Las cuentas se vinculan con los flujos implícitos y de código de autorización de OAuth 2.0 estándar de la industria. Tu servicio debe admitir extremos de autorización y de intercambio de tokens que cumplan con OAuth 2.0.
En el flujo implícito, Google abre el extremo de autorización en el navegador del usuario. Después de acceder correctamente, devuelves un token de acceso de larga duración a Google. Este token de acceso ahora se incluye en cada solicitud que se envía desde Google.
En el flujo de código de autorización, necesitas dos extremos:
El extremo de autorización, que presenta la IU de acceso a los usuarios que aún no accedieron El extremo de autorización también crea un código de autorización de corta duración para registrar el consentimiento de los usuarios para el acceso solicitado.
El extremo de intercambio de tokens, que es responsable de dos tipos de intercambios:
- Intercambia un código de autorización por un token de actualización de larga duración y un token de acceso de corta duración. Este intercambio se produce cuando el usuario pasa por el flujo de vinculación de cuentas.
- Intercambia un token de actualización de larga duración por un token de acceso de corta duración. Este intercambio se produce cuando Google necesita un nuevo token de acceso porque venció.
Elige un flujo de OAuth 2.0
Si bien el flujo implícito es más fácil de implementar, Google recomienda que los tokens de acceso emitidos por el flujo implícito nunca venzan. Esto se debe a que el usuario se ve obligado a volver a vincular su cuenta después de que vence un token con el flujo implícito. Si necesitas que el token venza por motivos de seguridad, te recomendamos que uses el flujo de código de autorización en su lugar.
Lineamientos de diseño
En esta sección, se describen los requisitos y las recomendaciones de diseño para la pantalla del usuario que alojas para los flujos de vinculación de OAuth. Después de que la app de Google le hace una llamada, tu plataforma le muestra al usuario una página de acceso a Google y una pantalla de consentimiento para la vinculación de cuentas. Se redirecciona al usuario a la app de Google después de que da su consentimiento para vincular las cuentas.
