توفّر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات "ماسح رموز Google" حلاً كاملاً لمسح الرموز ضوئيًا بدون أن يطلب تطبيقك إذن الوصول إلى الكاميرا، مع الحفاظ على خصوصية المستخدم. ويتم ذلك من خلال تفويض مهمة مسح الرمز إلى "خدمات Google Play" وإرجاع نتائج المسح الضوئي فقط إلى تطبيقك (الفيديو 1).
تتم جميع عمليات معالجة الصور على الجهاز، ولا تخزّن Google النتائج أو بيانات الصور. تتوافق واجهة برمجة التطبيقات مع تنسيقات الرموز نفسها التي تتوافق معها واجهة برمجة التطبيقات ML Kit Barcode Scanning API وتعرض Barcode الكائن نفسه.
تُعدّ واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه مثالية للتطبيقات التي تتطلّب مسحًا ضوئيًا سلسًا للرموز بدون الحاجة إلى واجهة مستخدم أو تجربة كاميرا مخصّصة. يتم تنفيذ هذه العملية بالكامل ضمن "خدمات Google Play"، ما يضمن الحد الأدنى من التأثير في حجم تطبيقك.
بدءًا من الإصدار 16.1.0، يمكنك تفعيل ميزة "التكبير التلقائي" للسماح للماسح الضوئي لرموز Google بمسح الرموز الشريطية تلقائيًا عندما تكون بعيدة عن الكاميرا. عندما يوجّه المستخدمون أجهزتهم إلى رمز شريطي، سيرصد الماسح الضوئي الرمز بشكل ذكي ويقرّب الصورة. يغنيك ذلك عن الحاجة إلى ضبط التكبير/التصغير يدويًا، ما يجعل عملية فحص الرموز الشريطية أسرع وأكثر دقة وأسهل (راجِع الفيديو 2).
 |
 |
| الفيديو 1 دمج الماسح الضوئي للرموز من Google | الفيديو 2 تأثير التكبير أو التصغير التلقائي |
بالنسبة إلى حالات الاستخدام الأكثر تعقيدًا التي تتطلّب واجهة مستخدم مخصّصة، ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات "مسح الرموز الشريطية" في ML Kit مباشرةً.
إذا كانت لديك أسئلة أو أردت إرسال خطأ أو كنت بحاجة إلى المساعدة، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة منتدى ML Kit.
قبل البدء
لإعداد تطبيقك، أكمِل الخطوات الواردة في الأقسام التالية.
إعداد تطبيقك
في ملف
settings.gradleذي المستوى الأعلى، أدرِج مستودع Maven من Google ومستودع Maven المركزي ضمن القسمdependencyResolutionManagement:dependencyResolutionManagement { repositories { google() mavenCentral() } }أضِف اعتمادية "خدمات Google Play" الخاصة
play-services-code-scannerبحزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) إلى ملف Gradle الخاص بالوحدة، والذي يكون عادةًapp/build.gradle:dependencies { implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-code-scanner:16.1.0' }يمكنك ضبط تطبيقك على أن تتيح "خدمات Google Play" تنزيل وحدة الفحص تلقائيًا على الجهاز أثناء تثبيت تطبيقك من "متجر Play".
<application ...> ... <meta-data android:name="com.google.mlkit.vision.DEPENDENCIES" android:value="barcode_ui"/> ... </application>يمكنك أيضًا التحقّق بشكل صريح من توفّر وحدة الفحص وطلب تنزيلها من خلال ModuleInstallClient API في "خدمات Google Play".
إذا لم تفعِّل عمليات تنزيل الوحدات في وقت التثبيت أو لم تطلب عمليات تنزيل صريحة، ولم تكن وحدة المسح الضوئي مثبَّتة من قبل لحالة استخدام أخرى، ستنزّل "خدمات Google Play" وحدة المسح الضوئي في المرة الأولى التي يتم فيها استخدامها.
