이 섹션의 문서에서는 Google 지도 모빌리티 주문형 이동 서비스로 이동을 만들고 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 다음 사항에 익숙하다고 가정합니다.
- Fleet Engine: Fleet Engine 구현 세부정보, 요청 메커니즘, 보안에 대해 잘 알고 있어야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 Fleet Engine 서비스란 무엇인가요? 및 Fleet Engine 설정의 보안 주제를 참고하세요.
- 주문형 서비스의 차량 기본사항 차량 소개를 참고하세요.
- 주문형 서비스의 여행 기본사항 주문형 이동을 참고하세요.
사용할 TripService는 gRPC 및 REST에 사용할 수 있습니다.
간단하게 하기 위해 필드 참조는 gRPC 규칙을 따릅니다.
주문형 서비스용 Fleet Engine에서 여정은 소비자의 음식 배달 또는 차량 요청의 이행을 모델링하는 여정 유형입니다. 여정에는 여정이 진행됨에 따라 Fleet Engine에 보고하는 상태(예: NEW, ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP 등)가 있습니다. 이동 상태는 차량에 할당된 지리적 위치가 지정된 경유지에 해당하며, Fleet Engine은 사용자가 이동을 업데이트할 때마다 이러한 차량 경유지를 수정합니다. 여행과 차량의 관계에 대한 자세한 내용은 Fleet Engine 기본사항의 주문형 이동을 참고하세요.
여행 수명
Fleet Engine에서 각 여정을 추적하려면 먼저 Trip 엔티티를 만들어야 합니다. gRPC 또는 REST를 참고하세요.
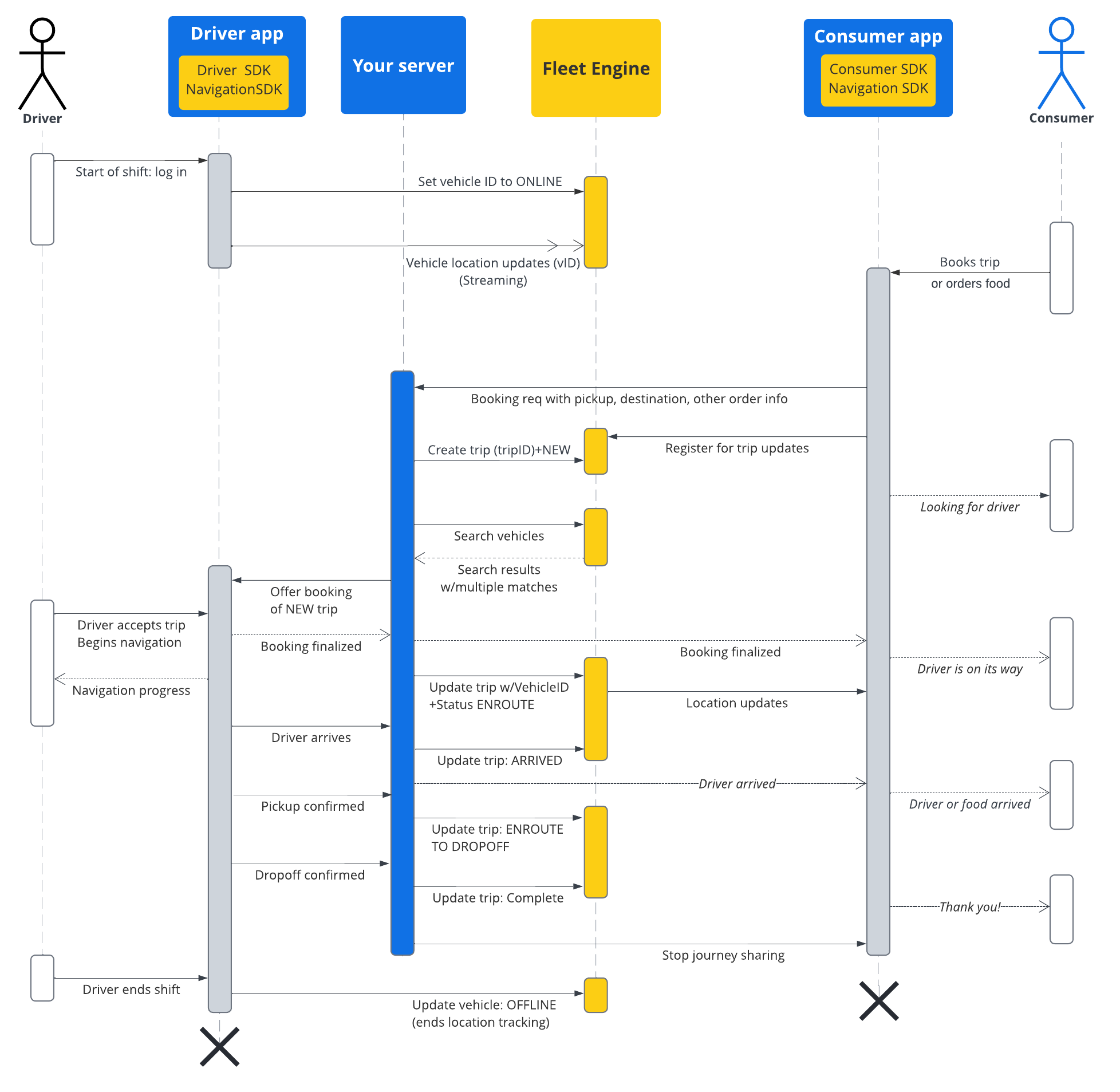
다음 표에서는 시스템에서 생성된 여정의 전체 흐름과 Fleet Engine의 수명 주기 단계를 보여줍니다. Fleet Engine을 설정했고 운전자 앱에서 위치 업데이트가 사용 설정된 차량을 여정에 할당했다고 가정합니다. Driver SDK: 주문형 이동을 참고하세요.
| 1 | 예약 요청을 받습니다. | Fleet Engine 여정이 시작되기 전에 예약 시스템은 먼저 앱이나 다른 예약 시스템을 통해 소비자로부터 차량 또는 배송 요청을 수신합니다. 그러면 시스템에서 픽업 위치와 같은 필수 필드를 사용하여 CreateTrip로 이동 항목을 만듭니다.
