Com a API de reconhecimento de tinta digital do Kit de ML, é possível reconhecer texto escrito à mão e classificar gestos em uma superfície digital em centenas de idiomas, além de classificar esboços. A API de reconhecimento de tinta digital usa a mesma tecnologia que impulsiona o reconhecimento de escrita manual no Gboard, Google Tradutor e no jogo Quick, Draw!.
O reconhecimento de tinta digital permite que você:
- Escreva na tela em vez de digitar em um teclado virtual. Isso permite que os usuários desenhem caracteres que não estão disponíveis no teclado, como ệ, अ ou 森 para teclados com alfabeto latino.
- Realizar operações de texto básicas (navegação, edição, seleção e assim por diante) usando gestos.
- Reconhecer formas e emojis desenhados à mão.
O reconhecimento de tinta digital funciona com os traços que o usuário desenha na tela. Se você precisar ler texto de imagens tiradas com a câmera, use a API Text Recognition.
O reconhecimento de tinta digital funciona totalmente off-line e compatível com Android e iOS.
Principais recursos
- Converte texto escrito à mão em sequências de caracteres Unicode
- Executado no dispositivo quase em tempo real
- A escrita à mão do usuário permanece no dispositivo, e o reconhecimento é realizado sem nenhuma conexão de rede.
- Oferece suporte para mais de 300 idiomas e mais de 25 sistemas de escrita. Consulte a
lista completa de idiomas com suporte
- Oferece suporte à classificação de gestos para esses idiomas usando
extensões
-x-gesture.
- Oferece suporte à classificação de gestos para esses idiomas usando
extensões
- Reconhece emojis e formas básicas
- Mantém baixo o armazenamento no dispositivo ao fazer o download dinâmico de pacotes de idiomas conforme necessário
O reconhecedor usa um objeto Ink como entrada. Ink é uma representação vetorial
do que o usuário escreveu na tela: uma sequência de traços, cada um sendo
uma lista de coordenadas com informações de tempo chamadas de pontos de contato. Um traço
começa quando o usuário coloca a stylus ou o dedo na tela e termina quando ele o levanta. O Ink é transmitido para um reconhecedor, que retorna um ou mais resultados de reconhecimento possíveis, com níveis de confiança.
Exemplos
Escrita à mão em inglês
A imagem à esquerda abaixo mostra o que o usuário desenhou na tela. A imagem à
direita é o objeto Ink correspondente. Ele contém os traços com pontos vermelhos
que representam os pontos de contato em cada traço.


Há quatro traços. Os dois primeiros traços no objeto Ink têm esta aparência:
| Tinta | ||
|---|---|---|
| Traço 1 | x
|
392, 391, 389, 287... |
y
|
52, 60, 76, 97... | |
t
|
0, 37, 56, 75... | |
| Traço 2 | x
|
497, 494, 493, 490... |
y
|
167, 165, 165, 165... | |
t
|
694, 742, 751, 770... | |
| ... | ||
Quando você envia esse Ink para um reconhecedor do idioma inglês, ele retorna
várias transcrições possíveis, contendo cinco ou seis caracteres. Elas são
ordenadas em ordem decrescente de confiança:
| RecognitionResult | |
|---|---|
| Candidato de reconhecimento 1 | Handw |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 2 | Handrw |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 3 | Harw |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 4 | Handu |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 5 | Handwe |
Gestos
Os classificadores de gestos classificam um traço de tinta em uma das nove classes de gestos listadas abaixo.
arch:abovearch:below |
 |
caret:abovecaret:below |
 |
circle |
 |
 |
|
scribble |
 |
strike |
 |
verticalbar |
 |
writing |
 |
Desenhos de emojis
A imagem à esquerda abaixo mostra o que o usuário desenhou na tela. A imagem à
direita é o objeto Ink correspondente. Ele contém os traços com pontos vermelhos
que representam os pontos de contato em cada traço.


O objeto Ink contém seis traços.
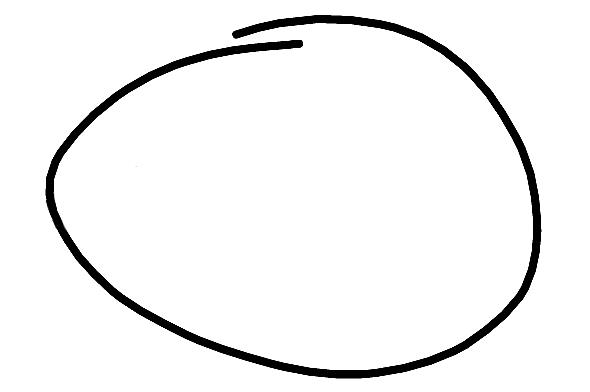





| Tinta | ||
|---|---|---|
| Traço 1 | x
|
269, 266, 262, 255... |
y
|
40, 40, 40, 41... | |
t
|
0, 36, 56, 75... | |
| Traço 2 | x
|
179, 182, 183, 185... |
y
|
157, 158, 159, 160... | |
t
|
2475, 2522, 2531, 2541... | |
| ... | ||
Ao enviar esse Ink ao reconhecedor de emojis, você recebe várias transcrições possíveis, ordenadas em ordem decrescente de confiança:
| RecognitionResult | |
|---|---|
| Candidato de reconhecimento 1 | 😂 (U+1f62d) |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 2 | 😅 (U+1f605) |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 3 | 😹 (U+1f639) |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 4 | CTRL (U+1f604) |
| Candidato de reconhecimento 5 | GPC (U+1f606) |
