این سند قالب webhook را برای برقراری ارتباط بین Actions on Google و یک سرویس تکمیلی که یک رابط کاربری مکالمه سفارشی را تعریف میکند، توصیف میکند.
درک نحوه ارتباط Actions on Google و اجرای شما از طریق قالبهای Actions on Google webhook بسیار مهم است:
- برای شرکت در مکالمات با Actions on Google، اجرای شما یک وبکهوک را پیادهسازی میکند که میتواند به درخواستهای HTTP از Actions on Google پاسخ دهد.
- وقتی کاربران Action شما را فراخوانی میکنند، انجام شما یک
HTTP POSTبا بار JSON دریافت میکند که درخواست کاربر را توضیح میدهد. - به نوبه خود، انجام شما مسئول خواندن پارامترها از بار درخواست، ایجاد یک پاسخ با فرمت JSON مناسب و ارسال پاسخ به دستیار با این پاسخ است.
انواع درخواست
این جدول انواع درخواست هایی را که وب هوک شما ممکن است از دستیار دریافت کند، خلاصه می کند:
| تایپ کنید | شرح | نمونه های JSON |
|---|---|---|
| درخواست های فراخوانی | اظهارات کاربر که مکالمه را با رضایت شما آغاز می کند یا اقدامات پیوند عمیق را آغاز می کند (به عنوان مثال، "برای یافتن دستور العمل های شام با سرآشپز شخصی صحبت کنید" ).
| |
| درخواست های مکالمه | اظهارات کاربران در همان جلسه پس از شروع گفتگو با شما. در قالب مکالمه webhook، اینها پاسخهای متن خام کاربر مربوط به مقاصد actions.intent.TEXT هستند که اجرای شما در نوبت قبلی درخواست کرده بود. | |
| نتایج کمکی | درخواستهایی که «دستیار» برای انجام شما ارسال میکند، زمانی که وبهوک شما در نوبت قبلی مکالمه یک هدف کمکی برای مدیریت بخشهایی از مکالمه درخواست کرده است (مثلا actions.intent.OPTION و actions.intent.PERMISSION ). |
درخواست ها و پاسخ های گفتگو
در یک سناریوی معمولی تعامل Actions on Google، کاربران عبارتی را برای فراخوانی یک Action بیان میکنند. برای ارائه پاسخ، Actions on Google انجام شده را پیدا میکند که با Action درخواست شده توسط کاربر مطابقت دارد و درخواست را به آنجا ارسال میکند.
هنگامی که Actions on Google مشخص کرد که انجام شما با فراخوانی کاربر مطابقت دارد، یک جلسه مکالمه را با ارسال یک درخواست HTTP که حاوی یک بار JSON با اطلاعات درخواست کاربر به نقطه پایانی شما است، شروع میکند. انجام شما درخواست را تجزیه می کند و پاسخی را برمی گرداند که حاوی بار JSON است. Actions on Google سپس بار را به گفتار رندر شده و خروجی چندرسانه ای برای کاربران تبدیل می کند.
