Bản đồ chuyên đề là một loại bản đồ chuyên đề trong đó các khu vực hành chính được tô màu hoặc đổ bóng theo một giá trị dữ liệu. Bạn có thể sử dụng một hàm tạo kiểu để tạo kiểu cho bản đồ dựa trên dữ liệu, trong đó mỗi khu vực hành chính được liên kết với một dải giá trị bằng số. Bản đồ ví dụ sau đây cho thấy một bản đồ chuyên đề cho các tiểu bang của Hoa Kỳ.
Trong ví dụ này, dữ liệu bao gồm mã địa điểm của tiểu bang. Hàm tạo kiểu có điều kiện tô màu từng trạng thái dựa trên giá trị băm của mã địa điểm cho trạng thái.
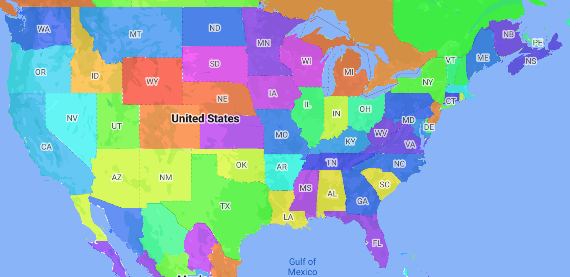
Nếu bạn chưa thực hiện, hãy làm theo các bước trong phần Bắt đầu để tạo mã bản đồ và kiểu bản đồ mới. Nhớ bật lớp đối tượng Khu vực hành chính cấp 1.
Lấy thông tin tham chiếu đến lớp đối tượng Khu vực hành chính cấp 1 khi bản đồ khởi tạo. Đối với Hoa Kỳ, các cấp hành chính này tương ứng với từng tiểu bang.
Java
private FeatureLayer areaLevel1Layer;
@Override public void onMapReady(GoogleMap map) { areaLevel1Layer = map.getFeatureLayer(new FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build());
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer(); }Kotlin
private var areaLevel1Layer: FeatureLayer? = null
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) { // Get the ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 feature layer. areaLevel1Layer = googleMap.getFeatureLayer(FeatureLayerOptions.Builder() .featureType(FeatureType.ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1) .build())
// Apply style factory function to ADMINISTRATIVE_AREA_LEVEL_1 layer. styleAreaLevel1Layer() }Tạo một hàm tạo kiểu và áp dụng hàm đó cho lớp đối tượng Khu vực hành chính cấp 1. Ví dụ sau đây áp dụng hàm cho đa giác đại diện cho từng tiểu bang của Hoa Kỳ.
Java
private void styleAreaLevel1Layer() { FeatureLayer.StyleFactory styleFactory = (Feature feature) -> { if (feature instanceof PlaceFeature) { PlaceFeature placeFeature = (PlaceFeature) feature;
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. int hueColor = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300; if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300; }
return new FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, new float[] {hueColor, 1, 1})) .build(); } return null; };
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory); }Kotlin
private fun styleAreaLevel1Layer() { val styleFactory = FeatureLayer.StyleFactory { feature: Feature -> if (feature is PlaceFeature) { val placeFeature: PlaceFeature = feature as PlaceFeature
// Return a hueColor in the range [-299,299]. If the value is // negative, add 300 to make the value positive. var hueColor: Int = placeFeature.getPlaceId().hashCode() % 300 if (hueColor < 0) { hueColor += 300 } return@StyleFactory FeatureStyle.Builder() // Set the fill color for the state based on the hashed hue color. .fillColor(Color.HSVToColor(150, floatArrayOf(hueColor.toFloat(), 1f, 1f))) .build() } return@StyleFactory null }
// Apply the style factory function to the feature layer. areaLevel1Layer?.setFeatureStyle(styleFactory) }
