Page Summary
-
App-to-app verification allows users to verify their identity within your app during Google Pay token provisioning, simplifying the process.
-
Issuers must configure settings with their TSP (Token Service Provider) and update their app to support app-to-app verification.
-
The Google Wallet app invokes the issuer's app during provisioning to facilitate user verification, requiring specific configurations in the issuer's app manifest.
-
Issuer apps must handle receiving the intent from Google Wallet, authenticating the user, activating the token, and securely returning the user to Google Wallet.
-
Security considerations include validating the calling activity, adhering to the Android security model, and ensuring proper user authentication and consent.
Issuers can offer app-to-app verification as an option for completing a yellow path ID&V challenge when provisioning a token. App-to-app verification is configured through your TSP and does not require any configuration by the Google Pay team. This page explains how your app interacts with the Google Wallet app based on the provisioning instructions we receive from your TSP.
When users choose to activate app-to-app verification, Google Wallet will invoke the issuer app by calling the Android Activity specified by the issuer through their TSP configuration. Once the user has verified their identity, the issuer app passes control back to Google Wallet to finish the provisioning flow.
If the app is not installed on the user's device, Google Wallet will open the Play Store page for your app. After installing the issuer app, the user needs to restart the flow.
To support app-to-app verification, you will need to:
- Configure TSP settings to enable the app-to-app flow.
- Update your app to support the app-to-app flow.
The flow shows an abstract user experience for the app-to-app verification process:
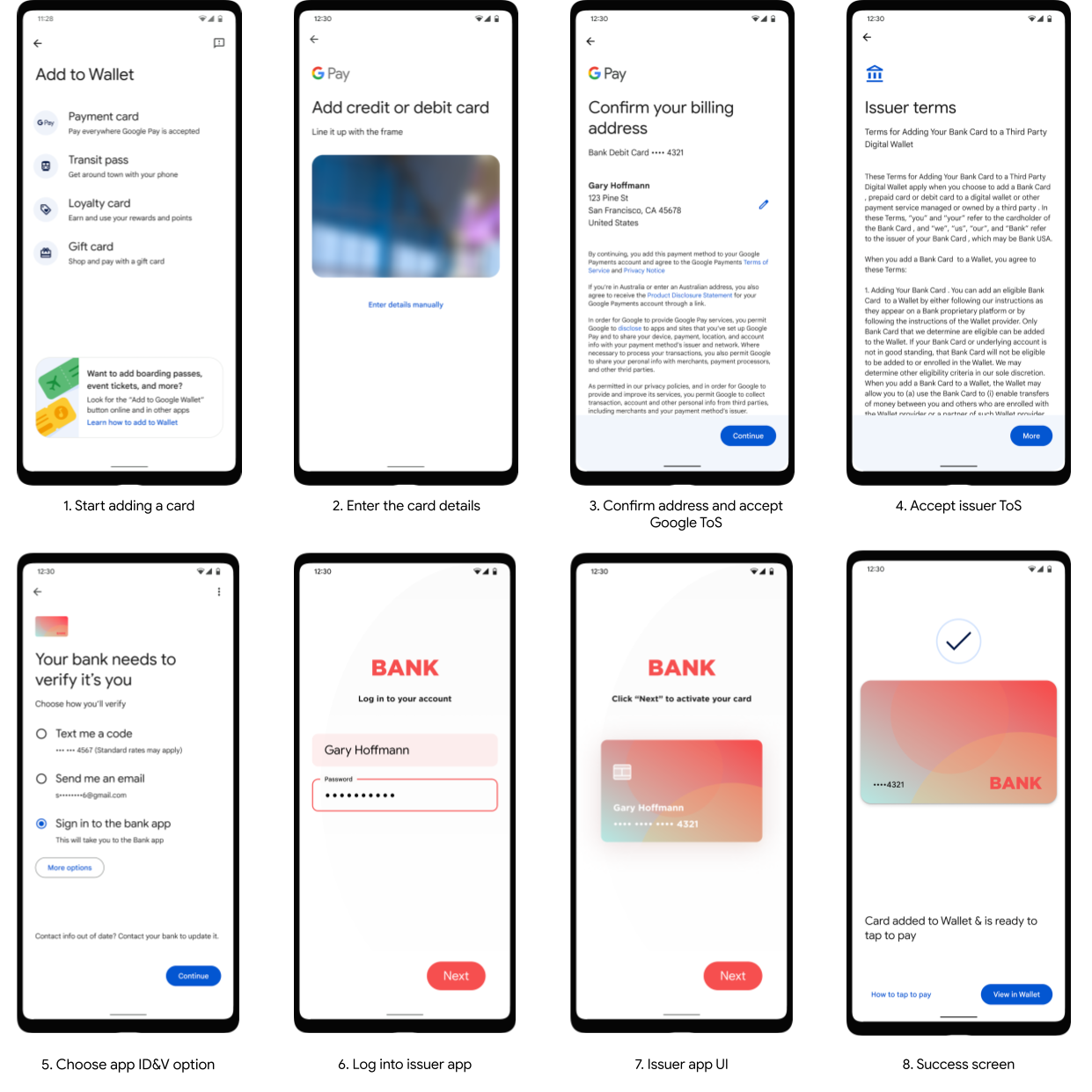
TSP settings
Issuers must provide the parameters below to their TSP. Google Pay receives these parameters from the TSP during the tokenization process and uses them to call your app.