이 시점에서 승객 및 하차 위치와 같은 다른 필드를 설정하거나 차량이 할당될 때까지 기다릴 수도 있습니다. 단일 목적지 여행 만들기를 참고하세요. |
| 2 | 차량 할당 | 시스템 내에서 직접 차량을 여정에 할당하고 할당을 Fleet Engine에 보고하거나 차량 검색 서비스를 사용하여 차량을 검색하고 여정과 차량 속성으로 필터링하여 여정을 완료하는 데 가장 적합한 차량을 찾을 수 있습니다. 검색 반경 내에 있는 온라인 차량은 Driver SDK에서 제공하는 위치 업데이트를 통해 근접성을 알립니다.
|
| 3 | 여행 업데이트 | 운전자가 여정을 수락하고 탑승 위치로 이동하기 시작하면 시스템에서 여정 상태를 NEW에서 ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP로 업데이트합니다. 앱에서 백엔드로 직접 연결하거나, Driver SDK에서 지속적으로 차량 위치 업데이트 스트림을 수신하는 Fleet Engine을 폴링하여 여정 내내 차량 위치를 계속 폴링합니다. 그러면 시스템에서 각 여정 주요 지점을 Fleet Engine에 보고하고 Fleet Engine은 이에 따라 차량의 경유지 목록을 업데이트합니다.
|
| 4 | 소비자와 여정 공유 | Fleet Engine은 경로 세부정보와 차량 위치를 Consumer SDK에서 사용할 수 있도록 합니다. Consumer SDK는 리스너를 사용하여 경로 업데이트를 수신하고 이를 소비자 앱에 표시합니다. Fleet Engine은 예상 도착 시간, 남은 거리, 경로, 남은 차량 경유지를 자동으로 업데이트합니다. 자세한 내용은 주문형 이동의 여정 공유를 참고하세요. |
| 5 | 여행 완료 | 차량이 여정의 목적지 경유지에 도착하고 운전자가 여정이 완료되었다고 표시하면 시스템에서 Fleet Engine의 TripStatus을 COMPLETE로 설정합니다. 차량과 마찬가지로 이동 엔티티는 상태와 관계없이 Fleet Engine 내에서 7일 동안 활성 상태로 유지되며, 그 후 삭제됩니다. |
여행 시퀀스 흐름
다음 다이어그램은 이 흐름을 더 자세히 보여줍니다.