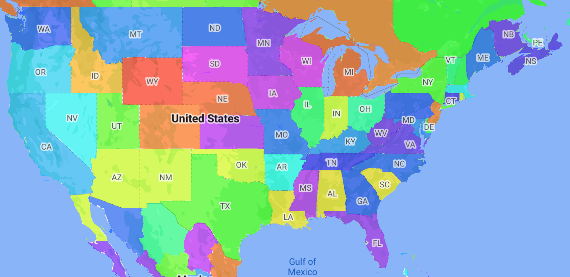
Une carte choroplèthe est un type de carte thématique dans laquelle les régions administratives sont colorées ou nuancées en fonction d'une valeur de données. Vous pouvez utiliser une fonction de fabrique de style pour styliser une carte en fonction de données où chaque région administrative est associée à une plage de valeurs numériques. L'exemple de carte suivant montre une carte choroplèthe pour les États des États-Unis.
Dans cet exemple, les données sont constituées de l'ID du lieu de l'État. La fonction de fabrique de style colore de manière conditionnelle chaque état en fonction d'une valeur hachée de l'ID de lieu de l'état.
Si ce n'est pas déjà fait, suivez les étapes de la section Commencer pour créer un ID et un style de carte. N'oubliez pas d'activer le calque d'éléments Zone administrative de niveau 1.
Obtenez une référence au calque d'éléments "Administrative Area Level 1" (Zone administrative de niveau 1) lors de l'initialisation de la carte. Pour les États-Unis, ces niveaux administratifs correspondent aux États individuels.
Java
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }Créez une fonction de fabrique de style et appliquez-la au calque d'entités "Administrative Area Level 1" (Région administrative de niveau 1). L'exemple suivant applique la fonction au polygone représentant chaque État des États-Unis.
Java
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }

