From Chrome 125, the Button Mode API is starting an origin trial on desktop. With the Button Mode API, identity providers can use FedCM API even if their users don't have active IdP sessions upon the API call. Users can then sign in to a website with their federated account without being navigated to the IdP site. The FedCM UI in the button mode is more prominent compared to the one from the existing widget flow because it's gated by a user gesture and better reflects the user's intention for signing in.
Button Mode API
FedCM user interface has been available as a widget displayed at the top-right corner on desktop, or as a bottom sheet on mobile, as soon as the API is invoked which could be when the user lands on the relying party (RP). This is called widget mode. To display the widget, the user must be signed in to the IdP before they land on the RP. FedCM by itself didn't have a reliable way to let the user sign in to the IdP before they could let the user sign in to the RP using the account available on the IdP. FedCM is about to add a way to do this.
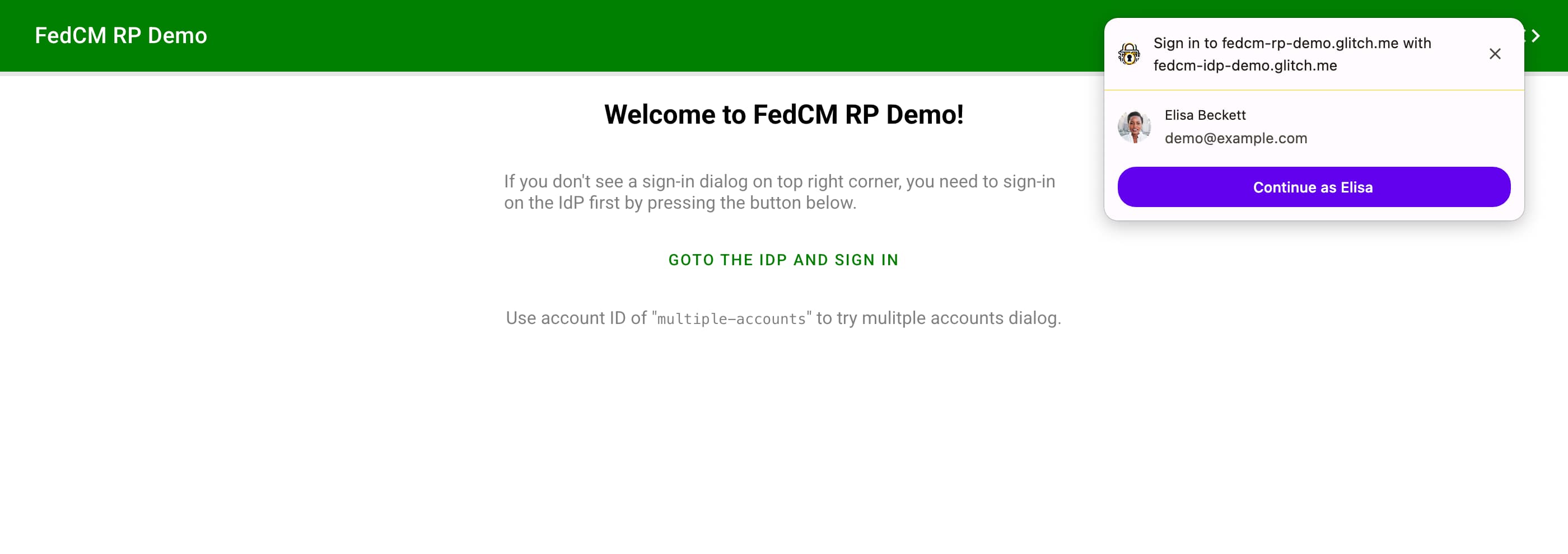
The new Button Mode API adds a new UI mode called button mode. Unlike the widget mode, button mode isn't meant to be invoked as soon as the user lands the RP. It instead is meant to be invoked when the user initiates a sign-in flow such as pressing a "Sign-in with IdP" button.
As soon as the button is pressed, FedCM checks if the user is signed in to the
IdP through a fetch to the accounts
endpoint or
a login status stored to the
browser. If the
user is not signed in yet, FedCM asks the user to sign in to the IdP using the
login_url
provided by the IdP through a popup window. If the browser knows that the user
is already signed in to the IdP or as soon as the user signs in to the IdP with
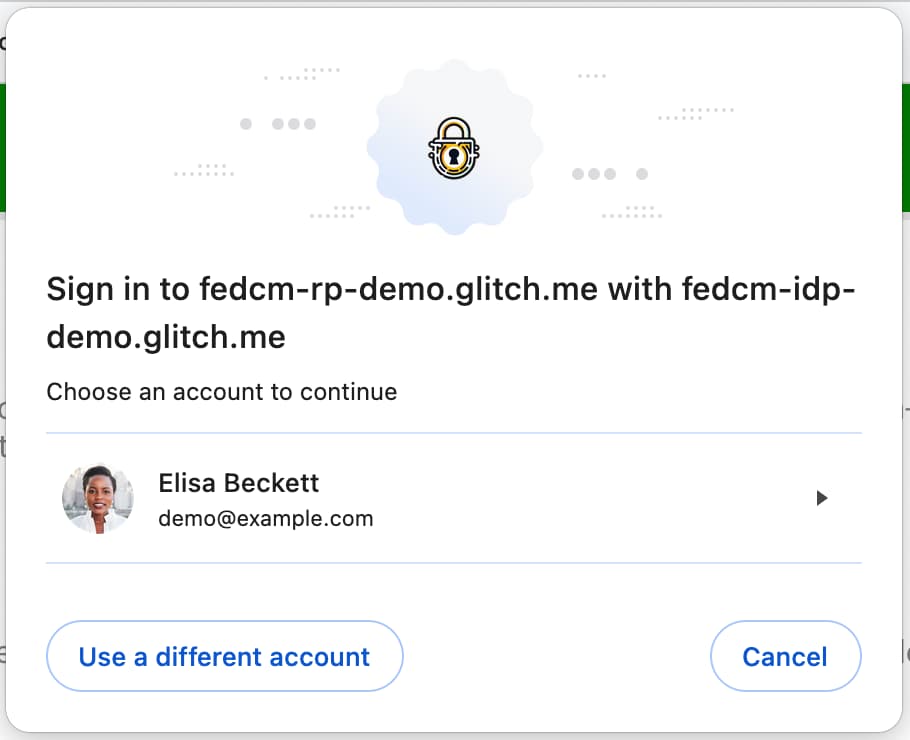
the popup window, FedCM opens a modal dialog for the user to choose an IdP
account to sign in with. By selecting an account, the user can proceed to sign
in to the RP using the IdP account.
