Project Action mengemas semua Action Anda ke dalam satu container. Anda memublikasikan project ini ke Actions on Google agar Asisten Google tahu cara menemukan dan memanggil pengalaman percakapan Anda.

Anda menggunakan komponen tingkat rendah berikut untuk membuat project Action:
Setelan dan resource menentukan metadata project dan sumber daya seperti ikon proyek. Google menggunakan informasi ini untuk memublikasikan Action Anda ke direktori Asisten, sehingga pengguna dapat menemukan dan memanggil mereka.
Intent mewakili tugas yang harus dilakukan, seperti beberapa input pengguna atau peristiwa sistem yang perlu diproses. Jenis yang paling umum dari yang akan Anda gunakan adalah intent pengguna. Intent ini memungkinkan Anda mendeklarasikan pelatihan frasa yang diperluas secara alami oleh NLU (natural language understanding) mesin telusur untuk menyertakan lebih banyak frasa serupa. NLU menggunakan agregasi dari frasa ini untuk melatih model bahasa yang digunakan Asisten untuk mencocokkan pengguna input teks. Selama percakapan, jika beberapa input pengguna cocok dengan bahasa intent khusus, runtime Asisten akan mengirimkan intent ke Action Anda, sehingga memprosesnya dan menanggapi pengguna.
Jenis memungkinkan Anda mengekstrak data terstruktur dari input pengguna. Menurut menganotasi frasa pelatihan dengan jenis, NLU dapat mengekstrak yang relevan, terstruktur data untuk Anda, sehingga Anda tidak perlu menguraikan input terbuka.
Scene memproses intent dan merupakan eksekutor logika utama untuk Actions Anda. Mereka dapat melakukan pengisian slot, mengevaluasi logika bersyarat, menampilkan kepada pengguna, dan bahkan memanggil layanan web eksternal untuk melakukan logika bisnis. Dikombinasikan dengan intent, scene memberi Anda cara ampuh untuk mendeteksi input pengguna atau kejadian sistem tertentu dan untuk melakukan logika.
Perintah menentukan respons statis atau dinamis yang Anda gunakan untuk menanggapi pengguna.
Webhook memungkinkan Anda mendelegasikan pekerjaan tambahan ke layanan web (fulfillment), seperti memvalidasi data atau membuat prompt. Tindakan Anda berkomunikasi dengan fulfillment Anda melalui protokol webhook berbasis JSON.
Kanvas Interaktif memungkinkan Anda membuat konten kaya dan pengalaman imersif dengan aplikasi web yang menggunakan HTML, CSS, dan JavaScript.
Membuat project
Anda harus membuat project di konsol Actions sebelum dapat mengembangkan Asisten Google. Untuk membuat project:
- Buka Konsol Actions.
- Klik Project baru.
- Masukkan nama untuk project Anda, lalu klik Create Project.
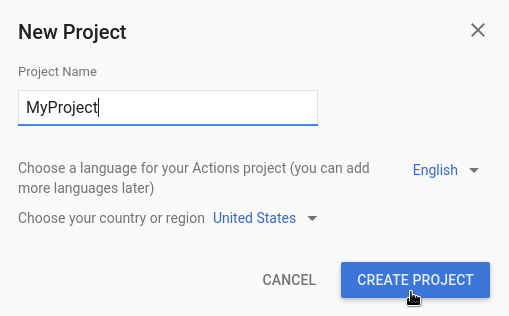
- Di layar What types of Action do you want to build?, pilih kategori yang paling mewakili project Anda, lalu klik Next.
- Di layar How do you want to build it, pilih cara untuk membuat dan klik Mulai membuat. Misalnya, Anda dapat memulai dengan proyek atau dengan suatu sampel.
Mendefinisikan informasi project
Pengaturan dan sumber daya proyek menentukan informasi tentang proyek seperti dukungan fitur dan platform, lokalitas yang didukung, nama tampilan, deskripsi, logo, dan lain-lain. Tabel berikut menjelaskan setelan dan resource utama yang Anda sediakan. Actions on Google menggunakan data informasi untuk men-deploy dan memublikasikan project Anda ke Asisten direktori.
