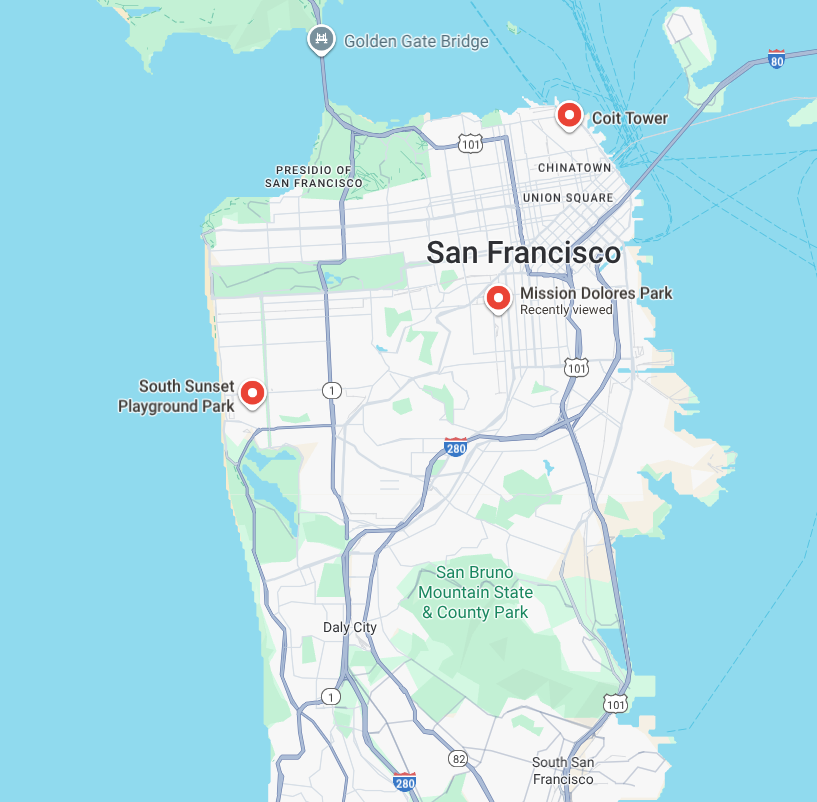
샌프란시스코에서 오전 7시부터 오후 7시까지 반려견 데이케어 서비스를 운영하고 있습니다. 오늘 아침에는 도시의 서로 다른 위치에서 두 마리의 개를 데려와야 합니다. 두 반려견 소유자 모두 오전 7시 30분에서 오전 9시 30분 사이에 픽업을 요청했습니다.
작업에 필요한 밴이 1대이고 운전자에게 시간당 27달러를 지불합니다. 운전자와 밴은 오전 7시에 어린이집에서 하루를 시작하며 점심시간을 위해 오전 12시까지 오전 픽업을 마치고 돌아와야 합니다.
오늘은 2024년 2월 13일이며 운전자는 다음과 같은 작업을 수행해야 합니다.
- 코잇 타워 근처에서 버니즈 마운틴 도그를 픽업합니다.
- 사우스 선셋 놀이터 공원에서 치와와를 데려오세요.
- 미션 돌로레스 공원의 반려견 데이케어 센터에 두 마리의 반려견을 맡깁니다.
승차 및 하차 요구사항을 충족하면서 개가 밴에 있는 시간을 최소화하는 경로가 필요합니다.
시작하기 전에
이 예시 시나리오의 코드를 실행하려면 먼저 Route Optimization API 설정의 안내를 완료해야 합니다.
1. 경로 최적화 접근 방식 선택
경로 최적화 API에는 최적화 문제의 복잡성에 따라 선택할 수 있는 여러 메서드가 있습니다.
이 애견 유치원 시나리오는 작고 간단한 요청이므로 작은 요청에 대한 결과를 빠르게 제공하는 차단 메서드(예: optimizeTours)를 사용합니다. Route Optimization API 메서드에 대한 자세한 내용은 동기 및 비동기 엔드포인트를 참고하세요.
다음 URL을 사용하여 optimizeTours 메서드에 대한 HTTP POST 요청을 실행합니다.
https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_OR_ID:optimizeTours
불필요한 대기 시간을 줄이려면 제한 시간과 기한 설정을 짧게 설정해야 합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 최적화 프로그램이 요청에 응답하는 데 많은 시간이 필요하지 않으므로 다음 설정을 사용하세요.
timeout매개변수를 2초로 설정합니다.- 기한 설정은 기본값(REST 요청의 경우 60초)으로 둡니다.
2. 요청 메시지 본문 구성
차단 optimizeTours 메서드를 선택하고 제한 시간 및 기한 설정을 정의한 후 다음 단계는 요청 메시지의 본문을 구성하는 것입니다.
이 시나리오에서 요청은 REST API에서 JSON으로 인코딩된 OptimizeToursRequest 메시지입니다.
요청 메시지를 구성하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
다음과 같은 기본 요청 구조로 시작합니다.