In the button mode UI, the displayed sign-in dialog is larger compared to the widget mode, and so should be the branding icon to maintain visual consistency. While the minimum icon size for the widget mode is 25x25px, the minimum size for the icon in button mode is 40x40px. The IdP's well-known file allows for specifying multiple icon URLs as follows:
{
// ... Other settings (like endpoints) here
"branding": {
"icons": [
{
"url": "https://size-25px-image",
"size": 25,
},
{
"url": "https://size-40px-image",
"size": 40
}
]
}
}
Try it out yourself using Chrome 125 at https://fedcm-rp-demo.glitch.me/button_flow.
To use the Button Mode API:
- Enable the experimental feature
FedCmButtonModeinchrome://flags. - Make sure to invoke the API behind transient user activation such as a button click.
- Invoke the API with the
modeparameter like so:
return await navigator.credentials.get({
identity: {
providers: [{
configURL: "https://idp.example/config.json",
clientId: "123",
nonce:"456",
}],
mode: "button"
}
});
The browser will send a new parameter to the ID assertion
endpoint
representing the request type by including mode=button:
POST /fedcm_assertion_endpoint HTTP/1.1
Host: idp.example
Origin: https://rp.example/
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Cookie: 0x23223
Sec-Fetch-Dest: webidentity
account_id=123&client_id=client1234&nonce=Ct60bD&disclosure_text_shown=true&is_auto_selected=false&mode=button
Feature detection
To determine whether the browser is eligible to use the button mode, you can examine with the following code:
let supportsFedCmMode = false;
try {
navigator.credentials.get({
identity: Object.defineProperty(
{}, 'mode', {
get: function () { supportsFedCmMode = true; }
}
)
});
} catch(e) {}
if (supportsFedCmMode) {
// The button mode is supported.
}
Use other account option
The RP can allow users to "use other accounts" in the account chooser, for example, when IdPs support multiple accounts or replacing the existing account.
To enable the option to use other account:
- Enable the experimental feature
FedCmUseOtherAccountinchrome://flagsor enroll the Button Mode API origin trial. - IdP specifies the following in the IdP config file:
{
"accounts_endpoint" : ...,
"modes: {
"button": {
"supports_use_other_account": true,
}
}
}
Participate in the origin trial
You can try the Button Mode API locally by turning on a Chrome
flag
chrome://flags#fedcm-button-mode on Chrome 125 or later.
IdPs can also enable the Button Mode by registering an origin trial:
- Register a third-party origin trial for the RP.
Origin trials allow you to try new features and give feedback on their usability, practicality, and effectiveness to the web standards community. For more information, check out the Origin Trials Guide for Web Developers.
The Button Mode API origin trial is available from Chrome 125 through Chrome 130.
- Go to the origin trial registration page.
- Click the Register button and fill out the form to request a token.
- Enter the IdP's origin as Web Origin.
- Check Third-party matching to inject the token with JavaScript on other origins.
- Click Submit.
- Embed the issued token on a third-party website.
To embed the token on a third-party website, add the following code to the IdP's JavaScript library or SDK served from the IdP's origin.
const tokenElement = document.createElement('meta');
tokenElement.httpEquiv = 'origin-trial';
tokenElement.content = 'TOKEN_GOES_HERE';
document.head.appendChild(tokenElement);
Replace TOKEN_GOES_HERE with your own token.
CORS and SameSite=None will be required in Chrome 125
CORS
Chrome will enforce CORS on the ID assertion endpoint starting from Chrome 125.
CORS (Cross-Origin-Resource-Sharing) is a system, consisting of transmitting
HTTP headers, that determines whether browsers block frontend JavaScript code
from accessing responses for cross-origin requests. The ID assertion endpoint on
the IdP server must respond to the request with additional headers. The
following is an example response header to a request from
https://fedcm-rp-demo.glitch.me:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://fedcm-rp-demo.glitch.me
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
SameSite=None
Cookie's SameSite
parameter declares whether
the cookie is restricted to a first-party or same-site context. By specifying it
to be None, the cookie can be sent to a third-party domain.
In FedCM, Chrome sends cookies to the accounts
endpoint,
the ID assertion
endpoint and
the disconnect
endpoint. Starting from
Chrome 125, Chrome will send those credentialed requests with only cookies
explicitly marked as SameSite=None.