| Parameter | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Package Name | com.example.myapp | The package name (applicationId) identifies the issuer mobile app that Google Pay should call during when invoking the Intent to start the app to app flow. If the app is not installed on the cardholder’s mobile device, the user will be prompted to install it from the Google Play Store. |
| Action | com.example.bank.action.ACTIVATE_TOKEN | When calling your app, we create an explicit Intent. The action must be provided in it's fully qualified form, including the package name. Also, the action must be specific for use in token activation. |
| Extra text | This parameter is used to pass extra data that will be included in the Intent. It is typically a JSON structure, Base64-encoded. The value of this string is opaque to Google and will be provided as-is in the standard field EXTRA_TEXT. |
Learn more about sending intents in Android and allowing intents in Android.
App development
When a user selects the app-to-app method to verify their identity, the issuer app must:
- Receive the Intent from Google Wallet.
- Authenticate the cardholder.
- Activate the token.
- Return the user to Google Wallet by calling
activity.setResult(RESULT_OK, ...)
Receive the intent
When a user chooses to verify their identity using the issuer's app,
Google Wallet calls your app using the package name, action, and EXTRA_TEXT
provided to Google Wallet by the TSP. To receive the Intent
from Google Wallet, you need to update your app manifest and
create an activity to activate the token.
App manifest
Issuers must update the Android manifest of their mobile app to handle the
Action
so Google Wallet can call it during the app-to-app flow.
Once your app's manifest has been updated, Google Wallet will be able to call your app to start the token activation activity in your app.
<activity android:name="AppToAppActivity">
<!-- This activity handles App To App ACTIVATE_TOKEN action -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.bank.action.ACTIVATE_TOKEN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Learn more about Android intents in the Android developer documentation and Android developer reference.
Token activation activity
To complete activation, your app must start an activity to complete token
activation using the activation parameters passed in the Intent. The
following code sample demonstrates how you can access the data from the
EXTRA_TEXT in the Intent.
/*
* Within issuer's mobile app AppToAppActivity
*/
// Validate caller is Google Wallet
// see Security Considerations section below
String data = getIntent().getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT);
// Parse base64 to retrieve the activation parameters as a JSON object in a String
String decodedData = new String(base64.decodeBase64(data));
// Read the JSON string
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JsonNode node = mapper.readTree(decodedData);
// Extract the activation parameters
String tokenRef = node.get("param0").asText());
String tokenParam = node.get("param1").asText());
// etc.
// Authenticate the user
...
Testing with Android Debug Bridge (adb)
You can simulate the intent that Google Wallet sends by using the
Android Debug Bridge (adb)
tool from the command line. This tests your app's intent handling in isolation.
Use the following command, replacing the placeholder values with your specific
configuration:
adb shell am start \
-a com.your.app.package.a2a \
-p com.your.app.package \
--es android.intent.extra.TEXT 'yourBase64EncodedExtraTextFromTSP'
In this command:
- -a: Corresponds to the Action configured with your TSP.
- -p: Is the Package Name of your application.
- --es: Specifies an extra string value. Use android.intent.extra.TEXT as the key and provide the Base64-encoded JSON payload as the value.
The values for Action and Package depend on your configuration with your TSP, as noted in the TSP Configuration bullet.
If the command is successful, your app's designated activity should launch. If it fails, the error message often indicates that the activity was not found, pointing to a mismatch in the package name or action. This helps confirm if your app is correctly set up to receive the app-to-app intent before you test the full end-to-end flow.
Troubleshooting: Intent opens the Play Store
When a user selects app-to-app verification, if Google Wallet opens the Play Store instead of your app, it indicates that Google Wallet was unable to resolve the Android Intent required to launch your app.
To successfully open your app, check the following:
- Package Name Mismatch: The package name of the app installed on the
device must exactly match the package name configured with your TSP.
A common error is testing with a debug build which may have a different
package name (e.g.,
com.example.app.debug) than the production package name (com.example.app) configured with the TSP. The package name is case sensitive. - Manifest Configuration: Verify that your app's
AndroidManifest.xmlis correctly configured to handle the intent action. The<action>tag in your manifest's<intent-filter>must be an exact, character-for-character match with the action string configured with your TSP. - TSP Configuration: The package name and action are sent to Google Pay from your TSP. Any corrections to these values must be made in the data you send to your TSP or in your TSP's configuration portal. Google Wallet doesn't adjust these values, they are passed through. For further information, see your TSP's documentation.
Activate the token
There are two ways to activate tokens:
- By calling TSP server APIs to activate the token directly.
- By obtaining an activation code from the TSP and passing
the activation code in the
Activityresult.
Activate using TSP server APIs
When the card issuing bank mobile app uses the TSP API to activate the token,
the card issuing bank app receives the Intent, authenticates the cardholder,
and activates the token by calling the TSP's API. At the end of this flow, you
indicate to Google Wallet whether or not the activation was successful
when returning the user to Google Wallet. Review your TSP technical documentation
for details on how you can activate tokens using their server APIs.
When activating through the TSP API, your app does not return a code to Google Wallet and the token activation happens "out of band" from the Google Pay perspective.
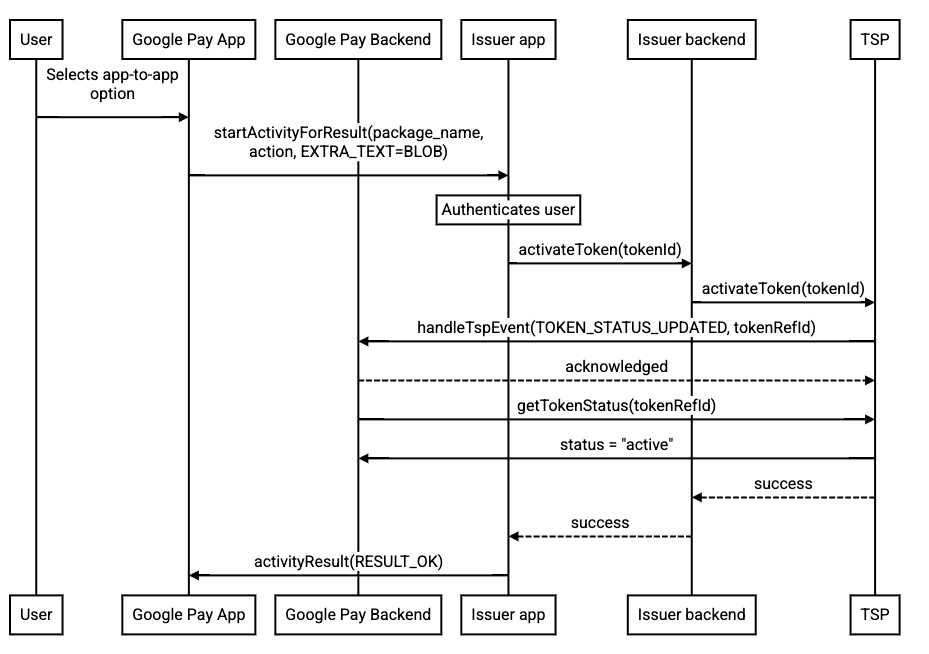
Code sample for how to return the user to Google Wallet after the activation process is complete using the TSP API technique.