{ "timeout": ..., "model": { "shipments": [...], "vehicles": [...], "globalStartTime": "...", "globalEndTime": "..." } }구조에 관한 자세한 내용은 기본 구조 (ShipmentModel, Shipment, Vehicle)의 주요 개념 가이드를 참고하세요.
배송을 정의합니다.
shipments필드에 아침에 픽업하고 드롭오프해야 하는 각 강아지에 대한Shipment메시지를 추가합니다. 여기에서 각 반려견 보호자가 선호하는 픽업 위치와 시간, 반려견을 데려다 줄 데이케어 센터의 위치와 시간을 정의합니다.각 강아지에 대해 픽업용
VisitRequest와 배송용VisitRequest를 만듭니다. 이 시나리오에서는 배송을 데이케어 드롭오프라고 합니다.픽업에서
arrivalWaypoint을 반려견의 픽업 위치 (베르네즈 마운틴 도그의 경우 코잇 타워, 치와와의 경우 사우스 선셋 플레이그라운드 파크)로 설정하고timeWindows을 주인이 요청한 픽업 시간 (오전 7시 30분~오전 9시 30분)으로 설정합니다.배송에서
arrivalWaypoint을 어린이집으로 설정하고timeWindows을 필요한 하차 시간 (오전 9시 30분~오전 11시 30분)으로 설정합니다.
시간 창에 대한 자세한 내용은 시간 창을 참고하세요.
label필드를 사용하여 '버니즈 마운틴 도그', '치와와'와 같은 각 배송의 식별자를 추가할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 응답에서 배송을 식별할 수 있습니다.
배송 정의에 대한 자세한 내용은 배송을 참고하세요.
차량 정의
vehicles필드에 어린이집을 시작점과 끝점으로 하는 밴 1대에 대한Vehicle메시지를 추가합니다. 여기에는 운전자의 임금과 밴의 운영 시간이 포함됩니다.밴의
startWaypoint과endWaypoint을 하루의 시작 및 종료 위치인 미션 돌로레스 파크 근처의 데이케어 센터로 설정합니다.운영 비용을 최소화하려면 비즈니스의 비용 제약 조건을 정의해야 합니다. 비용 매개변수
costPerHour을 27로 설정합니다. 이는 운전자에게 강아지 데이케어 밴 운전 비용으로 지불하는 금액입니다. 비용 매개변수에 대한 자세한 내용은 비용 모델을 참고하세요.최적화 프로그램이 밴의 운영 시간 내에 경로를 생성하도록 하려면 운전자가 밴을 운전하기 시작할 수 있는 허용 범위로
startTimeWindows를 정의하고 운전자가 어린이집으로 돌아와야 하는 허용 범위로endTimeWindows를 정의합니다. 시간 창에 대한 자세한 내용은 시간 창을 참고하세요.
차량 정의에 관한 자세한 내용은 차량을 참고하세요.
전역 시간 창을 설정합니다. 전역 시간대는 하루 종일 유치원에서 픽업 및 하차를 수행할 수 있는 시간대를 나타냅니다. 이 시나리오에서는 2024년 2월 13일의
globalStartTime을 오전 7시로,globalEndTime을 오후 7시로 설정합니다. 이는 반려견 데이케어 운영 시간을 나타냅니다.
3. 요청 전송
다음은 강아지 유치원 시나리오를 기반으로 하며 차단 optimizeTours 메서드를 사용하는 간단한 curl 요청입니다.
요청을 보내기 전에 샘플 코드의 PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID를 Google Cloud 프로젝트 ID로 바꿉니다.
curl -X POST 'https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID:optimizeTours' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)" \
--data @- << EOM
{
"timeout": "2s",
"model": {
"shipments": [
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.802395,
"longitude": -122.405822
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Bernese mountain dog"
},
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.738067,
"longitude": -122.498593
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Chihuahua"
}
],
"vehicles": [
{
"startWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"endWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"costPerHour": 27,
"startTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T07:15:00Z"
}
],
"endTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T11:45:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T12:00:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"globalStartTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"globalEndTime": "2024-02-13T19:00:00Z"
}
}
EOM
요청에 사용된 요청 매개변수
다음 표에서는 예시 시나리오의 요청 본문에 사용된 요청 매개변수를 설명합니다. 상위 항목 또는 텍스트 검색으로 콘텐츠를 필터링할 수 있습니다.
| 자녀 있음 | 매개변수 | 숙소 유형 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
OptimizeToursRequest |
model |
object (ShipmentModel) |
이것이 요청의 핵심입니다. 픽업 및 드롭오프해야 하는 모든 개 (shipments)와 차량의 밴(vehicles)을 비롯한 전체 문제를 정의하는 단일 객체입니다. 최적화해야 하는 문제의 전체 청사진이라고 생각하면 됩니다. |
timeout |
기간 | 이 파라미터는 서버가 응답을 반환하기 전에 요청에 대해 작업하는 최대 시간을 지정합니다. 이 매개변수를 사용하여 대기 시간을 단축하세요. 이 반려견 데이케어 시나리오와 같은 작고 빠른 요청의 경우 이 값을 2초로 설정합니다. | |
ShipmentModel |
shipments[] |
객체 배열 (Shipment) |
픽업 또는 드롭오프해야 하는 강아지를 각각 나타내는 객체의 배열입니다. |
vehicles[] |
객체 배열 (Vehicle) |
이는 객체의 배열이며 각 객체는 차량의 차량을 정의합니다. 여기에서 픽업 및 하차를 수행하는 차량과 같은 리소스를 설명합니다. 최적화된 경로를 얻으려면 차량을 하나 이상 정의해야 합니다. | |
globalStartTime |
타임스탬프 | 전체 모델에서 이벤트가 발생할 수 있는 가장 빠른 시간입니다. 이 매개변수는 시간 내에 최적화 문제를 좁히며 이는 정확한 트래픽 및 라우팅 계산에 중요합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 운전자가 당일 밴을 운전할 수 있는 가장 빠른 시간인 2024년 2월 13일 오전 7시로 설정합니다. | |
globalEndTime |
타임스탬프 | 전체 모델에서 이벤트가 발생할 수 있는 가장 늦은 시간입니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 밴이 운행을 종료할 것으로 예상되는 시간인 2024년 2월 13일 오후 7시로 설정합니다. | |
Shipment |
pickups[] |
객체 배열 (VisitRequest) |
배송의 가능한 모든 수령 옵션 목록입니다. 최적화 프로그램은 문제를 해결하기에 가장 적합한 것을 선택합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서 각 소유자가 각 개에 대해 제공한 픽업 장소와 시간대를 나열해 줘. |
deliveries[] |
객체 배열 (VisitRequest) |
배송의 가능한 모든 수령 옵션 목록입니다. 최적화 프로그램은 문제를 해결하기에 가장 적합한 것을 선택합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 애견 유치원 시설의 위치와 각 강아지의 점심 식사를 위해 운전자가 돌아와야 하는 시간대를 나열해 줘. | |
label |
문자열 | 요청의 특정 배송 식별자입니다. 요청에 라벨을 지정하면 대답을 더 쉽게 읽을 수 있습니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 API 응답을 받을 때 입력에 대한 솔루션을 일치시키기 위해 '치와와', '버니즈 마운틴 도그' 또는 강아지 이름과 같은 설명이 포함된 문자열을 사용합니다. | |
VisitRequest |
arrivalWaypoint[] |
object (Waypoint) |
경로에서 특정 방문의 위치입니다. 위도 및 경도 좌표, 장소 ID 또는 방위를 사용하여 이를 정의할 수 있습니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 pickups의 경우 주인이 제공한 위치로, deliveries의 경우 유치원 주소로 설정합니다. |
timeWindows[] |
객체 배열 (TimeWindow) |
픽업 또는 배송의 시간 제약 조건을 정의하는 객체의 배열입니다. 이 시나리오에서는 이를 사용하여 각 개의 픽업 시간대와 개를 데이케어 센터에 데려다 줄 수 있는 시간대를 정의합니다. | |
Vehicle |
startWaypoint[] |
object (Waypoint) |
위도 및 경도 좌표 또는 장소 ID로 정의된 차량 경로의 시작 위치입니다. 이 매개변수는 차량이 경로를 시작해야 하는 위치를 옵티마이저에 알려줍니다. 이 경유지를 정의하지 않으면 옵티마이저가 픽업 또는 배송 중 하나를 시작 위치로 선택합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 운전자가 유치원 시설에서 하루를 시작하므로 Mission Dolores Park의 좌표를 사용합니다. |
endWaypoint[] |
object (Waypoint) |
위도 및 경도 좌표 또는 장소 ID로 정의된 차량 경로의 최종 목적지입니다. 이 파라미터는 차량이 경로를 종료해야 하는 위치를 옵티마이저에 알려줍니다. 이 경유지를 정의하지 않으면 옵티마이저가 픽업 또는 배송 중 하나를 경로의 끝으로 선택합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 운전자가 유치원 시설에서 하루를 마쳐야 하므로 Mission Dolores Park의 좌표를 사용합니다. | |
costPerHour |
숫자 | 이 비용은 차량이 이동 중인지 정지 상태인지와 관계없이 차량을 사용하는 매시간마다 발생합니다. 이 애견 유치원 시나리오에서는 이를 사용하여 운전자의 시간당 임금을 모델링합니다. | |
startTimeWindows[] |
객체 배열 (TimeWindow) |
이 시간은 운전자가 아침에 개를 픽업하기 위해 밴을 운전하기 시작할 수 있는 허용되는 시간입니다. | |
endTimeWindows[] |
객체 배열 (TimeWindow) |
이 시간은 운전자가 밴 운전을 마치고 반려견 데이케어 센터에 다시 주차할 수 있는 시간입니다. |

