Die Google Code Scanner API bietet eine Komplettlösung zum Scannen von Code, ohne dass Ihre App eine Kameraberechtigung anfordern muss. Dabei wird die Privatsphäre der Nutzer geschützt. Dazu wird die Aufgabe des Scannens des Codes an die Google Play-Dienste delegiert und nur die Scanergebnisse werden an Ihre App zurückgegeben (Video 1).
Die gesamte Bildverarbeitung erfolgt auf dem Gerät. Google speichert weder die Ergebnisse noch die Bilddaten. Die API unterstützt dieselben Codeformate wie die ML Kit Barcode Scanning API und gibt dasselbe Barcode-Objekt zurück.
Diese API ist ideal für Apps, die ein nahtloses Scannen von Codes ohne benutzerdefinierte Benutzeroberfläche oder Kamerafunktionen erfordern. Die Implementierung erfolgt vollständig in den Google Play-Diensten, sodass die Größe Ihrer App nur minimal beeinflusst wird.
Ab Version 16.1.0 können Sie den automatischen Zoom aktivieren, damit der Google-Code-Scanner Barcodes, die weit von der Kamera entfernt sind, automatisch scannen kann. Wenn Nutzer ihre Geräte auf einen Barcode richten, erkennt der Scanner den Barcode automatisch und zoomt ihn heran. Dadurch entfällt die Notwendigkeit, den Zoom manuell anzupassen. Das Scannen von Barcodes wird so schneller, genauer und zugänglicher (siehe Video 2).
 |
 |
| Video 1. Integration des Google Code-Scanners | Video 2 Automatischer Zoom |
Für komplexere Anwendungsfälle, die eine benutzerdefinierte Benutzeroberfläche erfordern, empfehlen wir, die ML Kit Barcode Scanning API direkt zu verwenden.
Wenn Sie Fragen haben, einen Fehler melden möchten oder Unterstützung benötigen, sehen Sie sich die ML Kit-Community-Seite an.
Hinweis
Führen Sie die Schritte in den folgenden Abschnitten aus, um Ihre App vorzubereiten.
Eigene App konfigurieren
Fügen Sie in der Datei
settings.gradleauf oberster Ebene das Maven-Repository von Google und das Maven Central Repository unter demdependencyResolutionManagement-Block ein:dependencyResolutionManagement { repositories { google() mavenCentral() } }Fügen Sie die Google Play-Dienste-Abhängigkeit für das
play-services-code-scannerSDK der Gradle-Build-Datei Ihres Moduls hinzu, die in der Regelapp/build.gradleist:dependencies { implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-code-scanner:16.1.0' }Sie können Ihre App so konfigurieren, dass Google Play-Dienste das Scannermodul automatisch auf das Gerät herunterladen, während Ihre App aus dem Play Store installiert wird.