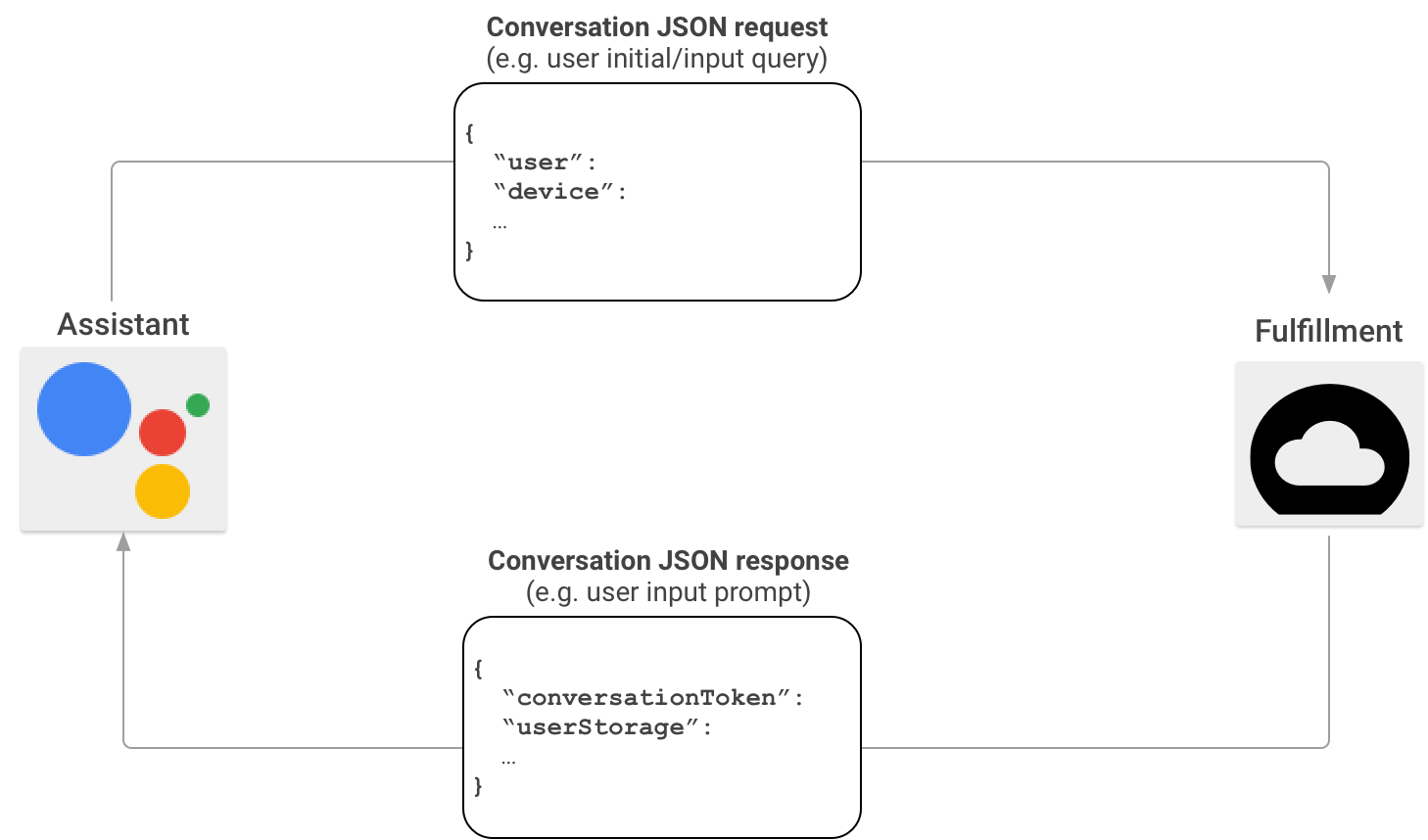
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد قالب بار JSON هنگامی که Actions on Google اجرای شما را از طریق Actions SDK فراخوانی می کند، به قالب گفتگوی وب هوک مراجعه کنید.
درخواست ها و پاسخ های جریان گفتگو
هنگامی که Actions را ایجاد می کنید، می توانید به صورت اختیاری از Dialogflow برای ساده سازی کار ساخت رابط های مکالمه استفاده کنید. در این سناریو، Dialogflow به عنوان یک پروکسی بین Actions on Google و انجام شما عمل می کند. به جای ارسال درخواست HTTP/JSON مستقیماً به نقطه پایانی شما، Actions on Google آن را به Dialogflow ارسال میکند.
Dialogflow محموله JSON موجود در درخواست اصلی را در قالب webhook Dialogflow قرار می دهد و درخواست حاصل را به انجام Dialogflow شما ارسال می کند.
برعکس، وقتی تکمیل شما پاسخی را به Dialogflow ارسال میکند، بار JSON پاسخ باید با قالب webhook Dialogflow مطابقت داشته باشد. تکمیل شما پارامترهای درخواست Dialogflow JSON را تجزیه می کند و پاسخی را در قالب webhook Dialogflow ایجاد می کند. سپس Dialogflow پاسخ از انجام شما را به پیام پاسخی تبدیل می کند که دستیار آن را درک می کند.