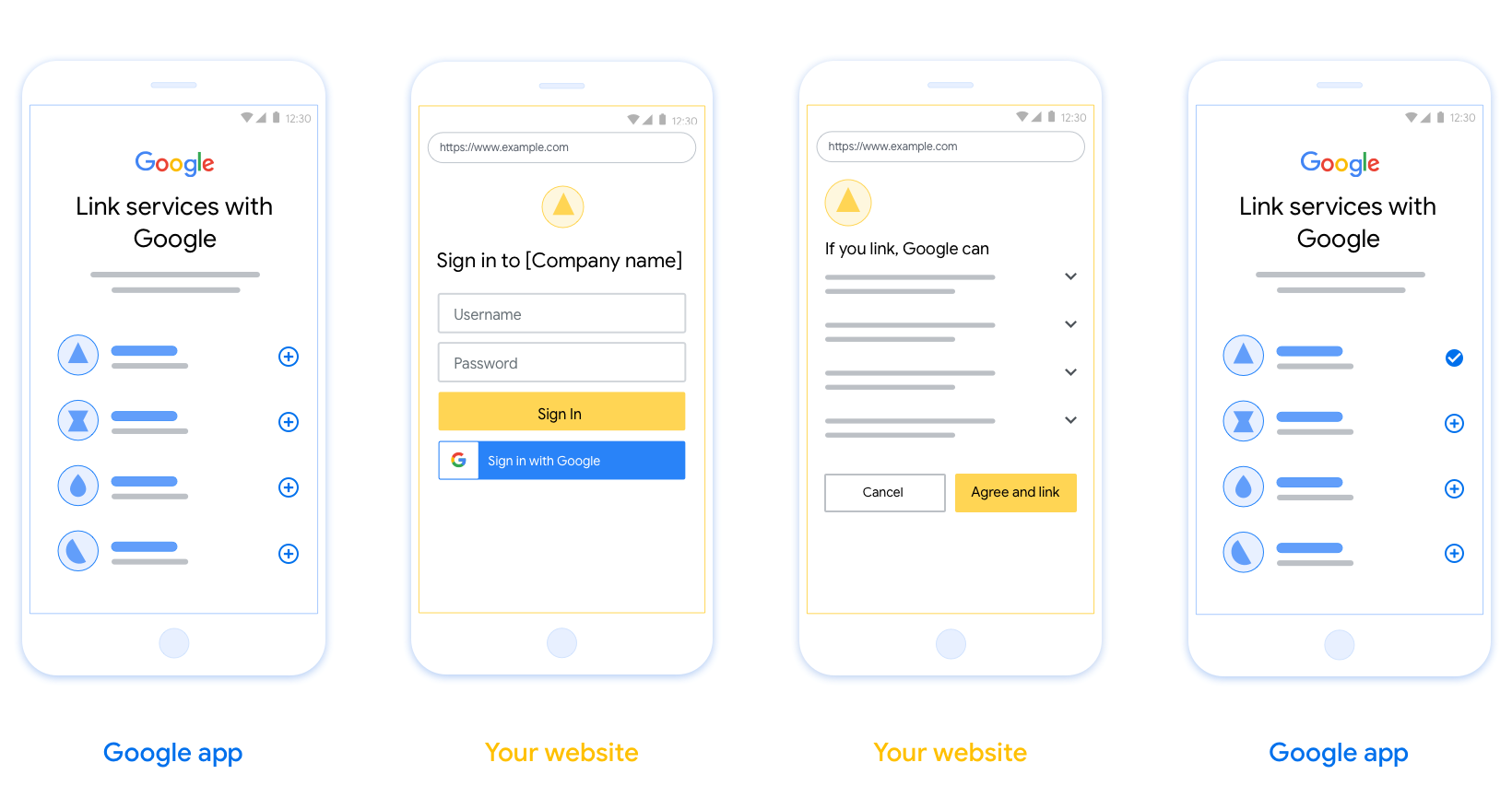
Requisitos
- Debes comunicar que la cuenta del usuario se vinculará a Google, no a un producto específico de Google, como Google Home o Asistente de Google.
Recomendaciones
Te recomendamos que hagas lo siguiente:
Mostrar la Política de Privacidad de Google Incluye un vínculo a la Política de Privacidad de Google en la pantalla de consentimiento.
Datos que se compartirán. Usa un lenguaje claro y conciso para indicarle al usuario qué datos requiere Google y por qué.
Llamado a la acción claro. Indica un llamado a la acción claro en la pantalla de consentimiento, como "Aceptar y vincular". Esto se debe a que los usuarios deben comprender qué datos deben compartir con Google para vincular sus cuentas.
Capacidad de cancelar. Proporciona una forma para que los usuarios regresen o cancelen si deciden no realizar la vinculación.
Proceso de acceso claro. Asegúrate de que los usuarios tengan un método claro para acceder a su Cuenta de Google, como campos para su nombre de usuario y contraseña, o Acceder con Google.
Capacidad de desvincular. Ofrece un mecanismo para que los usuarios se desvinculen, como una URL que dirija a la configuración de su cuenta en tu plataforma. Como alternativa, puedes incluir un vínculo a la Cuenta de Google en el que los usuarios puedan administrar su cuenta vinculada.
Capacidad de cambiar la cuenta de usuario. Sugiere un método para que los usuarios cambien de cuenta. Esto es especialmente beneficioso si los usuarios suelen tener varias cuentas.
- Si un usuario debe cerrar la pantalla de consentimiento para cambiar de cuenta, envía un error recuperable a Google para que el usuario pueda acceder a la cuenta deseada con la vinculación de OAuth y el flujo implícito.
Incluye tu logotipo. Mostrar el logotipo de tu empresa en la pantalla de consentimiento Usa tus lineamientos de estilo para colocar el logotipo. Si también deseas mostrar el logotipo de Google, consulta Logotipos y marcas comerciales.
Crea el proyecto
Para crear tu proyecto y usar la vinculación de cuentas, haz lo siguiente:
- Haz clic en Crear proyecto.
- Ingresa un nombre o acepta la sugerencia generada.
- Confirma o edita los campos restantes.
- Haz clic en Crear.
