یک پروژه اکشن تمام اکشن های شما را در یک ظرف واحد بسته بندی می کند. شما این پروژه را در Actions on Google منتشر میکنید تا «دستیار Google» بداند چگونه تجربیات مکالمهای شما را کشف و فراخوانی کند.

شما از اجزای سطح پایین زیر برای ساخت پروژه Actions خود استفاده می کنید:
تنظیمات و منابع ابرداده پروژه و منابعی مانند نمادهای پروژه را تعریف می کنند. Google از این اطلاعات برای انتشار Actions شما در فهرست راهنمای Assistant استفاده میکند تا کاربران بتوانند آنها را کشف کرده و فراخوانی کنند.
Intent ها وظیفه ای را نشان می دهند که باید انجام شود، مانند برخی از ورودی های کاربر یا یک رویداد سیستم که نیاز به پردازش دارد. متداول ترین نوع قصدی که استفاده می کنید، مقاصد کاربر است. این مقاصد به شما امکان میدهد عبارات آموزشی را که به طور طبیعی توسط موتور NLU (درک زبان طبیعی) گسترش مییابد تا عبارات مشابه بیشتری را شامل شود، اعلام کنید. NLU از تجمیع این عبارات برای آموزش یک مدل زبان استفاده می کند که دستیار برای مطابقت با ورودی کاربر استفاده می کند. در طول مکالمه، اگر برخی از ورودی های کاربر با مدل زبان intent مطابقت داشته باشد، Assistant runtime intent را به Action شما ارسال می کند تا بتواند آن را پردازش کرده و به کاربر پاسخ دهد.
انواع به شما امکان می دهد داده های ساخت یافته را از ورودی کاربر استخراج کنید. با حاشیه نویسی عبارات آموزشی با انواع، NLU می تواند داده های مرتبط و ساختار یافته را برای شما استخراج کند، بنابراین شما مجبور نیستید ورودی های باز را تجزیه کنید.
صحنه ها اهداف را پردازش می کنند و مجریان منطق اصلی برای Actions شما هستند. آنها می توانند پر کردن شکاف ها را انجام دهند، منطق شرطی را ارزیابی کنند، درخواست ها را به کاربر برگردانند، و حتی از خدمات وب خارجی برای اجرای منطق تجاری فراخوانی کنند. در ترکیب با مقاصد، صحنه ها راهی قدرتمند برای شناسایی ورودی های کاربر خاص یا رویدادهای سیستم و اجرای منطق مربوطه به شما می دهند.
درخواستها پاسخهای ایستا یا پویا را تعریف میکنند که از آنها برای پاسخ دادن به کاربران استفاده میکنید.
Webhooks به شما امکان میدهد کار اضافی را به سرویسهای وب واگذار کنید (تکمیل)، مانند اعتبارسنجی دادهها یا ایجاد درخواستها. اقدامات شما از طریق یک پروتکل webhook مبتنی بر JSON با انجام شما ارتباط برقرار می کند.
بوم تعاملی به شما امکان می دهد با برنامه های وب که از HTML، CSS و جاوا اسکریپت استفاده می کنند، تجربیات غنی و همه جانبه ایجاد کنید.
یک پروژه ایجاد کنید
قبل از اینکه بتوانید برای Google Assistant توسعه دهید، باید یک پروژه در کنسول Actions ایجاد کنید. برای ایجاد یک پروژه:
- به کنسول Actions بروید.
- پروژه جدید را کلیک کنید.
- یک نام برای پروژه خود وارد کنید و روی ایجاد پروژه کلیک کنید.
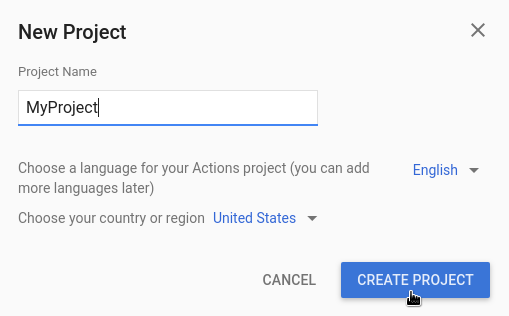
- در چه نوع اکشنی می خواهید بسازید؟ در صفحه، دسته ای را انتخاب کنید که به بهترین شکل پروژه شما را نشان می دهد و روی Next کلیک کنید.
- در صفحه چگونه می خواهید آن را بسازید ، روشی را برای ساخت انتخاب کنید و روی Start building کلیک کنید. به عنوان مثال، می توانید با یک پروژه خالی یا با یک نمونه شروع کنید.
تعریف اطلاعات پروژه
تنظیمات و منابع پروژه شما اطلاعاتی را درباره پروژه شما مانند پشتیبانی از ویژگی و سطح، مناطق پشتیبانی شده، نام نمایش، توضیحات، لوگوها و موارد دیگر تعریف می کند. جدول زیر تنظیمات اصلی و منابعی را که ارائه می کنید توضیح می دهد. Actions on Google از این اطلاعات برای استقرار و انتشار پروژه شما در فهرست راهنمای Assistant استفاده می کند.
| نام | توضیحات |
|---|---|
| اطلاعات دایرکتوری | اطلاعاتی را ارائه می دهد تا Actions on Google بتواند پروژه شما را در فهرست راهنمای Assistant منتشر کند. شامل متادیتا و توضیحاتی در مورد پروژه شما و منابع تصویری برای لوگوها و تصاویر بنر است. |
| مکان یابی | مناطقی را که Actions شما در آنها در دسترس هستند پیکربندی می کند. |
| قابلیت های سطحی | سطوحی را که Actions شما در آنها در دسترس هستند پیکربندی می کند. |
| جزئیات شرکت | اطلاعات تماس شرکت شما را مشخص می کند. |
| تایید برند | وبسایت یا برنامه اندرویدی را که مالک آن هستید وصل کنید تا از مزایای اضافی مانند نامهای فراخوان رزرو شده و پیوند وبسایت در Actions خود استفاده کنید. |
| رها کنید | نسخه های مختلف آزمایش و تولید را برای Action شما برای آزمایش و تولید پیکربندی می کند. |
| پیوندهای دستیار | به کاربران اجازه دهید تا Actions شما را از ویژگی های وب شما فراخوانی کنند. |
برای تعریف اطلاعات پروژه:
تست پروژه ها در شبیه ساز
کنسول Actions یک شبیهساز برای پیشنمایش اقدامات شما ارائه میکند. شبیهساز به شما امکان میدهد اطلاعات اشکالزدایی را ببینید، قابلیتهای دستگاه را تنظیم کنید، محلی را شبیهسازی کنید، و موارد دیگر.
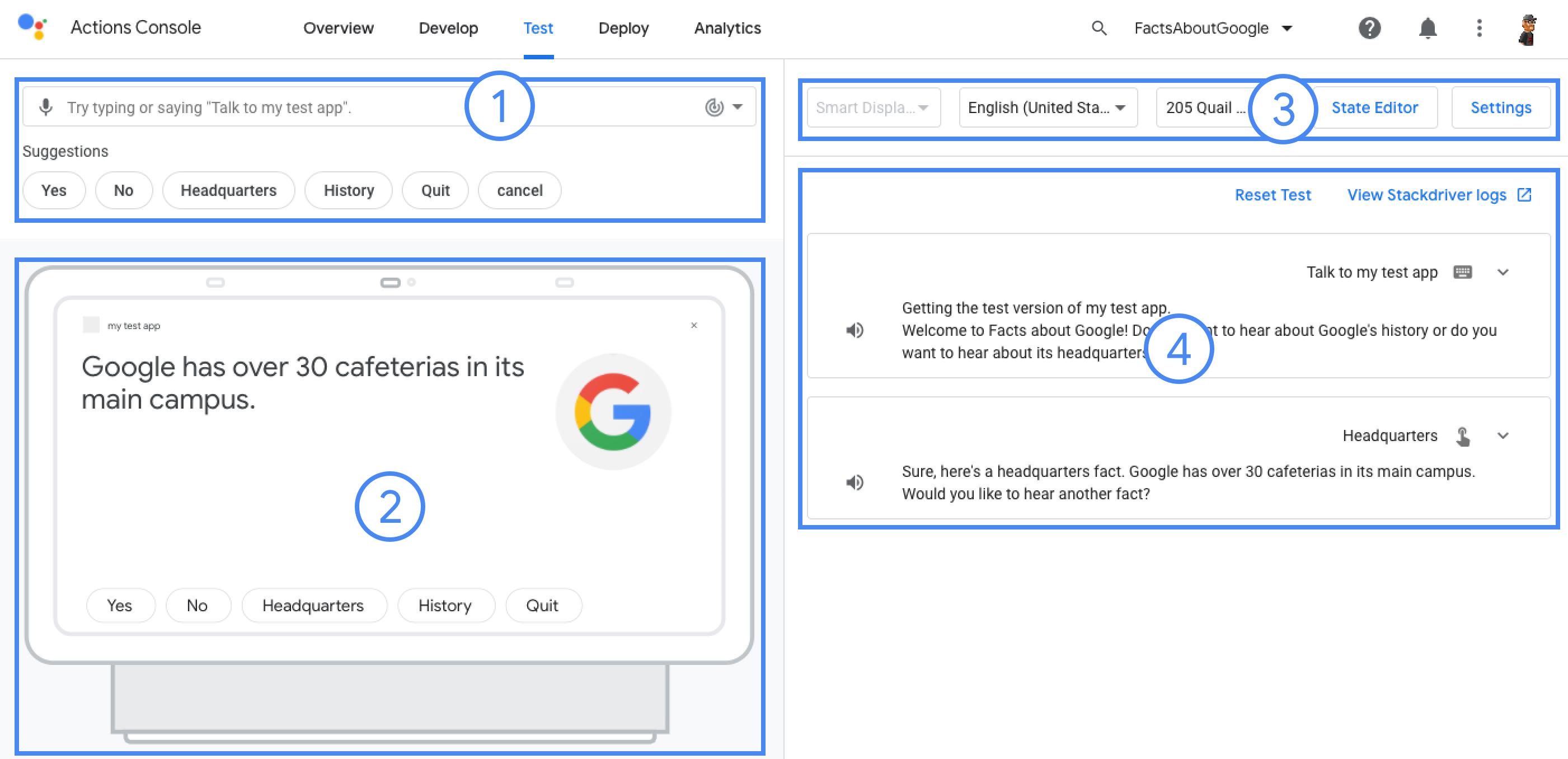
برای تست یک پروژه: