このドキュメントでは、実際のユースケース シナリオを使用して、Route Optimization API に最初のリクエストを行う方法について説明します。
わかりやすくするために、この例では HTTP と JSON を使用して REST API を示します。ただし、本番環境では、パフォーマンス上のメリットがあるため、gRPC を使用することをおすすめします。ただし、gRPC にはインストールが必要です。詳細については、Route Optimization API クライアント ライブラリをご覧ください。
シナリオ
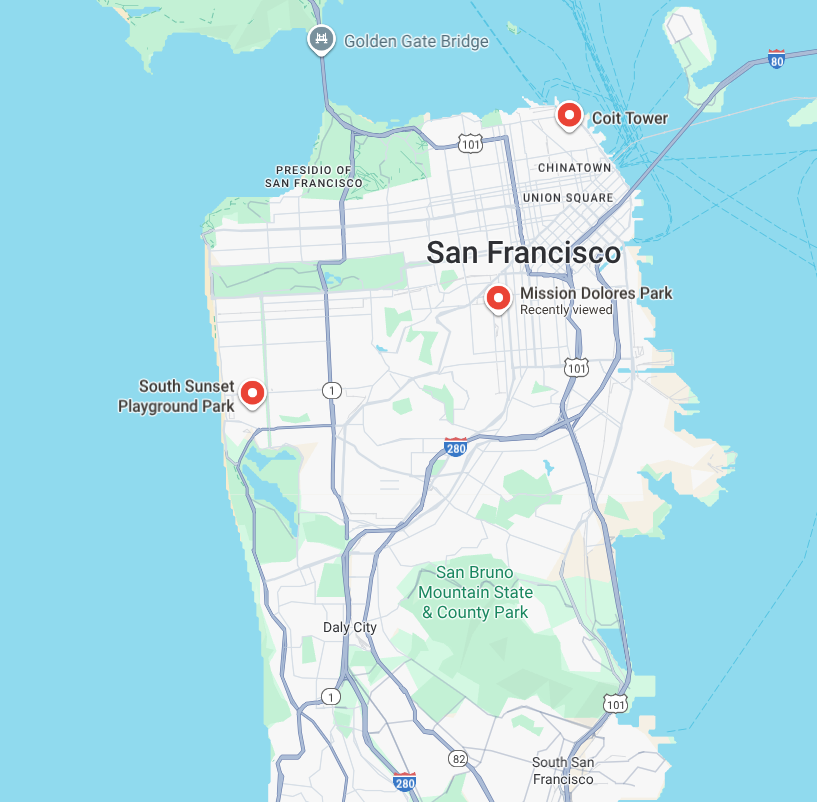
サンフランシスコで午前 7 時から午後 7 時まで犬のデイケア サービスを運営しています。今朝、あなたは市内の異なる場所で 2 匹の犬を迎えに行く必要があります。両方の犬の飼い主から、午前 7 時 30 分から午前 9 時 30 分までの受け取り時間枠が指定されています。
仕事には 1 台のバンを使用し、運転手には 1 時間あたり 27 ドルを支払います。運転手とバンは午前 7 時に保育園を出発し、午前中の送迎を終えて午後 12 時までに戻り、昼食休憩を取る必要があります。
今日は 2024 年 2 月 13 日で、運転手には次のタスクがあります。
- コイト タワーの近くでバーニーズ マウンテン ドッグを拾います。
- チワワはサウス サンセット プレイグラウンド パークでお受け取りください。
- ミッション ドロレス パークにある犬の保育園に 2 匹の犬を預けます。
犬がバンに乗っている時間を最小限に抑えながら、乗車と降車の要件を満たすルートが必要です。
始める前に
このシナリオ例のコードを実行するには、まず Route Optimization API を設定するの手順を完了する必要があります。
1. ルート最適化のアプローチを選択する
Route Optimization API には、最適化問題の複雑さに応じて選択できる複数のメソッドがあります。
この犬の保育園のシナリオは小規模で簡単なリクエストであるため、optimizeTours などのブロッキング メソッドを使用します。このメソッドは、小規模なリクエストの結果を迅速に返します。Route Optimization API メソッドの詳細については、同期エンドポイントと非同期エンドポイントをご覧ください。
次の URL を使用して、optimizeTours メソッドに HTTP POST リクエストを行います。
https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_OR_ID:optimizeTours
また、不要な待機時間を減らすために、タイムアウトと期限の設定を短くする必要があります。この犬のデイケアのシナリオでは、オプティマイザーがリクエストに応答するのにそれほど時間がかからないため、次の設定を使用します。
timeoutパラメータを 2 秒に設定します。- 期限の設定はデフォルトのままにします。REST リクエストの場合は 60 秒です。
2. リクエスト メッセージの本文を作成する
ブロッキング optimizeTours メソッドを選択し、タイムアウトと期限の設定を定義したら、次のステップとしてリクエスト メッセージの本文を構築します。
このシナリオでは、リクエストは REST API で JSON としてエンコードされた OptimizeToursRequest メッセージです。
リクエスト メッセージを作成する手順は次のとおりです。
基本的なリクエスト構造から始めます。これは次のとおりです。
{ "timeout": ..., "model": { "shipments": [...], "vehicles": [...], "globalStartTime": "...", "globalEndTime": "..." } }構造の詳細については、基本構造(ShipmentModel、Shipment、Vehicle)の主なコンセプト ガイドをご覧ください。
配送を定義します。[
shipments] フィールドに、朝に迎えに行って送り届ける必要がある犬ごとにShipmentメッセージを追加します。ここでは、犬の飼い主が希望する犬の受け取り場所と時間、犬を預けるデイケア センターの場所と時間を定義します。犬ごとに、お迎え用の
VisitRequestと、配達用のVisitRequestを作成します。このシナリオでは、配達用のVisitRequestは保育園の送迎と呼ばれます。ピックアップでは、
arrivalWaypointを犬のピックアップ場所(バーニーズ マウンテン ドッグの場合はコイト タワー、チワワの場合はサウス サンセット プレイグラウンド パーク)に設定し、timeWindowsを飼い主がリクエストしたピックアップ時間(午前 7 時 30 分~午前 9 時 30 分)に設定します。配達では、
arrivalWaypointを保育園に、timeWindowsを必要な配達時間(午前 9 時 30 分~午前 11 時 30 分)に設定します。
時間枠の詳細については、時間枠をご覧ください。
labelフィールドを使用して、各配送の識別子(「バーニーズ マウンテン ドッグ」、「チワワ」など)を追加できます。これにより、レスポンス内の配送を特定できます。