Para ver el ID de tu proyecto, haz lo siguiente:
- Busca tu proyecto en la tabla de la página de destino. El ID del proyecto aparece en la columna ID.
Configura tu pantalla de consentimiento de OAuth
El proceso de vinculación de la Cuenta de Google incluye una pantalla de consentimiento que les indica a los usuarios la aplicación que solicita acceso a sus datos, qué tipo de datos solicita y las condiciones que se aplican. Deberás configurar tu pantalla de consentimiento de OAuth antes de generar un ID de cliente de la API de Google.
- Abre la página Pantalla de consentimiento de OAuth de la consola de APIs de Google.
- Si se te solicita, selecciona el proyecto que acabas de crear.
En la página "Pantalla de consentimiento de OAuth", completa el formulario y haz clic en el botón "Guardar".
Nombre de la aplicación: Es el nombre de la aplicación que solicita el consentimiento. El nombre debe reflejar con precisión tu aplicación y ser coherente con el nombre de la aplicación que los usuarios ven en otros lugares. El nombre de la aplicación se mostrará en la pantalla de consentimiento de la vinculación de la cuenta.
Logotipo de la aplicación: Es una imagen en la pantalla de consentimiento que ayudará a los usuarios a reconocer tu app. El logotipo se muestra en la pantalla de consentimiento de vinculación de cuentas y en la configuración de la cuenta.
Correo electrónico de asistencia: Para que los usuarios se comuniquen contigo si tienen preguntas sobre su consentimiento.
Permisos para las APIs de Google: Los permisos permiten que tu aplicación acceda a los datos privados de Google de tus usuarios. En el caso de uso de la vinculación de la Cuenta de Google, el alcance predeterminado (correo electrónico, perfil, openid) es suficiente, por lo que no es necesario agregar alcances sensibles. Por lo general, se recomienda solicitar permisos de forma incremental, en el momento en que se requiere el acceso, en lugar de hacerlo por adelantado. Obtén más información.