| Nama | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Informasi direktori | Memberikan informasi agar Actions on Google dapat memublikasikan project ke direktori Assistant. Termasuk metadata dan pencemaran nama baik tentang project dan resource gambar Anda untuk gambar logo dan banner. |
| Penargetan lokasi | Mengonfigurasi lokalitas tempat Action Anda tersedia. |
| Kemampuan permukaan | Mengonfigurasi platform tempat Action Anda tersedia. |
| Detail perusahaan | Menentukan informasi kontak untuk perusahaan Anda. |
| Verifikasi merek | Hubungkan situs atau aplikasi Android milik Anda untuk mendapatkan manfaat tambahan seperti nama panggilan yang dicadangkan dan penautan situs dalam Action Anda. |
| Rilis | Mengonfigurasi berbagai rilis pengujian dan produksi untuk Action Anda untuk pengujian dan produksi. |
| Link Asisten | Izinkan pengguna memanggil Actions dari properti web Anda. |
Untuk mendefinisikan informasi proyek:
Menguji project di simulator
Konsol Actions menyediakan simulator untuk melihat pratinjau Actions Anda. Tujuan memungkinkan Anda melihat informasi debug, menyetel kemampuan perangkat, menyimulasikan lokal, dan lainnya.
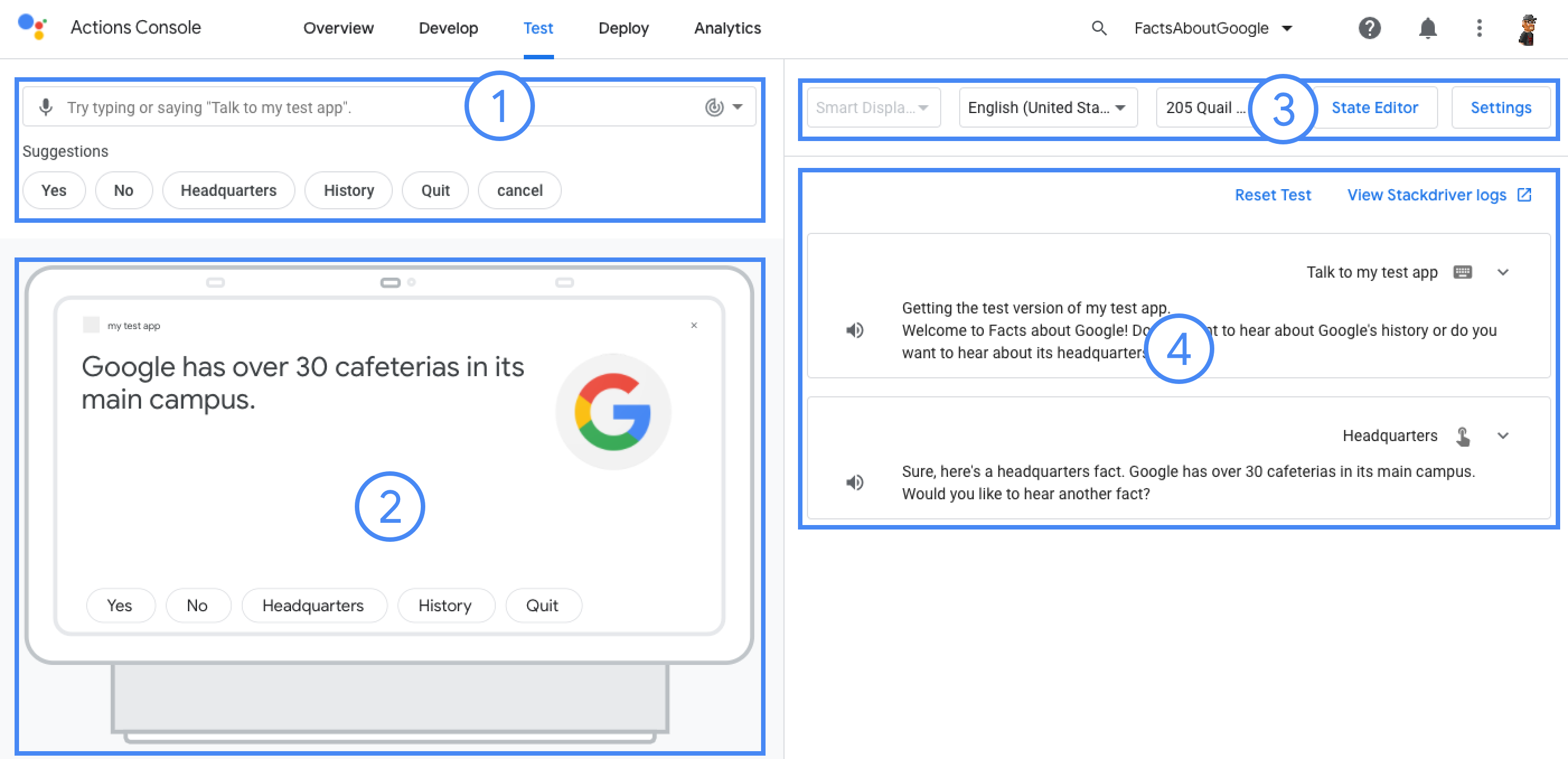
Untuk menguji project: