Interfejs Google Code Scanner API to kompletne rozwiązanie do skanowania kodów, które nie wymaga od aplikacji proszenia o uprawnienia do korzystania z aparatu, a jednocześnie chroni prywatność użytkowników. Osiąga się to przez przekazanie zadania skanowania kodu do usług Google Play i zwrócenie do aplikacji tylko wyników skanowania (film 1).
Przetwarzanie obrazu odbywa się na urządzeniu, a Google nie przechowuje wyników ani danych obrazu. Interfejs API obsługuje te same formaty kodu co interfejs ML Kit Barcode Scanning API i zwraca ten sam obiekt Barcode.
Ten interfejs API jest idealny w przypadku aplikacji, które wymagają płynnego skanowania kodów bez konieczności korzystania z niestandardowego interfejsu lub aparatu. Implementacja znajduje się w całości w Usługach Google Play, co zapewnia minimalny wpływ na rozmiar aplikacji.
Od wersji 16.1.0 możesz włączyć automatyczne powiększanie, aby skaner kodu Google automatycznie skanował kody kreskowe znajdujące się daleko od aparatu. Gdy użytkownicy skierują urządzenia na kod kreskowy, skaner inteligentnie go wykryje i powiększy. Eliminuje to konieczność ręcznego dostosowywania powiększenia, dzięki czemu skanowanie kodów kreskowych jest szybsze, dokładniejsze i łatwiejsze (patrz film 2).
 |
 |
| Film 1. Integracja ze skanerem kodów Google | Film 2. Efekt automatycznego powiększenia |
W przypadku bardziej złożonych zastosowań, które wymagają niestandardowego interfejsu, zalecamy bezpośrednie używanie interfejsu ML Kit Barcode Scanning API.
Jeśli masz pytania, chcesz zgłosić błąd lub potrzebujesz pomocy, odwiedź stronę społeczności ML Kit.
Zanim zaczniesz
Aby przygotować aplikację, wykonaj czynności opisane w poniższych sekcjach.
Konfiguracja aplikacji
W pliku
settings.gradlenajwyższego poziomu dodaj repozytorium Maven firmy Google i centralne repozytorium Maven w blokudependencyResolutionManagement:dependencyResolutionManagement { repositories { google() mavenCentral() } }Dodaj zależność Usług Google Play dla
play-services-code-scannerpakietu SDKapp/build.gradledo pliku build.gradle modułu. Jest to zwykleapp/build.gradle:dependencies { implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-code-scanner:16.1.0' }Możesz skonfigurować aplikację tak, aby Usługi Google Play automatycznie pobierały moduł skanera na urządzenie podczas instalowania aplikacji ze Sklepu Play.
<application ...> ... <meta-data android:name="com.google.mlkit.vision.DEPENDENCIES" android:value="barcode_ui"/> ... </application>Możesz też wyraźnie sprawdzić dostępność modułu skanera i poprosić o pobranie go za pomocą interfejsu ModuleInstallClient API w Usługach Google Play.
