Page Summary
-
Inline adaptive banners allow you to specify the ad width to determine the optimal size and maximize performance by optimizing ad size for each device.
-
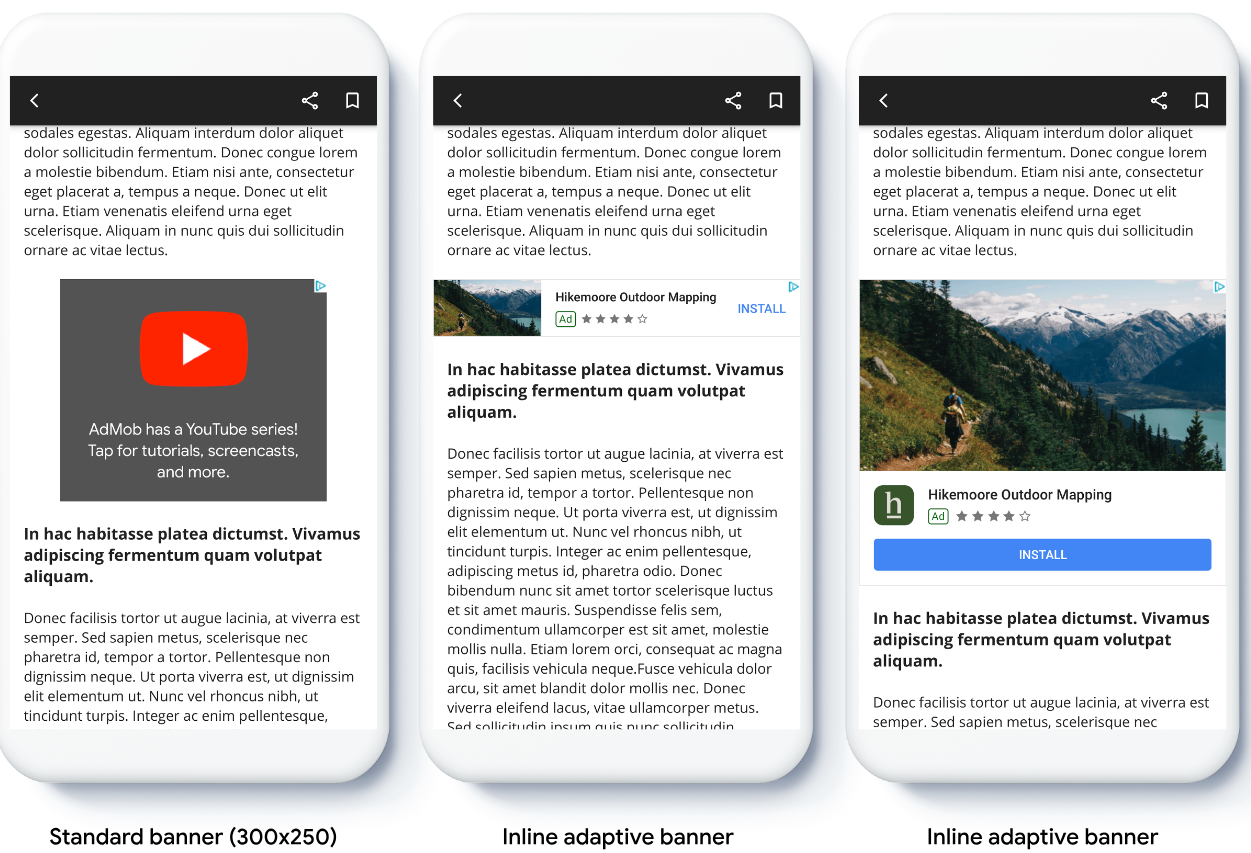
Compared to anchored adaptive banners, inline adaptive banners are larger, taller, use variable heights, and are placed in scrolling content.
-
To implement inline adaptive banners, you need to get the device width and then use a static method on the ad size class to get an inline adaptive ad size object.
-
You can specify the orientation for which to load the banner or limit the maximum height of the banner.
-
Sample applications are available on GitHub in both Java and Kotlin to demonstrate inline adaptive banners.
Adaptive banners let you specify the width of an ad to determine the optimal ad size. Adaptive banners also maximize performance by optimizing the ad size for each device. This approach results in opportunities for improved performance.
Compared to anchored adaptive banners, inline adaptive banners are larger, taller, and use variable instead of fixed heights. Inline adaptive banners are of variable height, and might encompass the entire screen or a maximum height that you specify.
You place inline adaptive banners in scrolling content, for example:
Before you begin
Before continuing, make sure you have completed the getting started guide, Banner ads.
Implement adaptive banners
Unlike anchored adaptive banners, inline adapter banners load using an inline adaptive banner size. To create an inline adaptive ad size, complete the following:
Get the width of the device in use, or set your own width if you don't want to use the full width of the screen.
Kotlin
private val adWidth: Int get() { val displayMetrics = resources.displayMetrics val adWidthPixels = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.R) { val windowMetrics: WindowMetrics = this.windowManager.currentWindowMetrics windowMetrics.bounds.width() } else { displayMetrics.widthPixels } val density = displayMetrics.density return (adWidthPixels / density).toInt() }Java
public int getAdWidth() { DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = getResources().getDisplayMetrics(); int adWidthPixels = displayMetrics.widthPixels; if (VERSION.SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.R) { WindowMetrics windowMetrics = this.getWindowManager().getCurrentWindowMetrics(); adWidthPixels = windowMetrics.getBounds().width(); } float density = displayMetrics.density; return (int) (adWidthPixels / density); }
