تُسهّل "مكتبة مصادر بيانات التمثيل البصري على Google" إنشاء مصدر بيانات التمثيل البصري. وتطبّق المكتبة بروتوكول السلك API المرئي من Google ولغة طلب البحث. وما عليك سوى كتابة الرمز المطلوب لإتاحة بياناتك للمكتبة على شكل جدول بيانات. جدول البيانات هو جدول ثنائي الأبعاد للقيم حيث يكون كل عمود من نوع واحد. أصبح كتابة الرمز الذي تحتاج إليه أسهل من خلال توفير الدروس التجريدية والوظائف المساعدة.
تتمثل أبسط عملية تنفيذ للمكتبة في اكتساب سمات من فئة واحدة وتنفيذ دالة عضو وتشغيل مصدر البيانات كمحرّك داخل حاوية سيرفل. في أبسط عمليات التنفيذ، يحدث التسلسل التالي للأحداث عندما يبحث التمثيل البصري عن مصدر البيانات:
- تُعالج حاوية محاولة الوصول إلى طلب البحث وتمريره إلى مكتبة مصدر بيانات Java.
- تحلّل المكتبة الطلب.
- يعرض رمز التنفيذ - الرمز الذي تكتبه - جدول بيانات إلى المكتبة.
- تنفّذ المكتبة الطلب في جدول البيانات.
- تعرض المكتبة جدول البيانات في الاستجابة المتوقعة من قِبل التمثيل البصري.
- تعرض حاوية بحثخة الاستجابة للتمثيل البصري.
وقد تم توضيح ذلك في الرسم البياني التالي:
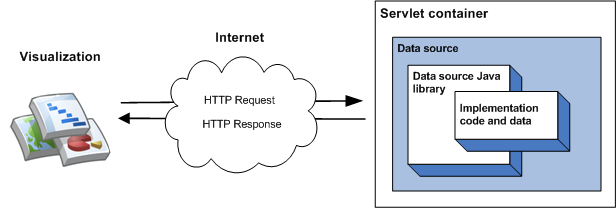
يوضّح قسم البدء في استخدام مصادر البيانات كيفية تنفيذ هذا النوع من مصادر البيانات.
يمكن تحديد البيانات التي يتم عرضها من خلال مصدر بيانات في رمز التنفيذ، ويمكن استخدام هذه البيانات لكميات صغيرة من البيانات الثابتة. وبالنسبة إلى مجموعات البيانات الأكبر حجمًا، من المرجّح أن تحتاج إلى استخدام مخزن بيانات خارجي، مثل ملف أو قاعدة بيانات خارجية. إذا كان مصدر البيانات يستخدم مخزن بيانات خارجيًا، سيحدث التسلسل التالي للأحداث عند طلب التمثيل البصري لمصدر البيانات:
- تتعامل حاوية بحث الخدمة مع طلب البحث وتنقله إلى مكتبة Java لمصدر البيانات.
- تحلّل المكتبة الطلب.
- يشير رمز التنفيذ - الرمز الذي تكتبه - إلى البيانات المحفوظة في مخزن البيانات وعرض جدول بيانات في المكتبة. إذا كانت مجموعة البيانات كبيرة وكان مخزن البيانات يحتوي على طلبات بحث لإمكانات، يمكنك اختياريًا استخدام هذه الإمكانات لزيادة كفاءة مصدر بياناتك.
- تنفّذ المكتبة الطلب في جدول البيانات.
- تعرض المكتبة جدول البيانات في الاستجابة المتوقعة من قِبل التمثيل البصري.
- تعرض حاوية بحث Service الاستجابة إلى التمثيل البصري.
وقد تم توضيح ذلك في الرسم البياني التالي:
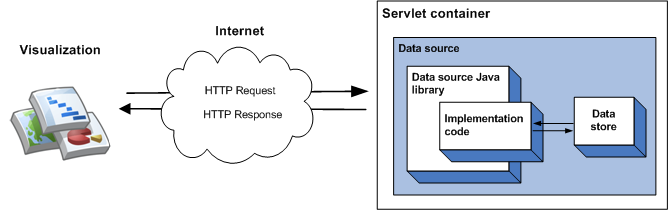
يوضّح قسم استخدام مخزن بيانات خارجي كيفية تنفيذ هذا النوع من مصادر البيانات.
