Tài liệu này giải thích cách Fleet Engine bảo mật việc trao đổi thông tin giữa 3 môi trường chính của hệ thống Fleet Engine: máy chủ phụ trợ, máy chủ Fleet Engine và các ứng dụng cũng như trang web của khách hàng.
Fleet Engine quản lý tính bảo mật theo 2 cách cơ bản, dựa trên nguyên tắc về đặc quyền tối thiểu:
Thông tin xác thực mặc định của ứng dụng (ADC): Dành cho các môi trường có đặc quyền cao, chẳng hạn như giao tiếp giữa các máy chủ. Được dùng khi máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn đang tạo và quản lý xe cũng như chuyến đi trong Fleet Engine. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem phần Thông tin xác thực mặc định của ứng dụng.
Mã thông báo web JSON (JWT): Đối với các môi trường có độ tin cậy thấp như ứng dụng khách chạy trên điện thoại thông minh và trình duyệt. Được dùng để hoàn thành các thao tác có đặc quyền thấp hơn, chẳng hạn như cập nhật vị trí xe trong Fleet Engine.
Các JWT mà môi trường có độ tin cậy thấp yêu cầu được máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn tạo và phát hành để bảo vệ khoá bí mật của tài khoản dịch vụ, đồng thời bao gồm các xác nhận quyền sở hữu bổ sung dành riêng cho Fleet Engine. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem Mã thông báo web JSON.
Ví dụ: nếu bạn có một ứng dụng dành cho tài xế, thì tài xế sẽ truy cập vào dữ liệu từ Fleet Engine thông qua ứng dụng. Ứng dụng này được xác thực bằng JWT mà ứng dụng nhận được từ máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn. Các xác nhận JWT được đưa vào, cùng với vai trò tài khoản dịch vụ, sẽ xác định những phần nào trong hệ thống mà ứng dụng dành cho người lái xe có quyền truy cập và những việc mà ứng dụng đó có thể làm. Phương pháp này giới hạn quyền truy cập chỉ vào dữ liệu cần thiết để hoàn thành nhiệm vụ lái xe.
Fleet Engine sử dụng các phương pháp bảo mật này để cung cấp những thông tin sau:
Xác thực xác minh danh tính của thực thể đưa ra yêu cầu. Fleet Engine sử dụng ADC cho các môi trường có độ tin cậy cao và JWT cho các môi trường có độ tin cậy thấp.
Uỷ quyền chỉ định những tài nguyên mà một thực thể đã xác thực có quyền truy cập. Fleet Engine sử dụng tài khoản dịch vụ có vai trò IAM của Google Cloud, cộng với các xác nhận quyền sở hữu JWT để đảm bảo các thực thể đã xác thực có quyền xem hoặc thay đổi dữ liệu mà chúng đang yêu cầu.
Thiết lập bảo mật máy chủ và ứng dụng
Để bật tính năng bảo mật bằng Fleet Engine, hãy thiết lập các tài khoản và chế độ bảo mật bắt buộc trên máy chủ phụ trợ, cũng như trên các ứng dụng và trang web của khách hàng.
Sơ đồ sau đây cho thấy thông tin tổng quan về các bước thiết lập bảo mật trên máy chủ phụ trợ và ứng dụng khách của bạn.
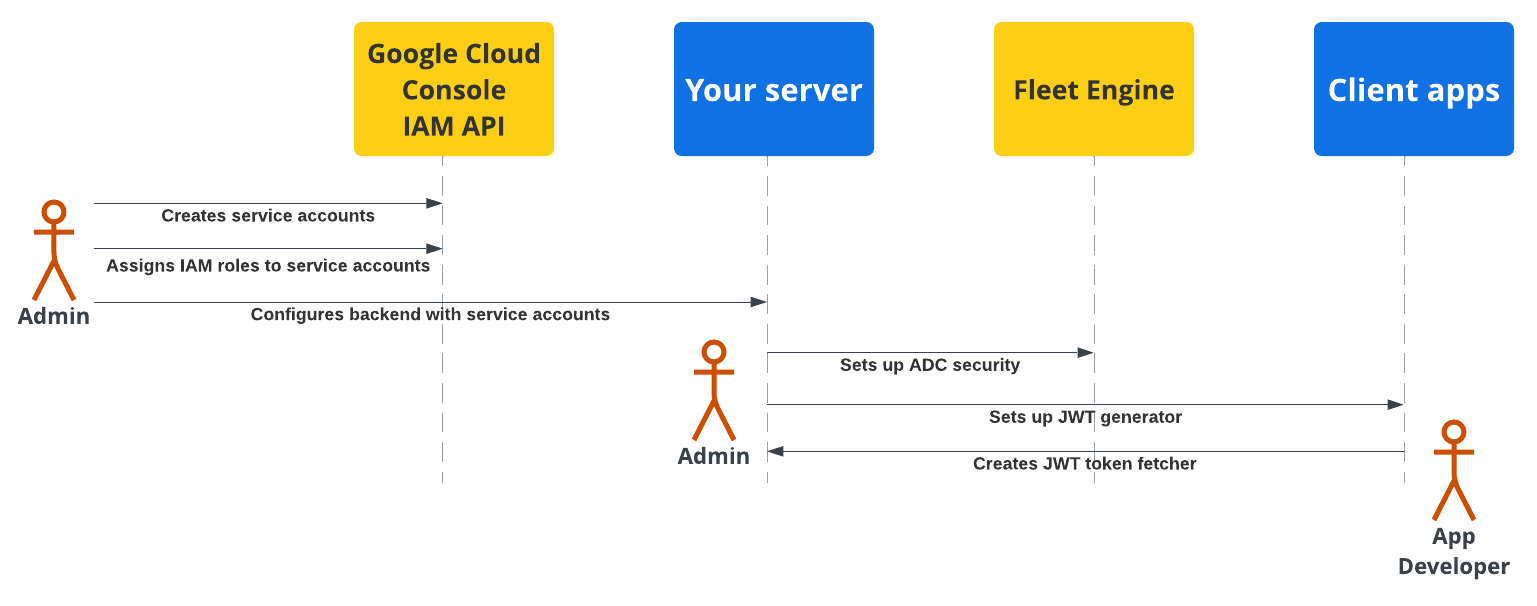
Để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem các phần sau.
