איור 1 מציג את הארכיטקטורה הטכנית של תשלום ב-Open Loop ואת האינטראקציה שלו עם Google Wallet:
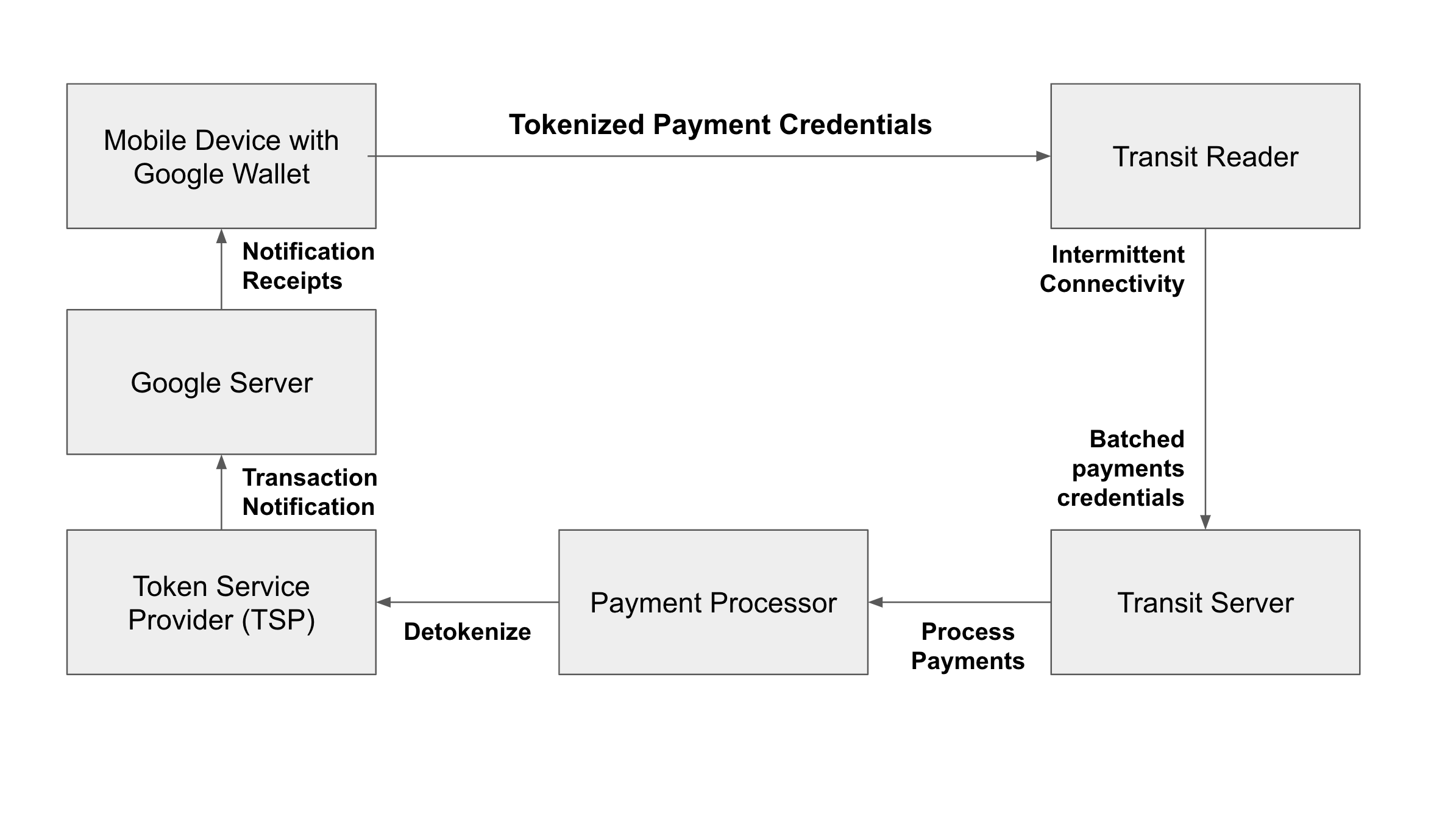
בהמשך מוצגות ההגדרות של כל חלק בארכיטקטורה הטכנית.
