Google 시각화 데이터 소스 라이브러리를 사용하면 시각화 데이터 소스를 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다. 라이브러리는 Google 시각화 API 전송 프로토콜과 쿼리 언어를 구현합니다. 라이브러리에 데이터를 사용할 수 있도록 하는 데 필요한 코드만 데이터 표 형식으로 작성합니다. 데이터 테이블은 모든 열이 단일 유형인 값의 2차원 테이블입니다. 추상 클래스와 도우미 함수를 프로비저닝하면 필요한 코드를 더 쉽게 작성할 수 있습니다.
라이브러리의 가장 간단한 구현은 단일 클래스에서 상속받고, 구성원 함수를 구현하고, 데이터 세트를 서블릿 컨테이너 내에서 서블릿으로 실행하는 것입니다. 가장 간단한 구현에서는 시각화가 데이터 소스를 쿼리할 때 다음과 같은 이벤트 시퀀스가 발생합니다.
- 서블릿 컨테이너는 쿼리를 처리하고 데이터 소스 자바 라이브러리에 전달합니다.
- 라이브러리가 쿼리를 파싱합니다.
- 개발자가 작성하는 코드인 구현 코드는 라이브러리에 데이터 테이블을 반환합니다.
- 라이브러리는 데이터 테이블에서 쿼리를 실행합니다.
- 라이브러리는 시각화에서 예상하는 응답으로 데이터 테이블을 렌더링합니다.
- 서블릿 컨테이너는 시각화에 응답을 반환합니다.
다음 다이어그램을 참조하세요.
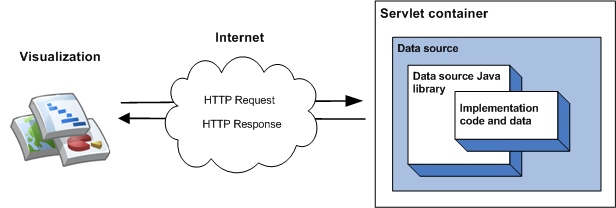
데이터 소스 시작하기 섹션에서는 이러한 유형의 데이터 소스를 구현하는 방법을 설명합니다.
데이터 소스에서 제공하는 데이터는 구현 코드에 지정할 수 있으며, 소량의 정적 데이터에 적합합니다. 큰 데이터 세트의 경우 외부 파일 또는 데이터베이스와 같은 외부 데이터 저장소를 사용해야 할 가능성이 높습니다. 데이터 소스가 외부 데이터 저장소를 사용하는 경우 시각화에서 데이터 소스를 쿼리할 때 다음과 같은 이벤트 시퀀스가 발생합니다.
- 서블릿 컨테이너는 쿼리를 처리하고 데이터 소스 자바 라이브러리에 전달합니다.
- 라이브러리가 쿼리를 파싱합니다.
- 구현 코드(작성하는 코드)는 데이터 저장소에 저장된 데이터를 읽고 데이터 테이블을 라이브러리에 반환합니다. 데이터 세트가 많고 데이터 저장소에 쿼리 기능이 있다면 선택적으로 이러한 기능을 사용하여 데이터 소스의 효율성을 높일 수 있습니다.
- 라이브러리는 데이터 테이블에서 쿼리를 실행합니다.
- 라이브러리는 시각화에서 예상하는 응답으로 데이터 테이블을 렌더링합니다.
- 서블릿 컨테이너는 시각화에 응답을 반환합니다.
다음 다이어그램을 참조하세요.
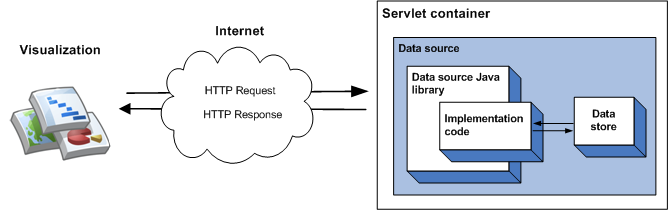
외부 데이터 저장소 사용 섹션에서는 이 유형의 데이터 소스를 구현하는 방법을 설명합니다.