Thiết lập bảo mật máy chủ phụ trợ
Quản trị viên đội xe cần làm theo các bước sau:
Tạo và định cấu hình tài khoản dịch vụ:
Trong Google Cloud Console, hãy tạo tài khoản dịch vụ.
Chỉ định các vai trò IAM cụ thể cho tài khoản dịch vụ.
Định cấu hình máy chủ phụ trợ bằng các tài khoản dịch vụ đã tạo. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem bài viết Các vai trò của tài khoản dịch vụ.
Thiết lập thông tin liên lạc an toàn với Fleet Engine (ADC): Định cấu hình phần phụ trợ để giao tiếp với phiên bản Fleet Engine bằng Thông tin đăng nhập mặc định của ứng dụng với Tài khoản dịch vụ quản trị thích hợp. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem phần Thông tin xác thực mặc định của ứng dụng.
Định cấu hình hoạt động giao tiếp an toàn với các ứng dụng khách (JWT): Tạo một trình tạo Mã thông báo Web JSON để tạo JWT có các xác nhận quyền sở hữu phù hợp cho các ứng dụng khách và trang web giám sát. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem phần Phát hành mã thông báo web JSON.
Thiết lập bảo mật ứng dụng
Nhà phát triển ứng dụng cần có cách để tìm nạp Mã thông báo web JSON do máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn tạo trong các ứng dụng hoặc trang web của ứng dụng khách, đồng thời sử dụng các mã thông báo này để giao tiếp an toàn với Fleet Engine. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem hướng dẫn thiết lập trong tài liệu Trải nghiệm của người lái xe hoặc Trải nghiệm của người tiêu dùng cho các ứng dụng bạn cần.
Luồng bảo mật ứng dụng máy chủ và ứng dụng khách
Sơ đồ trình tự sau đây minh hoạ quy trình xác thực và uỷ quyền ứng dụng máy khách và máy chủ bằng Fleet Engine bằng cách sử dụng ADC với máy chủ phụ trợ và JWT với các ứng dụng và trang web của ứng dụng.
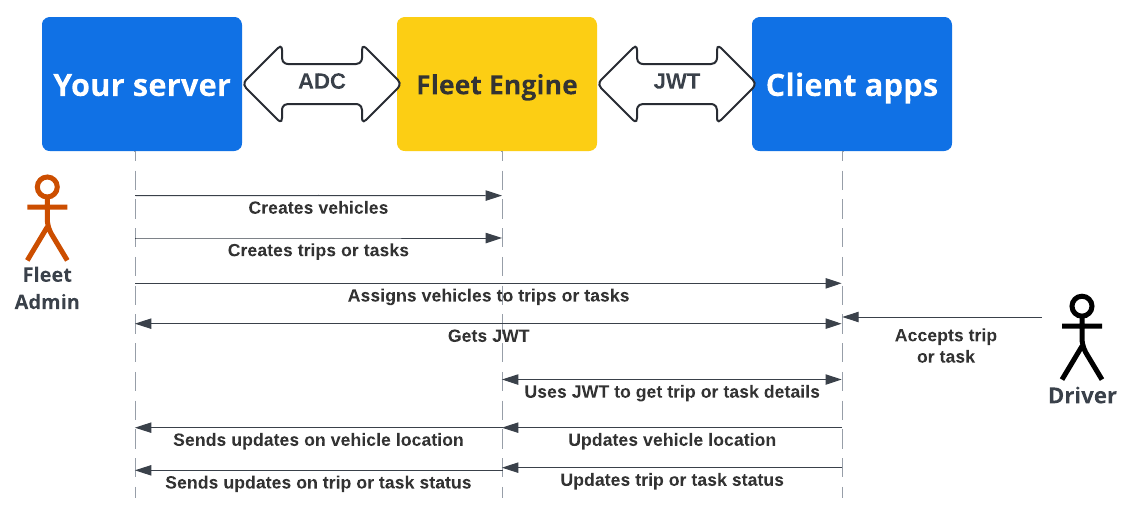
Máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn tạo các xe và chuyến đi hoặc nhiệm vụ trong Fleet Engine.
Máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn sẽ gửi một chuyến đi hoặc nhiệm vụ đến một chiếc xe: Khi hoạt động, ứng dụng dành cho người lái xe sẽ truy xuất thông tin được giao.
Máy chủ phụ trợ của bạn: Ký và phát hành JWT cho tài khoản dịch vụ tương ứng với vai trò IAM phù hợp cho nhiệm vụ hoặc chuyến đi được chỉ định.
Ứng dụng khách: Ứng dụng khách sử dụng JWT nhận được để gửi thông tin cập nhật về vị trí xe cho Fleet Engine.
Bước tiếp theo
- Tạo dự án Fleet Engine.
- Tìm hiểu cách Phát hành mã thông báo web JSON từ máy chủ của bạn.
- Tìm hiểu thêm về Các vai trò của tài khoản dịch vụ.
- Tìm hiểu thêm về JWT.