配送の定義について詳しくは、配送をご覧ください。
車両を定義します。
vehiclesフィールドに、保育園を始点と終点とする 1 台のバンに関するVehicleメッセージを追加します。このメッセージには、運転手の賃金とバンの運行時間を含めます。バンの
startWaypointとendWaypointを、1 日の開始地点と終了地点(ミッション ドロレス パーク近くの保育園)に設定します。運用コストを最小限に抑えるには、ビジネスのコスト制約を定義する必要があります。費用パラメータ
costPerHourを 27 に設定します。これは、犬のデイケア バンを運転する運転手に支払う金額です。費用パラメータの詳細については、費用モデルをご覧ください。最適化ツールがバンの運行時間内にルートを作成するようにするには、
startTimeWindowsを運転手がバンの運行を開始できる許容範囲に、endTimeWindowsを運転手が保育園に戻らなければならない許容範囲に定義します。時間枠の詳細については、時間枠をご覧ください。
車両の定義について詳しくは、車両をご覧ください。
グローバル時間枠を設定します。グローバル時間枠は、1 日を通して保育園の送迎を行うことができる時間帯を表します。このシナリオでは、犬の保育園の営業時間を示す 2024 年 2 月 13 日の
globalStartTimeを午前 7 時、globalEndTimeを午後 7 時に設定します。
3. リクエストを送信する
次の例は、犬の託児所のシナリオに基づいたシンプルな curl リクエストで、ブロッキング optimizeTours メソッドを使用しています。
リクエストを送信する前に、サンプルコードの PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID を Google Cloud プロジェクト ID に置き換えます。
curl -X POST 'https://routeoptimization.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NUMBER_OR_ID:optimizeTours' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)" \
--data @- << EOM
{
"timeout": "2s",
"model": {
"shipments": [
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.802395,
"longitude": -122.405822
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Bernese mountain dog"
},
{
"pickups": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.738067,
"longitude": -122.498593
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"deliveries": [
{
"arrivalWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"timeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T11:30:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"label": "Chihuahua"
}
],
"vehicles": [
{
"startWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"endWaypoint": {
"location": {
"latLng": {
"latitude": 37.760202,
"longitude": -122.426796
}
}
},
"costPerHour": 27,
"startTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T07:15:00Z"
}
],
"endTimeWindows": [
{
"startTime": "2024-02-13T11:45:00Z",
"endTime": "2024-02-13T12:00:00Z"
}
]
}
],
"globalStartTime": "2024-02-13T07:00:00Z",
"globalEndTime": "2024-02-13T19:00:00Z"
}
}
EOM
リクエストで使用されるリクエスト パラメータ
次の表に、シナリオ例のリクエスト本文で使用されるリクエスト パラメータを示します。コンテンツは、親またはテキスト検索でフィルタできます。
| 親 | パラメータ | プロパティ タイプ | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
OptimizeToursRequest |
model |
object(ShipmentModel) |