Dominios autorizados: Para protegerte a ti y a tus usuarios, Google solo permite que las aplicaciones que se autentican con OAuth usen dominios autorizados. Los vínculos de tus aplicaciones deben alojarse en dominios autorizados. Obtén más información.
Vínculo a la página principal de la aplicación: Es la página principal de tu aplicación. Debe estar alojado en un dominio autorizado.
Vínculo a la Política de Privacidad de la aplicación: Se muestra en la pantalla de consentimiento de la vinculación de la Cuenta de Google. Debe estar alojado en un dominio autorizado.
Vínculo a las Condiciones del Servicio de la aplicación (opcional): Debe estar alojado en un dominio autorizado.
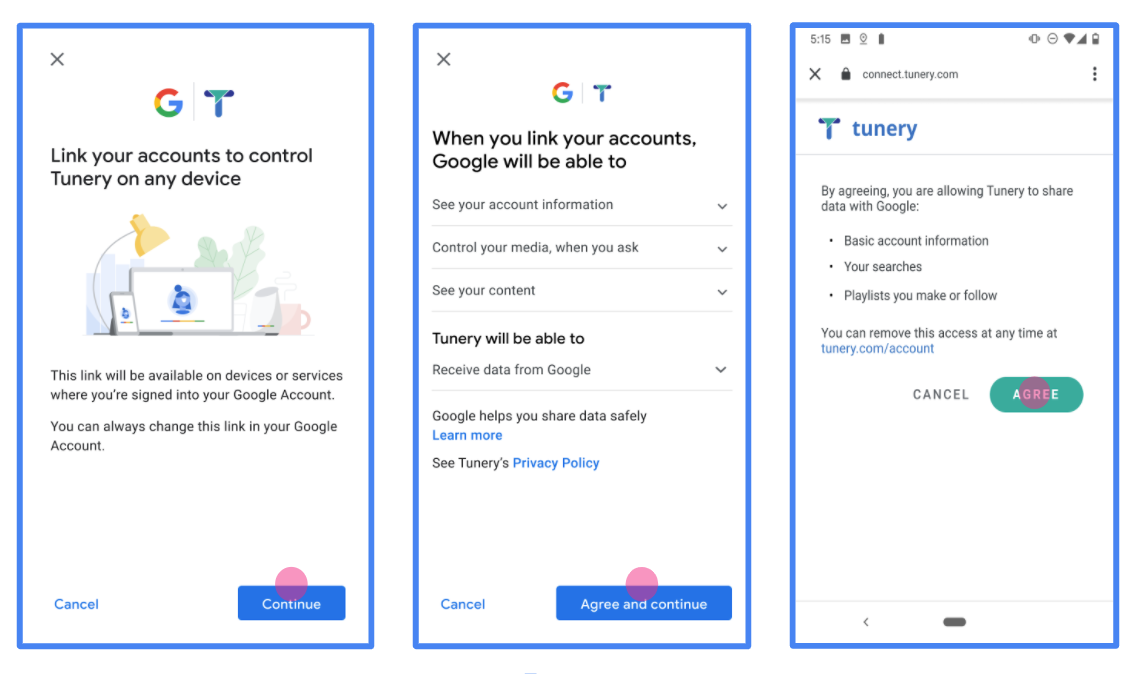
Figura 1. Pantalla de consentimiento de vinculación de la Cuenta de Google para una aplicación ficticia, Tunery
Verifica el "Estado de verificación". Si tu aplicación necesita verificación, haz clic en el botón "Enviar para verificación" para enviar tu aplicación a verificación. Consulta los requisitos de verificación de OAuth para obtener más detalles.
Implementa tu servidor de OAuth
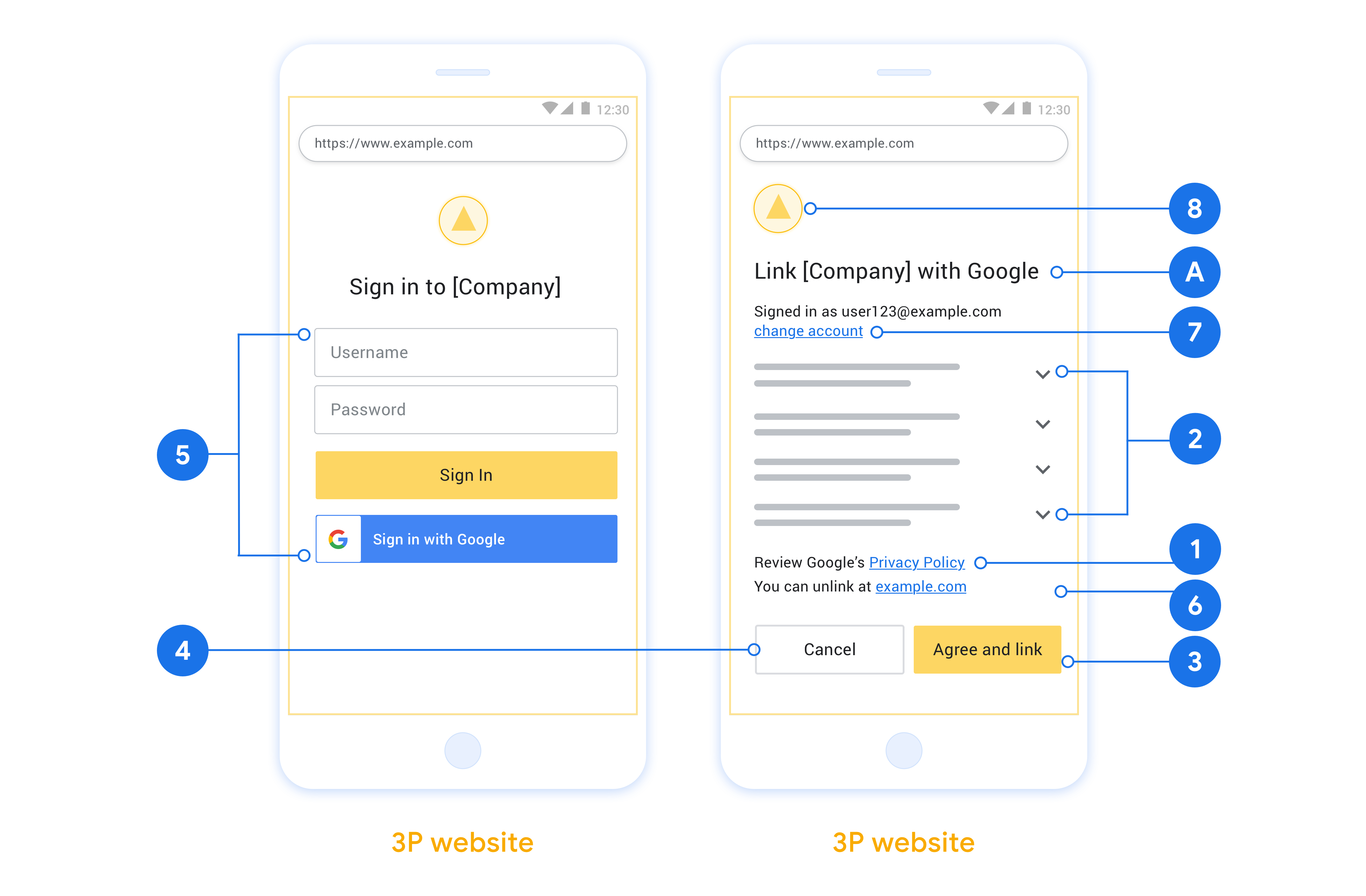
Para admitir el flujo implícito de OAuth 2.0, tu servicio hace una autorización de destino disponible a través de HTTPS. Este extremo es responsable de la autenticación y obtener el consentimiento de los usuarios para acceder a los datos. El extremo de autorización presenta una IU de acceso a los usuarios que aún no accedieron y registra el acceso solicitado.
Cuando una aplicación de Google necesita llamar a una de las APIs autorizadas de tu servicio Google usa este extremo a fin de obtener permiso de los usuarios para llamar a estas APIs por ellos.
Una sesión típica de flujo implícito de OAuth 2.0 que inicia Google tiene la siguiente flujo:
- Google abre el extremo de autorización en el navegador del usuario. El usuario accede a la cuenta, si aún no lo hizo, y le otorga permiso a Google para acceder a sus datos con tu API, si aún no han otorgado permiso.