<application ...> ... <meta-data android:name="com.google.mlkit.vision.DEPENDENCIES" android:value="barcode_ui"/> ... </application>Sie können die Verfügbarkeit des Scanner-Moduls auch explizit prüfen und den Download über die ModuleInstallClient API der Google Play-Dienste anfordern.
Wenn Sie keine Modul-Downloads bei der Installation aktivieren oder explizite Downloads anfordern und das Scanner-Modul nicht bereits für einen anderen Anwendungsfall installiert ist, lädt Google Play-Dienste das Scanner-Modul beim ersten Mal herunter, wenn es verwendet wird.
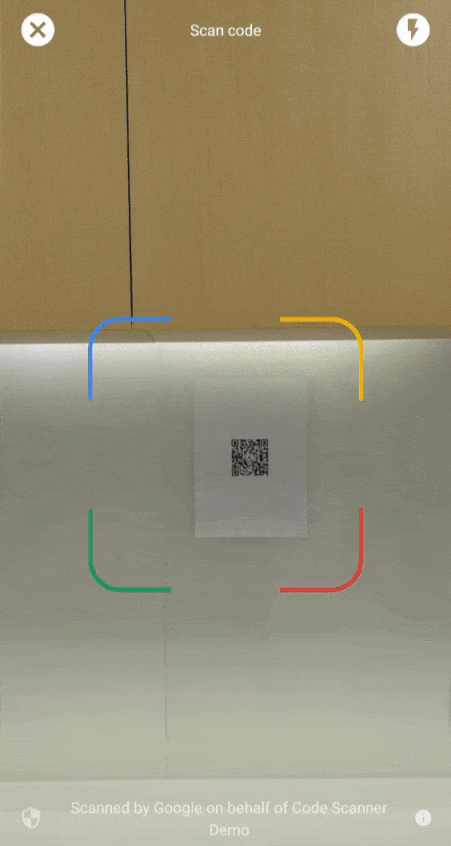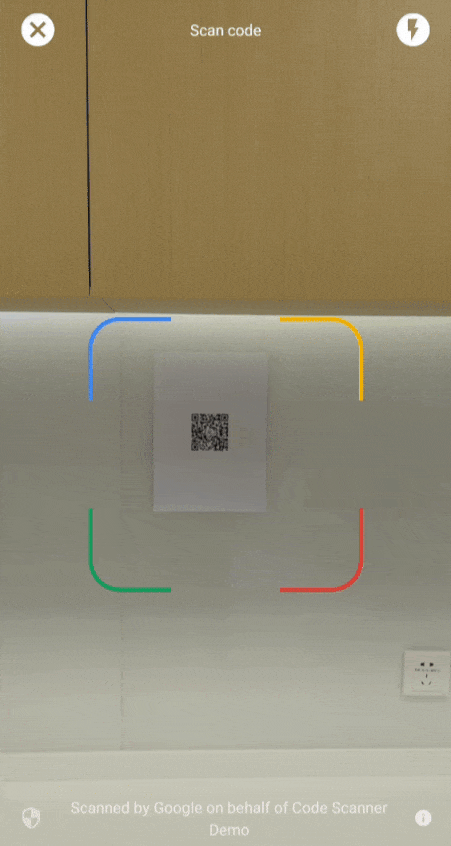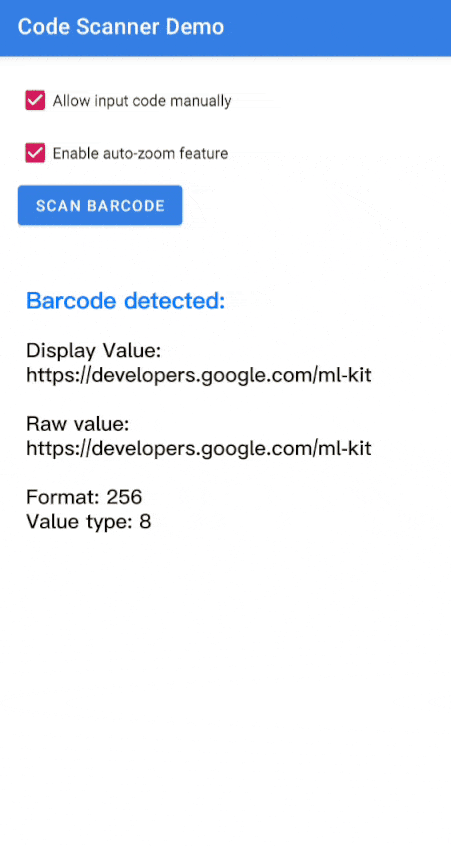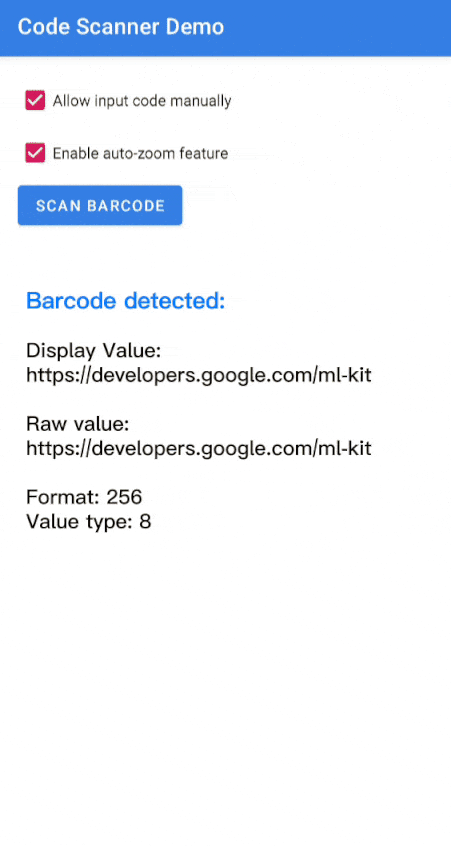
Code scannen
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, um einen Barcode zu scannen.
Optional: Code-Scanner konfigurieren
Wenn Sie wissen, welche Barcodeformate Sie lesen möchten, können Sie die Geschwindigkeit des Barcode-Scanners verbessern, indem Sie ihn so konfigurieren, dass er nur diese Formate erkennt. Wenn Sie beispielsweise nur Aztec- und QR-Codes erkennen möchten, erstellen Sie ein
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions-Objekt wie im folgenden Beispiel:Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build()
Java
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build();
Der automatische Zoom ist standardmäßig deaktiviert. Wenn Sie den automatischen Zoom ab Version 16.1.0 aktivieren möchten, rufen Sie
enableAutoZoom()auf, wie im folgenden Codebeispiel gezeigt.Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build()
Java
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build();
Rufen Sie eine Instanz von
GmsBarcodeScannerab, wie im Codebeispiel gezeigt:Kotlin
val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this) // Or with a configured options // val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this, options)
Java
GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this); // Or with a configured options // GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(context, options);
Wenn Sie einen Code scannen möchten, rufen Sie
startScan()auf.Kotlin
scanner.startScan() .addOnSuccessListener { barcode -> // Task completed successfully } .addOnCanceledListener { // Task canceled } .addOnFailureListener { e -> // Task failed with an exception }
Java
scanner .startScan() .addOnSuccessListener( barcode -> { // Task completed successfully }) .addOnCanceledListener( () -> { // Task canceled }) .addOnFailureListener( e -> { // Task failed with an exception });
Verarbeiten Sie das resultierende
Barcode.Kotlin
val rawValue: String? = barcode.rawValue
Java
String rawValue = barcode.getRawValue();

