يوضِّح هذا المستند تنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب للتواصل بين "المهام مع مساعد Google" وخدمة تنفيذ الطلبات التي تُحدِّد واجهة مستخدم محادثات مخصَّصة.
من المهم فهم كيفية تواصل "المهام مع مساعد Google" وتنفيذك من خلال تنسيقات الردّ التلقائي على الويب في "المهام مع مساعد Google":
- للمشاركة في محادثات باستخدام "المهام مع مساعد Google"، يتم تنفيذ ردّ تلقائي على الويب يمكنه الردّ على طلبات HTTP من "المهام مع مساعد Google".
- عندما يستدعي المستخدمون الإجراء الخاص بك، تتلقّى عملية تنفيذ الإجراء
HTTP POSTمع حمولة بيانات JSON تصف طلب المستخدم. - في المقابل، يكون التنفيذ مسؤولاً عن قراءة المعلَمات من حمولة الطلب وإنشاء استجابة بتنسيق JSON مناسب وإرسال ردّ إلى "مساعد Google" يتضمّن هذا الردّ.
أنواع الطلبات
يلخّص هذا الجدول أنواع الطلبات التي قد يتلقّاها الردّ التلقائي على الويب من "مساعد Google":
| Type | الوصف | أمثلة على JSON |
|---|---|---|
| طلبات الاستدعاء | العبارات التي يألفها المستخدم والتي تبدأ المحادثة مع الطلب أو تؤدّي إلى تنفيذ إجراءات برابط لصفحة في التطبيق (على سبيل المثال، "التحدّث إلى طاهٍ شخصي للعثور على وصفات طعام العشاء")
|
|
| طلبات المحادثات | العبارات التي قالها المستخدمون في الجلسة نفسها بعد بدء المحادثة مع
قسم التنفيذ. في تنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب للمحادثة، هذه هي
الردود النصية الأولية من المستخدم والتي تتوافق مع نوايا actions.intent.TEXT
التي طلبها تنفيذك في الدور السابق. |
|
| النتائج المساعدة | الطلبات التي أرسلها "مساعد Google" إلى عملية التنفيذ عندما يطلب الردّ التلقائي على الويب
نيّة مساعد
في المرحلة السابقة من المحادثة للتعامل مع أجزاء
من المحادثة (على سبيل المثال، actions.intent.OPTION
وactions.intent.PERMISSION). |
طلبات المحادثات والردود
في سيناريو تفاعل "المهام مع مساعد Google" النموذجي، ينطق المستخدمون عبارة لاستدعاء إجراء. لتقديم رد، تعثر ميزة "المهام مع مساعد Google" على التنفيذ الذي يطابق الإجراء الذي استدعاه المستخدم ويرسل الطلب إلى هناك.
بعد أن تثبت خدمة Actions on Google أنّ عملية تنفيذ طلبك مطابقة مناسبة لاستدعاء المستخدم، يتم بدء جلسة محادثة عن طريق إرسال طلب HTTP يتضمّن حمولة JSON بمعلومات طلب المستخدم إلى نقطة نهاية التنفيذ. يحلل التنفيذ الذي تقوم به الطلب ويعرض ردًا يحتوي على حمولة JSON. ثم تحوّل "المهام مع مساعد Google" الحمولة إلى كلام وإخراج وسائط متعددة معروض للمستخدمين.