- Tu servicio crea un token de acceso y lo devuelve a Google. Para ello, vuelve a redireccionar el navegador del usuario a Google con el permiso de acceso. token asociado a la solicitud.
- Google llama a las APIs de tu servicio y adjunta el token de acceso con cada solicitud. Tu servicio verifica que el token de acceso otorgue a Google autorización para acceder a la API y, luego, completa la llamada a la API.
Maneja solicitudes de autorización
Cuando una aplicación de Google necesita vincular cuentas mediante OAuth 2.0 implícito, Google envía al usuario a tu extremo de autorización con un que incluya los siguientes parámetros:
| Parámetros del extremo de autorización | |
|---|---|
client_id |
El ID de cliente que le asignaste a Google |
redirect_uri |
La URL a la que envías la respuesta a esta solicitud. |
state |
Un valor de contabilidad que se devuelve a Google sin modificar en el URI de redireccionamiento. |
response_type |
Es el tipo de valor que se debe mostrar en la respuesta. Para el OAuth 2.0 implícito
el tipo de respuesta siempre es token. |
user_locale |
La configuración de idioma de la Cuenta de Google en RFC5646 que se usa para localizar tu contenido en el idioma de preferencia del usuario. |
Por ejemplo, si tu extremo de autorización está disponible en
https://myservice.example.com/auth, una solicitud podría verse de la siguiente manera:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&response_type=token&user_locale=LOCALE
Para que tu extremo de autorización controle las solicitudes de acceso, haz lo siguiente pasos:
Verifica los valores
client_idyredirect_uripara evita que se otorgue acceso a apps cliente no deseadas o configuradas incorrectamente:- Confirma que
client_idcoincida con el ID de cliente que asignados a Google. - Confirma que la URL especificada por
redirect_uritiene la siguiente forma:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Confirma que
Verifica si el usuario accedió a tu servicio. Si el usuario no está firmado completa el flujo de acceso o registro del servicio.