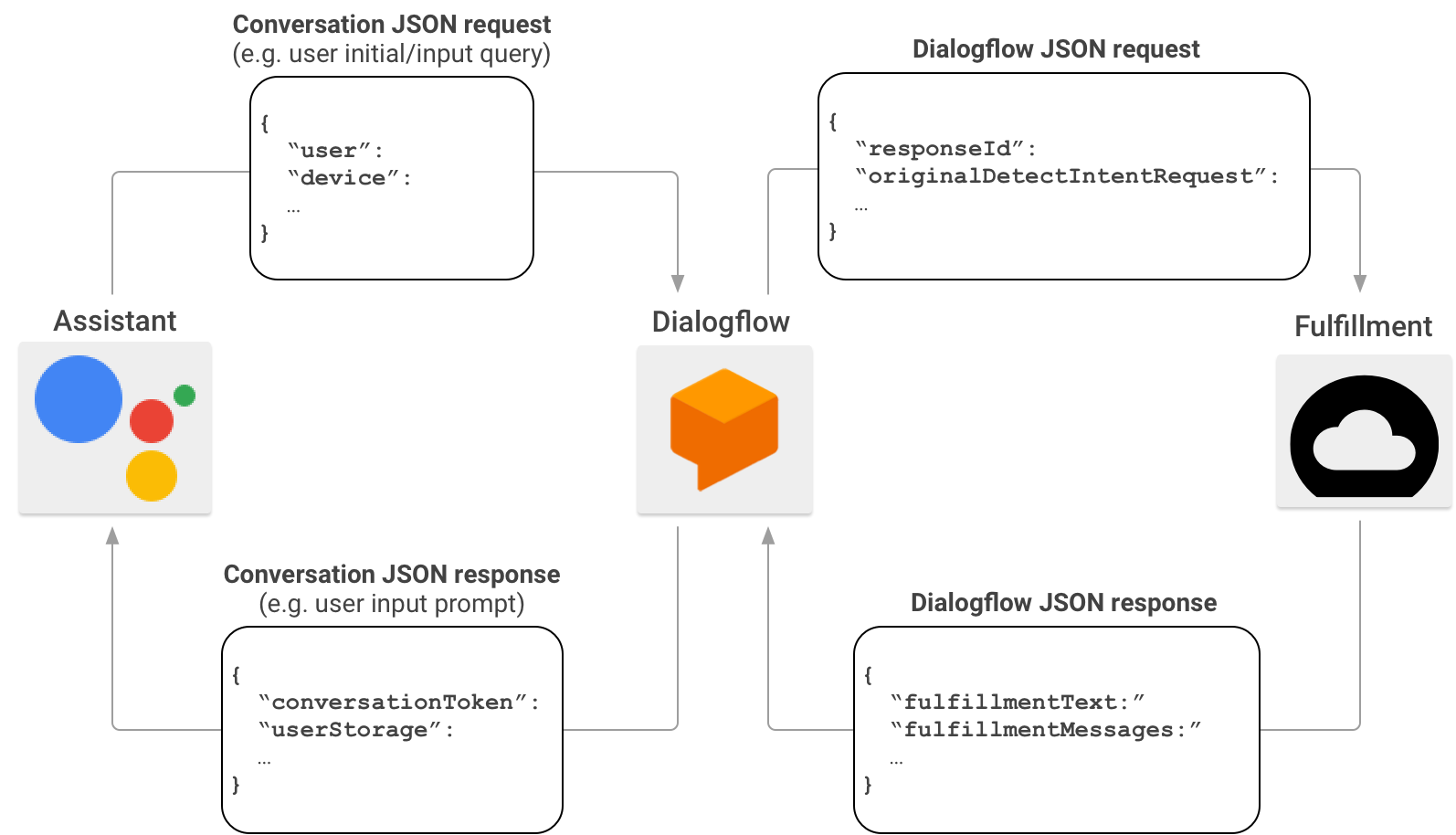
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد فرمت بار JSON هنگامی که Actions on Google اجرای شما را از طریق Dialogflow فراخوانی میکند، به قالب webhook Dialogflow مراجعه کنید.