借助 Google 可视化数据源库,您可以轻松创建可视化数据源。该库实现了 Google 可视化 API 传输协议和查询语言。您只需以数据表的形式编写将数据提供给库所需的代码。数据表是二维值表,其中每一列都是单一类型。通过提供抽象类和辅助函数,您可以更轻松地编写所需的代码。
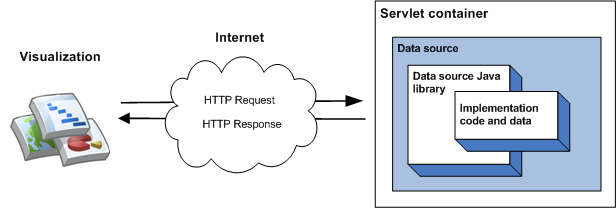
该库最简单的实现方式包括从单个类继承、实现成员函数,以及将数据源作为 servlet 容器中的 servlet 运行。在最简单的实现中,当可视化查询数据源时,会发生以下事件序列:
- servlet 容器会处理查询并将其传递给数据源 Java 库。
- 该库会解析查询。
- 实现代码(您编写的代码)会将数据表返回到库。
- 该库会对数据表执行查询。
- 该库会将数据表呈现到可视化图表预期的响应中。
- 该 servlet 容器返回对可视化图表的响应。
下图对此进行了说明:
数据源使用入门部分介绍了如何实现这种类型的数据源。
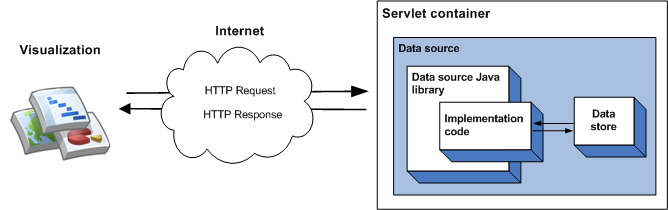
您可以在实现代码中指定数据源提供的数据,这适用于少量静态数据。对于较大的数据集,您更可能需要使用外部数据存储,如外部文件或数据库。如果数据源使用外部数据存储区,则当可视化查询数据源时,会发生以下事件序列:
- servlet 容器会处理查询并将其传递给数据源 Java 库。
- 该库会解析查询。
- 实现代码(您编写的代码)会读取保存在数据存储区中的数据,并将数据表返回到库。如果数据集很大,并且数据存储区具有查询功能,则可以选择使用这些功能提高数据源的效率。
- 该库会对数据表执行查询。
- 该库会将数据表呈现到可视化图表预期的响应中。
- 该 servlet 容器返回对可视化图表的响应。
下图对此进行了说明:
使用外部数据存储区部分介绍了如何实现这种类型的数据源。