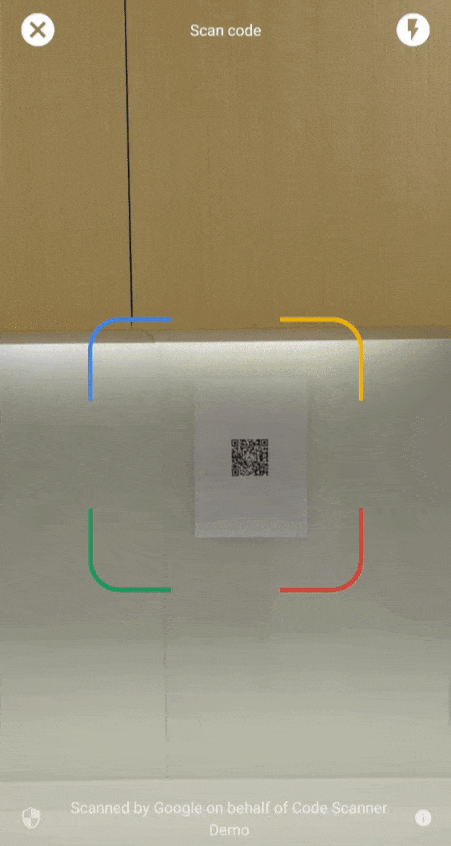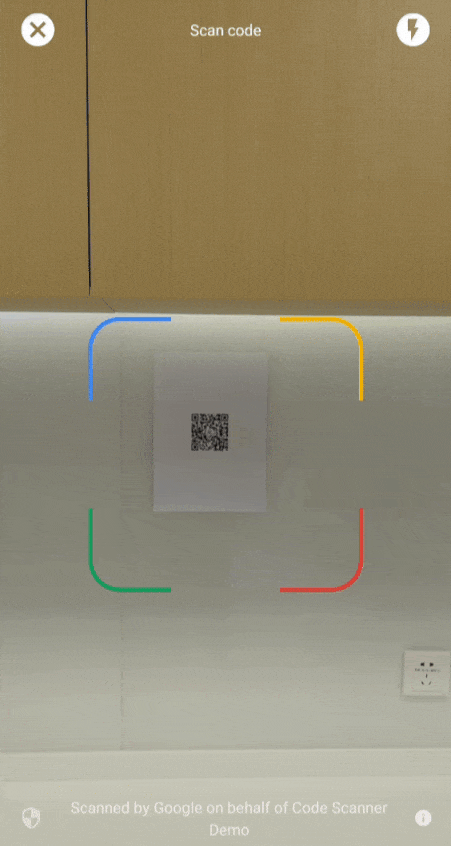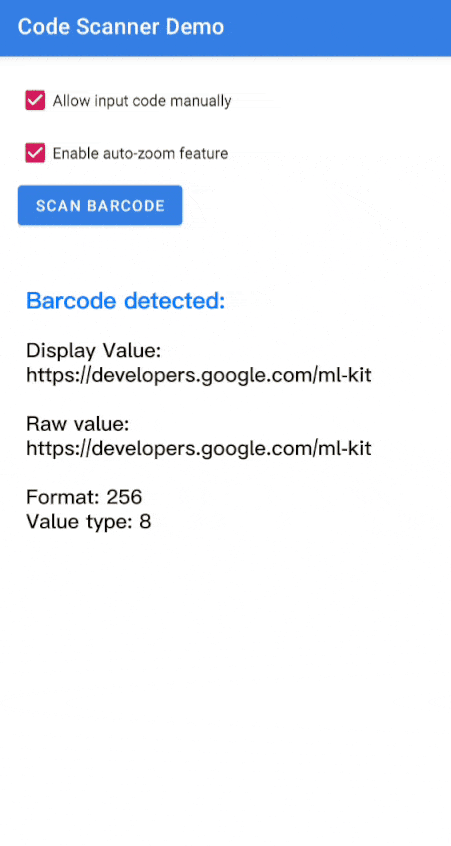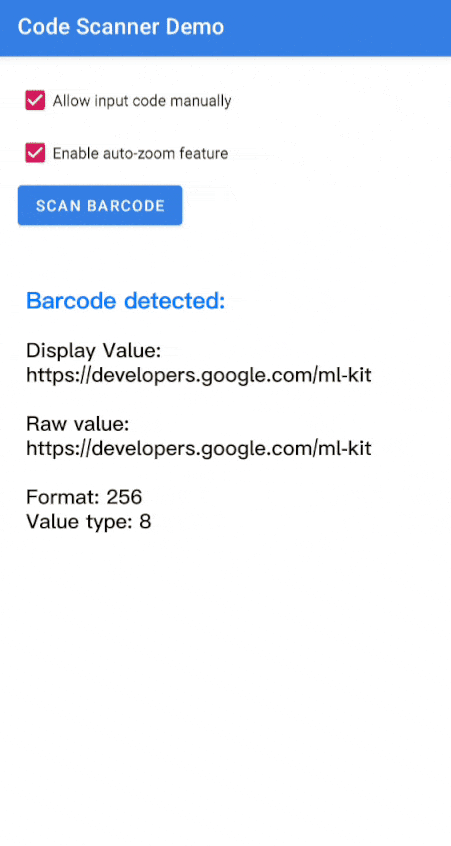
مسح رمز ضوئيًا
اتّبِع الخطوات التالية لمسح رمز شريطي ضوئيًا.
اختياري: اضبط إعدادات الماسح الضوئي للرموز.
إذا كنت تعرف تنسيقات الرموز الشريطية التي تتوقّع قراءتها، يمكنك تحسين سرعة أداة رصد الرموز الشريطية من خلال ضبطها على رصد هذه التنسيقات فقط. على سبيل المثال، للكشف عن رموز Aztec ورموز الاستجابة السريعة فقط، أنشئ عنصر
GmsBarcodeScannerOptionsكما في المثال التالي:Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build()
جافا
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build();
يتم إيقاف ميزة "التكبير التلقائي" تلقائيًا. لتفعيل وظيفة "التكبير التلقائي" بدءًا من الإصدار 16.1.0، استدعِ الدالة
enableAutoZoom()كما هو موضّح في مثال الرمز البرمجي التالي.Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build()
جافا
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build();
احصل على مثيل من
GmsBarcodeScanner، كما هو موضّح في مثال الرمز البرمجي:Kotlin
val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this) // Or with a configured options // val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this, options)
جافا
GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this); // Or with a configured options // GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(context, options);
اطلب مسح رمز ضوئيًا من خلال الاتصال بالرقم
startScan().Kotlin
scanner.startScan() .addOnSuccessListener { barcode -> // Task completed successfully } .addOnCanceledListener { // Task canceled } .addOnFailureListener { e -> // Task failed with an exception }
جافا
scanner .startScan() .addOnSuccessListener( barcode -> { // Task completed successfully }) .addOnCanceledListener( () -> { // Task canceled }) .addOnFailureListener( e -> { // Task failed with an exception });
تعامَل مع
Barcodeالناتج.Kotlin
val rawValue: String? = barcode.rawValue
جافا
String rawValue = barcode.getRawValue();
