Gambar 1 menunjukkan arsitektur teknis untuk pembayaran loop terbuka dan interaksinya dengan Google Wallet:
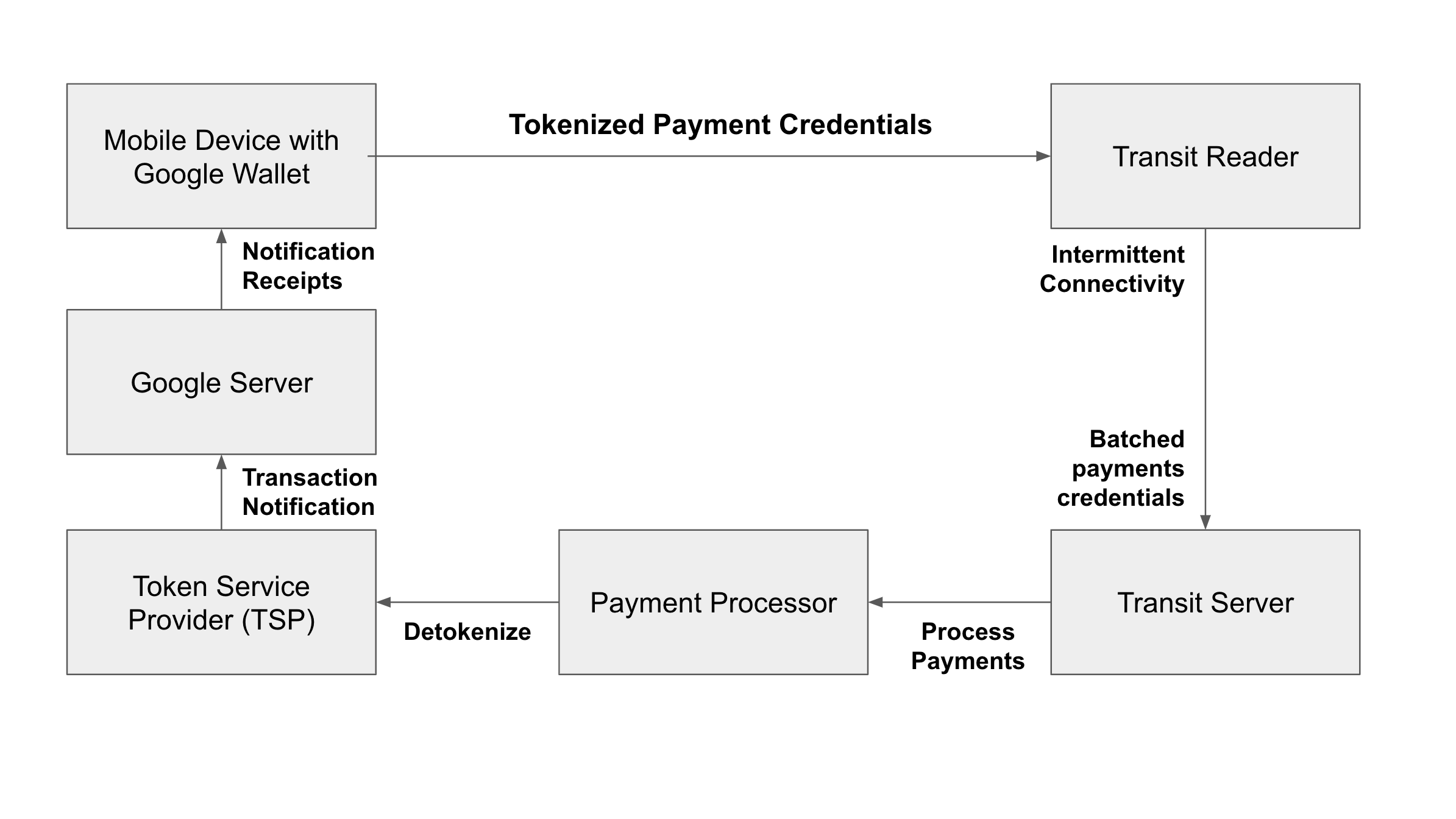
Berikut ini adalah definisi untuk setiap bagian arsitektur teknis.
- Perangkat Seluler dengan Google Wallet
Perangkat seluler yang didukung oleh Android OS memungkinkan pengguna untuk menambahkan kartu dengan aman ke Google Wallet. Google Wallet memfasilitasi proses tokenisasi, yaitu saat jaringan pembayaran membuat token kartu dan menambahkan token khusus perangkat pada perangkat seluler. Sebagai informasi selengkapnya tentang tokenisasi, lihat Cara kerja pembayaran.
Google Wallet kompatibel dengan sebagian besar perangkat Android modern di berbagai produsen, dan faktor bentuk. Untuk persyaratan minimum, lihat Prasyarat.
- Pembaca Transit
Pembaca tiket multi-trip biasanya adalah pembaca kartu di stasiun transportasi umum atau titik masuk bus. Tujuan pembaca dan terminal transportasi umum menerima kredensial pembayaran dari Google Wallet dengan cara yang sama cara mereka menerima kredensial pembayaran dari kartu kredit atau debit fisik tanpa kontak. Untuk menerima pembayaran nirsentuh, pembaca tiket multi-trip harus mematuhi protokol EMV. Untuk informasi selengkapnya, lihat Persyaratan fungsi dasar.
Agar pembaca dapat mematuhi kebijakan dan mendukung pembayaran EMV seluler, mereka mungkin membutuhkan peningkatan versi perangkat lunak. Untuk informasi selengkapnya tentang persyaratan Google untuk tag EMV, lihat Persyaratan fungsi dasar.
Untuk pembaca yang offline atau tanpa koneksi internet berkecepatan tinggi yang andal, operasi transisi diperlukan untuk mengaktifkan autentikasi perangkat offline (ODA). Untuk persyaratan minimum, lihat Prasyarat.
- Server Transit
- Server backend. Operator transportasi umum atau integrator sistem mereka biasanya mengoperasikannya. Pembaca kartu sering kali terhubung ke server secara berkala dan menggabungkan transaksi secara massal. Server menerima permintaan pemrosesan batch dan meneruskan permintaan ke pemroses pembayaran operator transportasi umum.
- Pemroses Pembayaran
- Pemroses pembayaran adalah perusahaan yang menangani transaksi. Ini mende-token-kan tokenisasinya kredensial pembayaran dan menyelesaikan transaksi dengan bank penerbit. Untuk informasi selengkapnya tentang pemrosesan pembayaran, lihat Cara kerja pembayaran.
- Penyedia Layanan Token (TSP)
- TSP untuk jaringan pembayaran menyediakan layanan untuk membuat token dan membatalkan token kartu kredit dan debit. Prosesor memanfaatkan TSP untuk mengambil kredensial pembayaran berdasarkan token yang Aplikasi Google Wallet mengirimkannya kepada pengguna tersebut.
- Server Google
- Server menyediakan link antara partner Google dan perangkat seluler pengguna yang didukung Android perangkat seluler. TSP mengirimkan notifikasi transaksi, seperti notifikasi otorisasi dan penyelesaian, ke server Google. Server Google menggunakan informasi ini untuk menampilkan notifikasi dan tanda terima transaksi kepada pengguna.