Jeśli nie włączysz pobierania modułów w momencie instalacji ani nie poprosisz o wyraźne pobieranie, a moduł skanera nie jest jeszcze zainstalowany w innym przypadku użycia, Usługi Google Play pobiorą go przy pierwszym użyciu.
Zeskanuj kod
Aby zeskanować kod kreskowy, wykonaj te czynności.
Opcjonalnie: skonfiguruj skaner kodów.
Jeśli wiesz, jakie formaty kodów kreskowych chcesz odczytywać, możesz zwiększyć szybkość działania detektora kodów kreskowych, konfigurując go tak, aby wykrywał tylko te formaty. Aby na przykład wykrywać tylko kody Aztec i QR, utwórz obiekt
GmsBarcodeScannerOptionsjak w tym przykładzie:Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build()
Java
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats( Barcode.FORMAT_QR_CODE, Barcode.FORMAT_AZTEC) .build();
Domyślnie automatyczne powiększanie jest wyłączone. Aby włączyć tę funkcję od wersji 16.1.0, wywołaj
enableAutoZoom(), jak pokazano w przykładzie kodu poniżej.Kotlin
val options = GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build()
Java
GmsBarcodeScannerOptions options = new GmsBarcodeScannerOptions.Builder() .setBarcodeFormats(...) .enableAutoZoom() // available on 16.1.0 and higher .build();
Uzyskaj instancję
GmsBarcodeScanner, jak pokazano w przykładowym kodzie:Kotlin
val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this) // Or with a configured options // val scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this, options)
Java
GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(this); // Or with a configured options // GmsBarcodeScanner scanner = GmsBarcodeScanning.getClient(context, options);
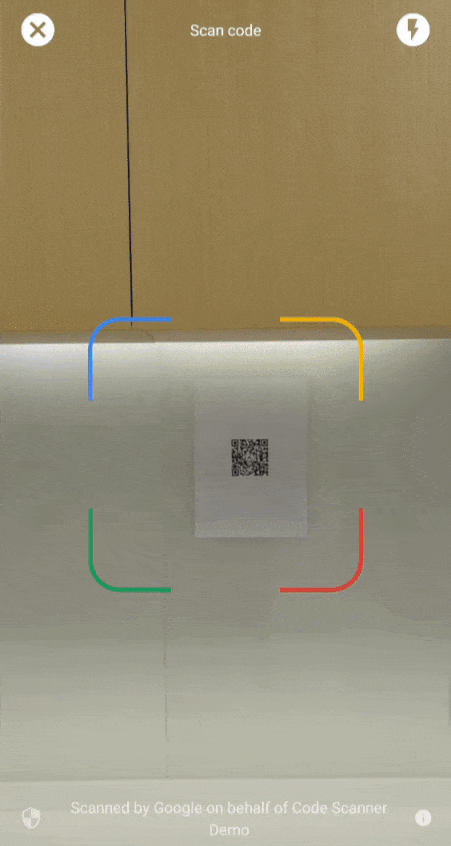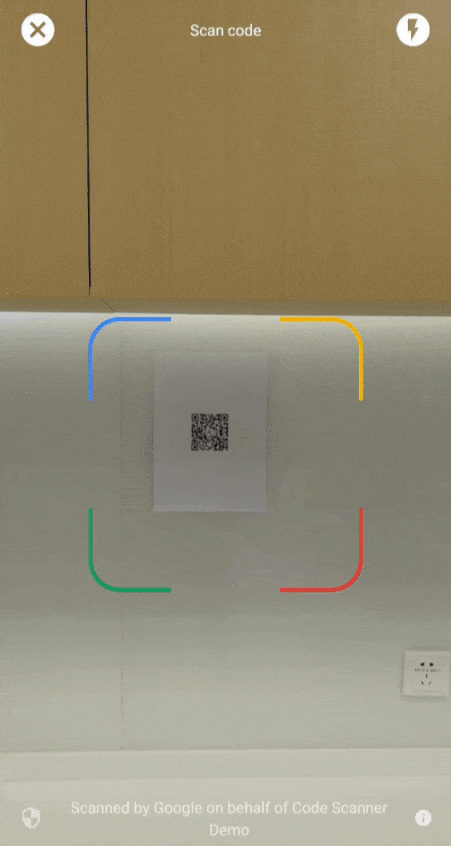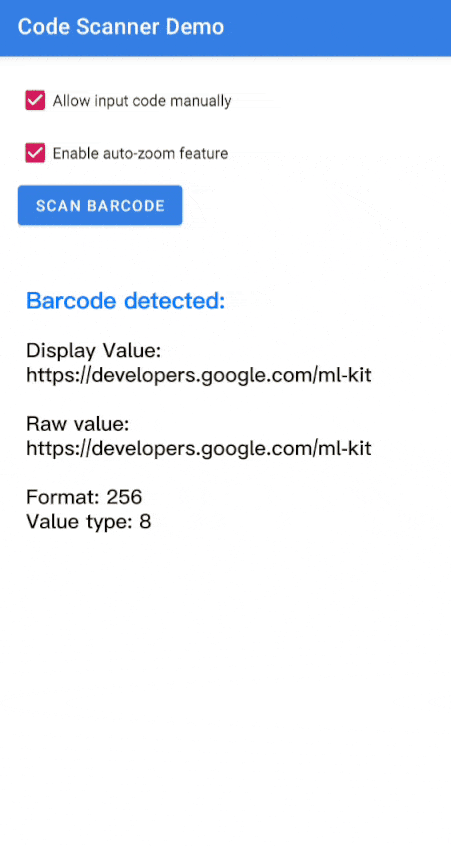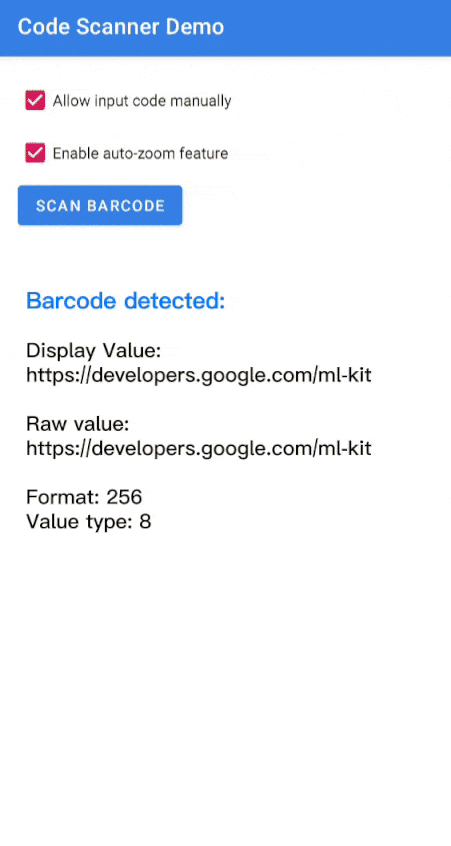
Poproś o zeskanowanie kodu, dzwoniąc pod numer
startScan().Kotlin
scanner.startScan() .addOnSuccessListener { barcode -> // Task completed successfully } .addOnCanceledListener { // Task canceled } .addOnFailureListener { e -> // Task failed with an exception }
Java
scanner .startScan() .addOnSuccessListener( barcode -> { // Task completed successfully }) .addOnCanceledListener( () -> { // Task canceled }) .addOnFailureListener( e -> { // Task failed with an exception });
Obsłuż wynikowy
Barcode.Kotlin
val rawValue: String? = barcode.rawValue
Java
String rawValue = barcode.getRawValue();
