Giới thiệu
Mã vạch xoay trông giống như mã vạch thông thường nhưng thay đổi định kỳ, thường mỗi phút và thiết bị đầu cuối/đầu đọc được lập trình để chỉ chấp nhận email gần đây nhất. Biện pháp bảo mật này giúp giảm rủi ro liên quan đến ảnh chụp màn hình mã vạch, cụ thể là hành vi trộm cắp vé hoặc vé trái phép bán lại. Việc xoay mã vạch cũng có thể đóng vai trò là phương án dự phòng cho các thiết bị không thể tận dụng công nghệ Chạm thông minh do không hỗ trợ NFC (thiếu phần cứng, hoặc phần mềm bị tắt).
Tài liệu tham khảo API
Để biết chi tiết kỹ thuật về Xoay mã vạch, xem
Loại RotatingBarcode.
Tải trọng mẫu
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
Cơ chế dự phòng
Trên thiết bị của người dùng, chỉ một cơ chế đổi thưởng được sử dụng tại một thời điểm nhất định, tuỳ thuộc vào cách định cấu hình thẻ và vé cũng như khả năng của thiết bị. Các loại đổi thưởng sau đây được sử dụng theo thứ tự ưu tiên:
-
Chạm thông minh: Nếu có chỉ định tải trọng của thao tác nhấn thông minh và thiết bị có hỗ trợ
NFC/HCE
- Lưu ý rằng người dùng có thể ghi đè giá trị này bằng cách nhấp vào "Hiển thị mã". sẽ buộc hiển thị mã vạch/mã vạch tĩnh đang xoay.
- Mã vạch xoay: Nếu tải trọng mã vạch xoay được chỉ định
- Mã vạch tĩnh: Nếu tải trọng mã vạch được chỉ định
Việc chỉ định nhiều tải trọng đổi thưởng có thể đảm bảo tất cả người dùng đều được hỗ trợ nhưng có thể ảnh hưởng đến tính bảo mật. Cụ thể, việc sử dụng mã vạch tĩnh làm dự phòng cho mã vạch xoay phủ định hầu hết các lợi ích bảo mật khi sử dụng xoay vòng mã vạch. Mã vạch dự phòng tĩnh sẽ chỉ xuất hiện trong các chế độ xem trên web hoặc trên các ứng dụng không hỗ trợ mã vạch xoay. Kể từ hôm nay, chúng tôi dự kiến tất cả ứng dụng khách Google Wallet hỗ trợ mã vạch xoay.
Lưu quy trình
API Google Wallet cung cấp một số quy trình, bao gồm:
- Tạo các lớp phương tiện công cộng mà không phải tốn thời gian hoặc sớm hơn
- Gửi các đối tượng hoàn chỉnh trong JWT hoặc lưu các đối tượng trước sau đó tham chiếu chúng theo mã nhận dạng trong JWT của bạn
- Cập nhật đối tượng sau khi lưu
Trường Mã vạch xoay được đề xuất tương thích với tất cả các quy trình này, tuy nhiên, để tăng cường tính bảo mật, bạn nên làm như sau:
-
Gọi API
object:insertđể chèn thẻ/vé vào Máy chủ Google Wallet và định cấu hình nút Thêm vào Google Wallet để tham chiếu đối tượng cụ thể theo mã nhận dạng trong JWT của bạn. Điều này đảm bảo rằng kết quả JWT không bao gồm khoá bí mật của mã vạch xoay. - Sử dụng khoá bí mật OTP trong phạm vi một lượt truyền
- Trừ phi được cập nhật, khoá này sẽ có hiệu lực trong vòng đời thẻ/vé. Chúng tôi dự kiến sẽ không cập nhật khoá này theo tần suất bất kỳ trong quá trình hoạt động bình thường.
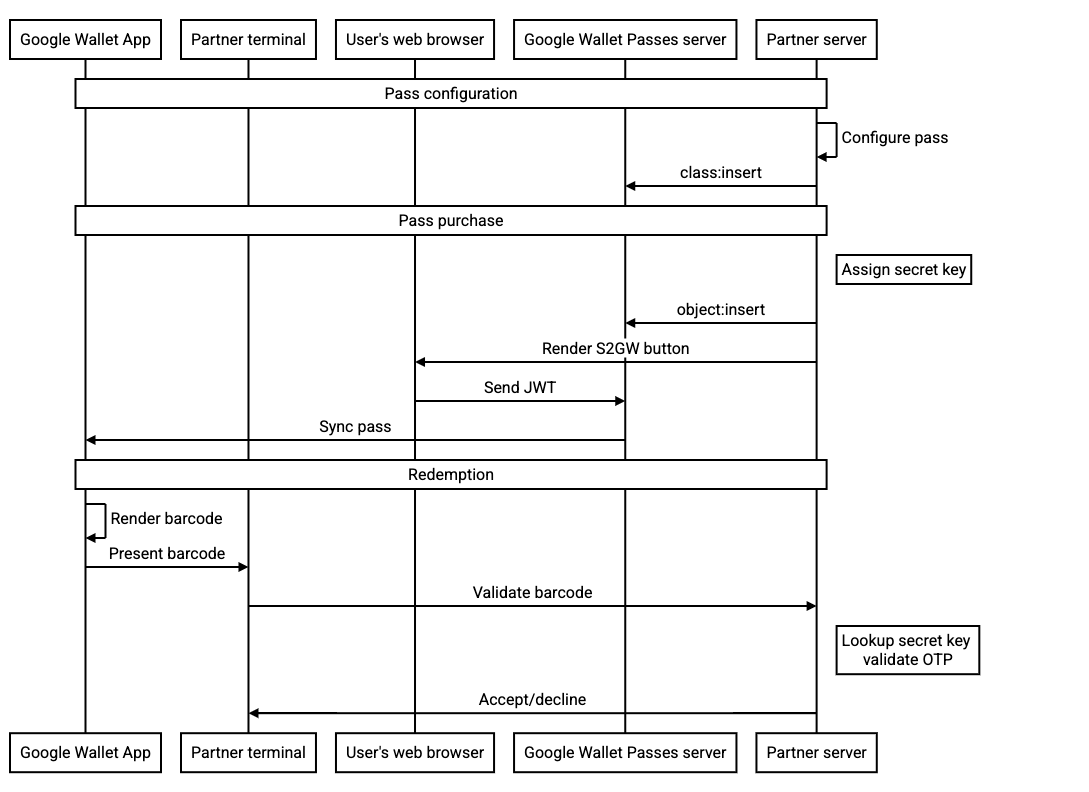
Sơ đồ trình tự dưới đây minh hoạ luồng giữa các tác nhân khác nhau cho một tích hợp thông thường: