등치 지역도는 데이터 값에 따라 행정 구역에 색상이 지정되거나 음영 처리되는 주제별 지도입니다. 스타일 팩토리 함수를 사용하여 각 행정 구역이 숫자 값의 범위와 연결되는 데이터를 기반으로 지도의 스타일을 지정할 수 있습니다. 다음 예시 지도는 미국의 주에 대한 등치지역도를 보여줍니다.
이 예에서 데이터는 주의 장소 ID로 구성됩니다. 스타일 팩토리 함수는 상태의 장소 ID의 해시 값을 기반으로 각 상태의 색상을 조건부로 지정합니다.
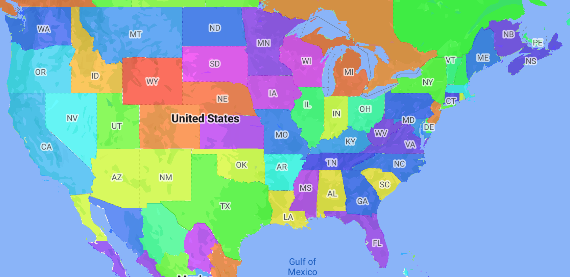
새 지도 ID와 지도 스타일을 아직 만들지 않았다면 시작하기의 단계에 따라 만드세요. 행정 구역 1단계 지형지물 레이어를 사용 설정해야 합니다.
지도가 초기화될 때 행정 구역 단위 1 지형지물 레이어에 대한 참조를 가져옵니다. 미국의 경우 이러한 행정 구역 수준은 개별 주에 해당합니다.
자바
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }스타일 팩토리 함수를 만들고 이를 행정 구역 단위 1 지형지물 레이어에 적용합니다. 다음 예에서는 미국의 각 주를 나타내는 다각형에 함수를 적용합니다.
자바
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