これがリクエストの核となります。これは、回収と配達が必要なすべての犬(shipments)やフリート内のバン(vehicles)など、問題全体を定義する単一のオブジェクトです。最適化する必要がある問題の完全なブループリントと考えることができます。 |
timeout |
所要時間 | このパラメータは、サーバーがレスポンスを返す前にリクエストを処理する最大時間を指定します。このパラメータを使用して、待機時間を短縮します。この犬の保育園のシナリオのような小規模で迅速なリクエストの場合は、この値を 2 秒に設定します。 | |
ShipmentModel |
shipments[] |
オブジェクトの配列(Shipment) |
これは、受け取りまたは配達が必要な犬を表すオブジェクトの配列です。 |
vehicles[] |
オブジェクトの配列(Vehicle) |
これは、各オブジェクトがフリート内の車両を定義するオブジェクトの配列です。ここでは、集荷と配達を行うバンなどのリソースを記述します。最適化されたルートを取得するには、少なくとも 1 台の車両を定義する必要があります。 | |
globalStartTime |
タイムスタンプ | これは、モデル全体でイベントが発生する可能性のある最も早い時間です。このパラメータは、最適化問題を時間的に絞り込みます。これは、トラフィックとルートの正確な計算に不可欠です。この犬の託児所のシナリオでは、運転手がその日にバンを運転できる最も早い時間(2024 年 2 月 13 日の午前 7 時)に設定します。 | |
globalEndTime |
タイムスタンプ | これは、モデル全体でイベントが発生する可能性のある最も遅い時間です。この犬のデイケアのシナリオでは、バンが運行を終了する予定の時刻(2024 年 2 月 13 日の午後 7 時)に設定します。 | |
Shipment |
pickups[] |
オブジェクトの配列(VisitRequest) |
これは、配送で利用可能なすべての受け取りオプションのリストです。オプティマイザーは、問題を解決する最適なものを選択します。この犬のデイケアのシナリオでは、各犬の飼い主が指定した送迎場所と時間帯をリストします。 |
deliveries[] |
オブジェクトの配列(VisitRequest) |
これは、配送で利用可能なすべての受け取りオプションのリストです。オプティマイザーは、問題を解決する最適なものを選択します。この犬のデイケアのシナリオでは、犬のデイケア施設の場所と、各犬の昼食のためにドライバーが戻る必要のある時間帯をリストします。 | |
label |
文字列 | これは、リクエスト内の特定の配送の識別子です。リクエストでラベルを指定すると、レスポンスを読みやすくなります。この犬のデイケアのシナリオでは、「チワワ」、「バーニーズ マウンテン ドッグ」、犬の名前などの説明的な文字列を使用して、API レスポンスを受信したときにソリューションを入力と照合します。 | |
VisitRequest |
arrivalWaypoint[] |
object(Waypoint) |
これは、ルート上の特定の訪問場所です。これは、緯度と経度の座標、プレイス ID、または見出しを使用して定義できます。この犬の託児所のシナリオでは、pickups には飼い主が提供した場所を、deliveries には託児所の住所を設定します。 |
timeWindows[] |
オブジェクトの配列(TimeWindow) |
これは、受け取りまたは配達の時間制約を定義するオブジェクトの配列です。このシナリオでは、各犬の受け取り時間帯と、犬を託児所に預けることができる時間帯を定義します。 | |
Vehicle |
startWaypoint[] |
object(Waypoint) |
これは、車両のルートの出発地です。緯度と経度の座標またはプレイス ID で定義されます。このパラメータは、車両がルートを開始する場所をオプティマイザーに伝えます。このウェイポイントを定義しない場合、オプティマイザーは集荷または配達のいずれかを開始地点として選択します。この犬の託児所のシナリオでは、運転手が託児所で 1 日を始めるため、ミッション ドロレス パークの座標を使用します。 |
endWaypoint[] |
object(Waypoint) |
これは、車両のルートの最終目的地です。緯度と経度の座標またはプレイス ID で定義されます。このパラメータは、車両がルートを終了する場所をオプティマイザーに伝えます。この経由地を定義しない場合、オプティマイザーは集荷または配達のいずれかをルートの終点として選択します。この犬の託児所のシナリオでは、ドライバーは託児所で 1 日を終える必要があるため、ミッション ドロレス パークの座標を使用します。 | |
costPerHour |
数値 | これは、車両が走行中か停止中かに関係なく、車両が使用された 1 時間ごとに発生する費用です。この犬の託児所のシナリオでは、これを使用してドライバーの時給をモデル化します。 | |
startTimeWindows[] |
オブジェクトの配列(TimeWindow) |
これは、ドライバーが午前中の犬の送迎のためにバンを運転し始めることができる許容範囲です。 | |
endTimeWindows[] |
オブジェクトの配列(TimeWindow) |
これは、ドライバーがバンでの運転を終えて、犬の保育園に戻って駐車するまでの許容時間です。 |