- מכשיר נייד עם Google Wallet
מכשירים ניידים שמבוססים על Android OS מאפשרים למשתמשים להוסיף כרטיסים באופן מאובטח אל Google Wallet. Google Wallet מאפשרת את תהליך היצירה של אסימון (tokenization), שבו רשתות התשלומים יוצרות אסימון של הכרטיס ומוסיפות אסימון ספציפי למכשיר בנייד. עבור מידע נוסף על יצירת אסימונים זמין איך מתבצעים תשלומים.
Google Wallet תואם לרוב מכשירי Android המודרניים, ליצרנים שונים ולגורמי צורה. הדרישות המינימליות מפורטות בקטע דרישות מוקדמות.
- קריאה ב-Google Transit
קוראי כרטיסים לתחבורה ציבורית הם בדרך כלל קוראי כרטיסים בתחנות תחבורה ציבורית או בנקודות כניסה לאוטובוסים. קוראים בתחבורה ציבורית ומסופים מקבלים פרטי כניסה מ-Google Wallet באותו אופן כך שהם יקבלו אסמכתה לתשלום מכרטיס אשראי או כרטיס חיוב מיידי פיזי שמצמידים ומשלמים. כדי לאפשר תשלומים ללא מגע, קורא הכרטיסים בתחבורה הציבורית צריך לעמוד בתקן EMV. לקבלת מידע נוסף מידע נוסף, ראה דרישות פונקציונליות בסיסיות.
כדי שהקוראים לעמוד בדרישות ולתמוך בתשלומים באמצעות EMV בנייד, הם עשויים צריכים שדרוגי תוכנה. מידע נוסף על הדרישות של Google לגבי תגי EMV זמין בכתובת דרישות פונקציונליות בסיסיות.
לקוראים שאינם מחוברים לאינטרנט או שאין להם חיבור אינטרנט אמין במהירות גבוהה, נדרשות פעולות תחבורה ציבורית כדי לאפשר אימות מכשיר במצב אופליין (ODA). הדרישות המינימליות מפורטות בקטע דרישות מוקדמות.
- שרת מעבר
- שרת הקצה העורפי. בדרך כלל, מפעילי התחבורה הציבורית או מיזוגני המערכות שלהם מפעילים אותה. קלפים קוראים מתחברים בדרך כלל לשרת לסירוגין ומבצעים עסקאות באצווה יחד. השרתים מקבלים בקשות לעיבוד באצווה ומעבירים אותן לחברת התחבורה הציבורית לצורך עיבוד התשלומים.
- מעבד התשלומים
- הספק של שירותי התשלומים הוא החברה שמטפלת בעסקאות. היא מבטלת את האסימונים של פרטי התשלום ומבצעת את העסקה מול הבנק המנפיק. למידע נוסף על עיבוד תשלומים, קראו את המאמר איך פועלים התשלומים.
- ספק שירותי אסימונים (TSP)
- ה-TSP לרשתות תשלומים מספק שירותים להמרת אסימון ולביטול אסימונים (TSP) של אשראי וחיוב כרטיסיות. מעבדים משתמשים ב-TSP כדי לאחזר פרטי כניסה לתשלום על סמך האסימונים אפליקציית Google Wallet שולחת אליהם.
- שרת Google
- השרת מספק קישור בין השותפים של Google לבין הנייד של המשתמש המבוסס על Android במכשיר. ה-TSP שולח התראות על עסקאות, כמו התראות על אישור ועל הסדרה, לשרתים של Google. השרתים של Google משתמשים במידע הזה כדי להציג התראות וקבלות על עסקאות למשתמש.