Genera un token de acceso para que Google acceda a tu API. El el token de acceso puede ser cualquier valor de cadena, pero debe representar de forma única usuario y cliente para el que es el token y no se debe poder adivinar.
Envía una respuesta HTTP que redirecciona el navegador del usuario a la URL especificadas por el parámetro
redirect_uri. Incluye todos los siguientes parámetros en el fragmento de URL:access_token: El token de acceso que acabas de generartoken_type: Es la cadenabearer.state: Es el valor de estado sin modificar del original. solicitud
El siguiente es un ejemplo de la URL resultante:
https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID#access_token=ACCESS_TOKEN&token_type=bearer&state=STATE_STRING
El controlador de redireccionamiento de OAuth 2.0 de Google recibe el token de acceso y confirma
que el valor de state no haya cambiado. Después de que Google obtiene una
token de acceso para tu servicio, Google lo conectará a las llamadas posteriores
a tus APIs de servicio.
Controla las solicitudes userinfo
El extremo userinfo es un recurso protegido de OAuth 2.0 que muestra reclamos sobre el usuario vinculado. La implementación y el alojamiento del extremo userinfo son opcionales, excepto en los siguientes casos de uso:
- Acceso a la cuenta vinculada con Google One Tap.
- Suscripción sin inconvenientes en Android TV.
Una vez que el token de acceso se recupera correctamente del extremo del token, Google envía una solicitud al extremo userinfo para recuperar la información básica de perfil del usuario vinculado.
| Encabezados de la solicitud del extremo userinfo | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
El token de acceso del tipo portador. |
Por ejemplo, si el extremo userinfo está disponible en
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo, una solicitud podría verse de la siguiente manera:
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
Para que tu extremo userinfo controle las solicitudes, sigue estos pasos:
- Extrae el token de acceso del encabezado de autorización y muestra la información del usuario asociada con el token de acceso.
- Si el token de acceso no es válido, muestra un error HTTP 401 No autorizado con el encabezado de respuesta
WWW-Authenticate. A continuación, se muestra un ejemplo de una respuesta de error de userinfo:HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
Si el token de acceso es válido, devuelve una respuesta HTTP 200 con el siguiente objeto JSON en el cuerpo del protocolo HTTPS respuesta:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }respuesta del extremo userinfo subUn ID único que identifica al usuario en tu sistema. emailDirección de correo electrónico del usuario. given_nameOpcional: Es el nombre del usuario. family_nameOpcional: Apellido del usuario. nameOpcional: Es el nombre completo del usuario. pictureOpcional: Foto de perfil del usuario.
Cómo validar la implementación
Puedes validar tu implementación con la herramienta OAuth 2.0 Playground.
En la herramienta, sigue estos pasos:
- Haz clic en Configuración para abrir la ventana de configuración de OAuth 2.0.
- En el campo Flujo de OAuth, selecciona Del cliente.
- En el campo Extremos de OAuth, selecciona Personalizado.
- Especifica tu extremo de OAuth 2.0 y el ID de cliente que le asignaste a Google en los campos correspondientes.
- En la sección Paso 1, no selecciones ningún alcance de Google. En su lugar, deja este campo en blanco o escribe un alcance válido para tu servidor (o una cadena arbitraria si no usas permisos de OAuth). Cuando termines, haz clic en Autorizar APIs.
- En las secciones Paso 2 y Paso 3, revisa el flujo de OAuth 2.0 y verifica que cada paso funcione según lo previsto.
Puedes validar tu implementación con la herramienta de demostración de vinculación de Cuentas de Google.
En la herramienta, sigue estos pasos:
- Haz clic en el botón Acceder con Google.
- Elige la cuenta que quieres vincular.
- Ingresa el ID del servicio.
- De forma opcional, ingresa uno o más permisos para los que solicitarás acceso.
- Haz clic en Iniciar demostración.
- Cuando se te solicite, confirma que puedes dar tu consentimiento y rechazar la solicitud de vinculación.
- Confirma que se te redireccionó a tu plataforma.