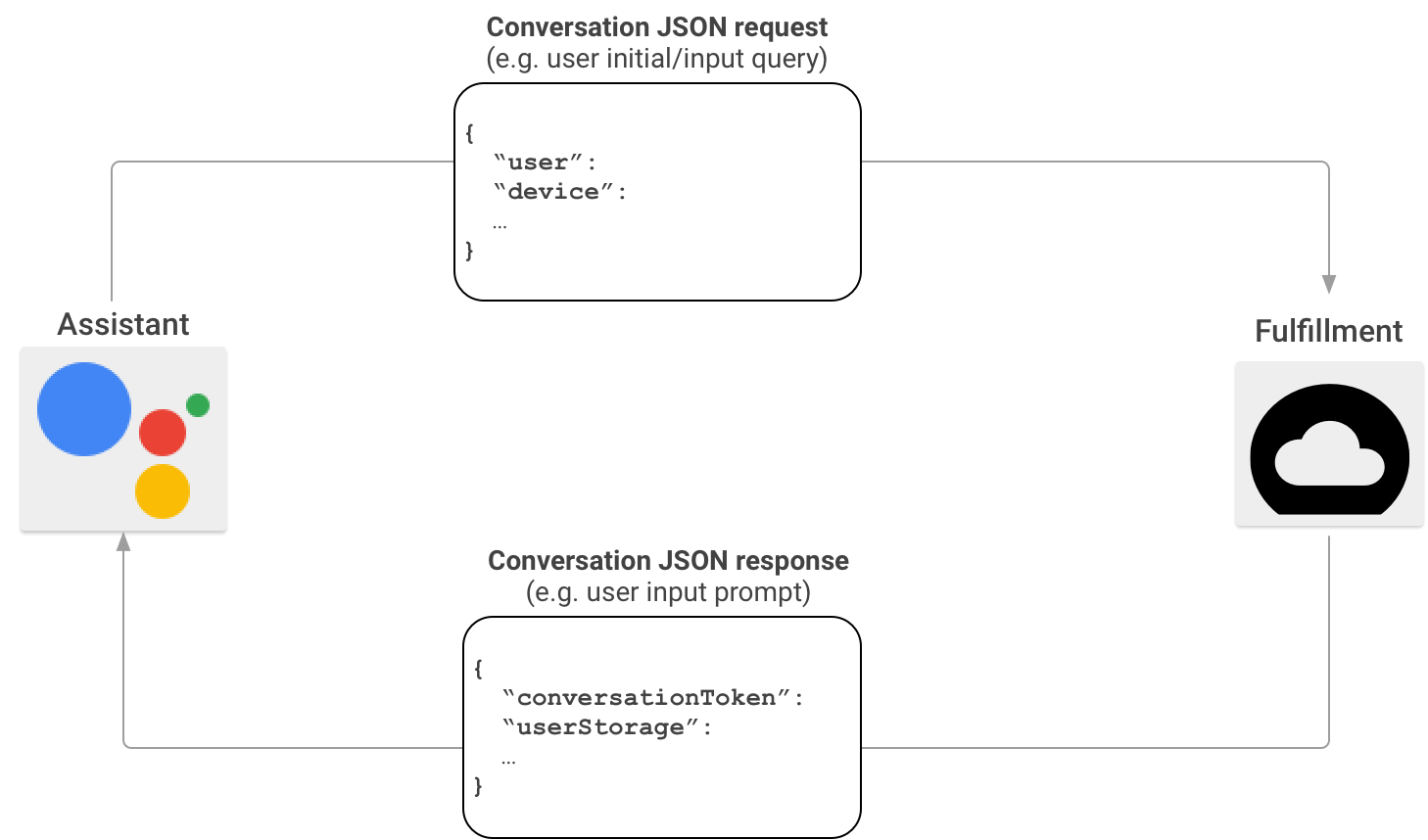
لمزيد من المعلومات عن تنسيق حمولة JSON عندما تستدعي "المهام مع مساعد Google" عملية التنفيذ من خلال حزمة تطوير البرامج "للمهام"، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب للمحادثة.
الطلبات والردود في Dialogflow
عند إنشاء "المهام"، يمكنك استخدام Dialogflow لتبسيط مهمة إنشاء واجهات محادثات. في هذا السيناريو، يعمل Dialogflow كوكيل بين "المهام مع مساعد Google" وتنفيذك. وبدلاً من إرسال طلب HTTP/JSON مباشرةً إلى نقطة نهاية التنفيذ، يرسله "المهام مع مساعد Google" إلى Dialogflow.
يدمج Dialogflow حمولة بيانات JSON المضمّنة في الطلب الأصلي بتنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب في Dialogflow، ويُعيد توجيه الطلب الناتج إلى تنفيذ Dialogflow.
وفي المقابل، عندما يرسل التنفيذ ردًا إلى Dialogflow، يجب أن تتوافق حمولة JSON للاستجابة مع تنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب في Dialogflow. يحلّل التنفيذ المعلَمات من طلب Dialogflow JSON وينشئ ردًا بتنسيق الرد التلقائي على الويب في Dialogflow. يحوّل Dialogflow الرد من تنفيذك إلى رسالة رد يفهمها مساعد Google.