Intent resultIntent = new Intent();
resultIntent.putExtra("BANKING_APP_ACTIVATION_RESPONSE", "approved");
// or "declined", or "failure"
activity.setResult(RESULT_OK, resultIntent);
Activate using Android Intent result and TSP activation code
When the card issuing bank mobile app obtains an activation code from the TSP and returns it to Google Wallet, the issuer app returns an activation code to Google Wallet using an intent result.
This method requires an activation code generated by your TSP. Consult with your TSP on whether this method is supported and how to generate an activation code, sometimes called an authentication code or Tokenization Authentication Value (TAV).
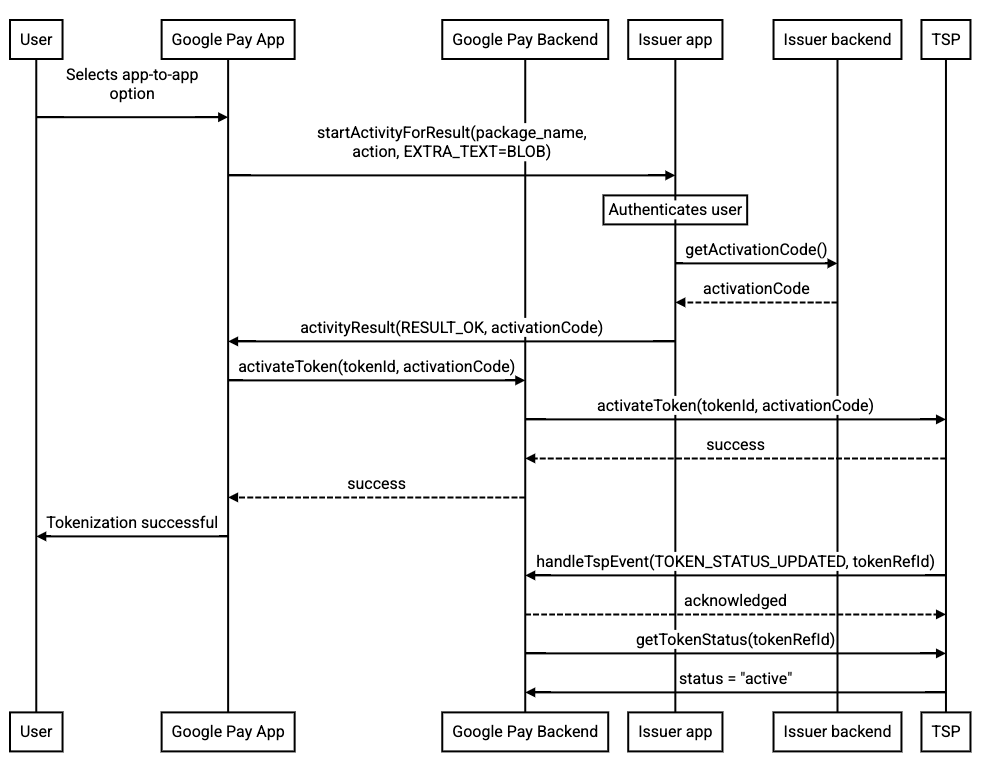
The following is sample code for how to return the user to Google Wallet with an activation code.
Intent resultIntent = new Intent();
resultIntent.putExtra("BANKING_APP_ACTIVATION_RESPONSE", "approved");
// or "declined", or "failure"
// if "approved", also pass the code
resultIntent.putExtra("BANKING_APP_ACTIVATION_CODE", activationCode);
activity.setResult(RESULT_OK, resultIntent);
Mobile app security
The card issuing bank mobile app must have the ability to adhere to the Android
security model, especially concerning the use of intents. Upon receiving the
intent, use Activity.getCallingPackage to validate that the calling activity
is actually Google Wallet as indicated below.
// Validate caller is Google Wallet (Google Play Services)
if ("com.google.android.gms".equals(getCallingPackage())) {
// Proceed with token activation
...
} else {
// Abort token activation: handle error
...
}
Make sure that your mobile app does the following:
- Authenticates the cardholder's identity.
- Obtains cardholder consent to every digitization request.
- Verifies that the digitization relates to the correct cardholder account.
Review your TSP’s technical documentation on token activation and the Android
developer site for sending, allowing,
and receiving
Intents.