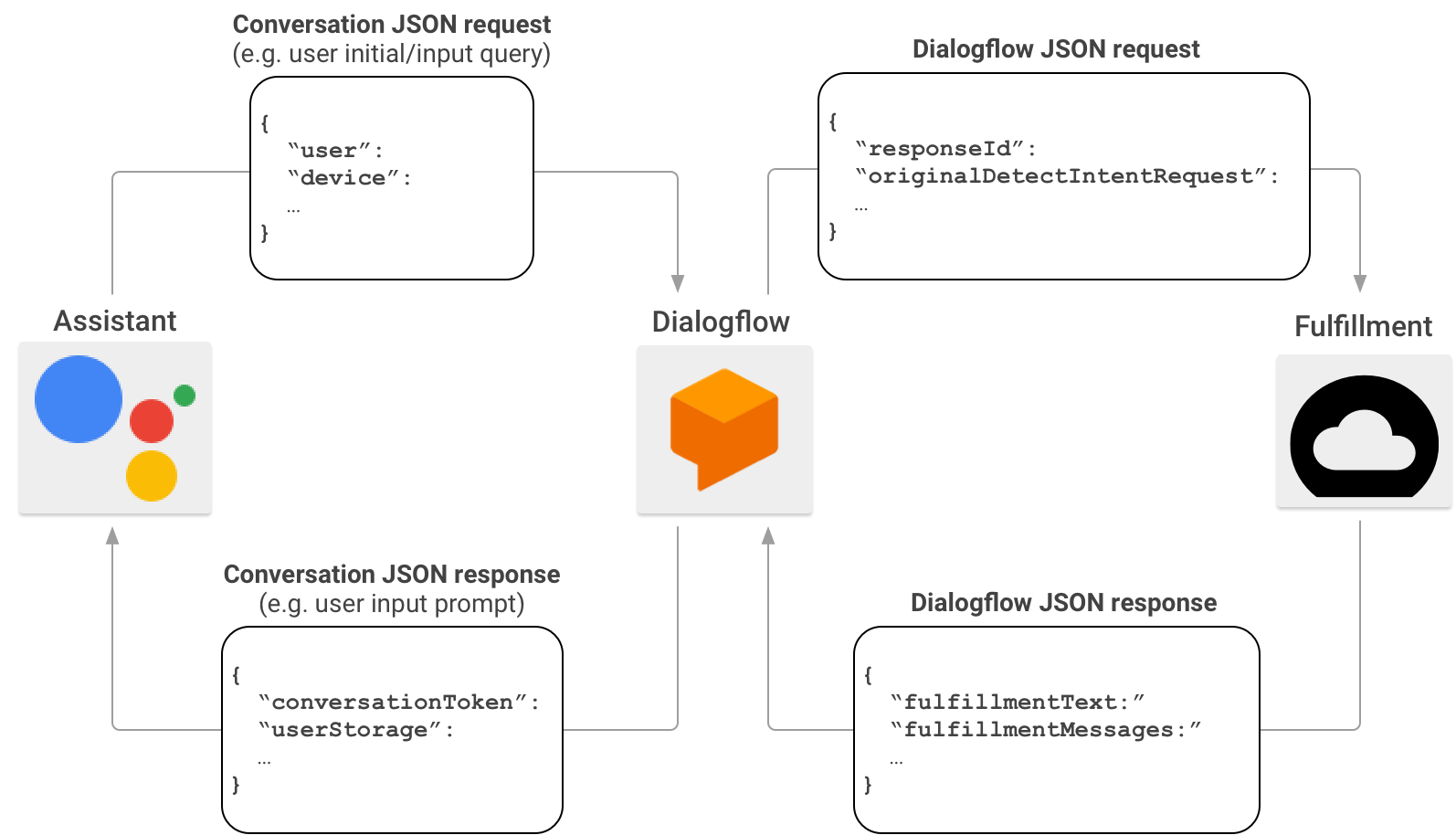
لمزيد من المعلومات عن تنسيق حمولة JSON عندما تستدعي "المهام مع مساعد Google" عملية التنفيذ من خلال Dialogflow، يمكنك الاطّلاع على تنسيق الردّ التلقائي على الويب في Dialogflow.