Bu bölümdeki belgelerde, Google Haritalar Mobility on-demand geziler hizmetini kullanarak gezileri nasıl oluşturacağınız ve bunlarla nasıl çalışacağınız gösterilmektedir. Aşağıdaki konular hakkında bilgi sahibi olduğunuz varsayılır:
- Fleet Engine: Fleet Engine'in uygulanmasıyla ilgili ayrıntılar, istek mekanizmaları ve güvenlik hakkında bilgi sahibi olmanız gerekir. Bu konuda bilgi edinmek için Fleet Engine hizmeti nedir? başlıklı makaleyi ve Fleet Engine'i ayarlama bölümündeki güvenlik konularını inceleyin.
- İsteğe bağlı hizmetler için araçlarla ilgili temel bilgiler. Araçlara giriş başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
- İsteğe bağlı hizmetler için seyahatle ilgili temel bilgiler. Talep üzerine yolculuklar başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Kullanacağınız TripService, gRPC ve REST için kullanılabilir.
Kolaylık sağlamak için alan referansları gRPC kuralına uygundur.
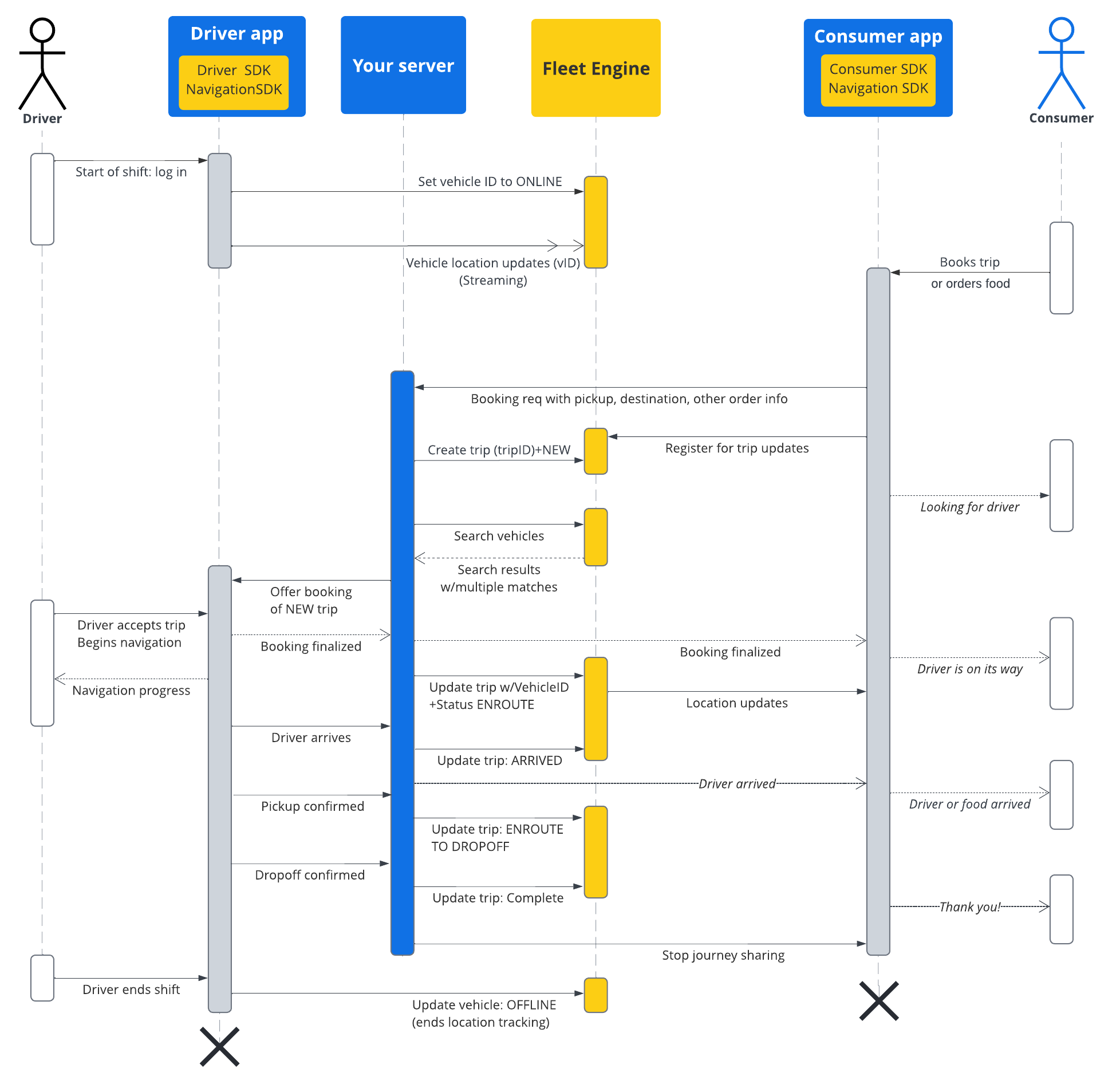
Talep üzerine hizmetler için Fleet Engine'de yolculuk, tüketicilerinizden gelen yemek teslimatı veya yolculuk isteğinin karşılanmasını modelleyen bir tür seyahattir. Bir yolculuğun, yolculuk ilerledikçe Fleet Engine'e bildirdiğiniz bir durumu vardır. Örneğin, NEW, ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP ve daha fazlası. Seyahat durumu, araca atanan coğrafi konumlu yol noktalarına karşılık gelir ve Fleet Engine, yaptığınız her seyahat güncellemesiyle bu araç yol noktalarını değiştirir. Geziler ve araçlarla ilişkileri hakkında daha fazla bilgi için Fleet
Engine Essentials'daki İsteğe bağlı geziler bölümüne bakın.
Gezinin ömrü
Fleet Engine'deki her yolculuğu izlemek için öncelikle bir Trip
oluşturmanız gerekir. Referans için gRPC veya REST'e bakın.
Aşağıdaki tabloda, sisteminizde oluşturulan bir seyahatin uçtan uca akışına ve Fleet Engine'deki yaşam döngüsü aşamalarına dair bir örnek açıklanmaktadır. Fleet Engine'i ayarladığınız ve sürücü uygulamasında konum güncellemeleri etkinleştirilmiş olarak geziye atayacağınız bir aracınız olduğu varsayılır. Driver SDK: Talep üzerine geziler başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
| 1 | Rezervasyon isteği alma | Bir Fleet Engine yolculuğu başlamadan önce, rezervasyon sisteminiz ilk olarak uygulamanız veya başka bir rezervasyon sistemi aracılığıyla tüketiciden yolculuk ya da teslimat isteği alır. Sisteminiz daha sonra CreateTrip ile yolculuk öğesini oluşturur. Bu öğe, teslim alma konumu gibi gerekli alanları içerir.
Bu noktada yolcular ve bırakma konumu gibi diğer alanları da ayarlayabilir veya bir araç atanana kadar bekleyebilir. Tek varış noktalı gezi oluşturma başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin. |
| 2 | Aracı atayın. | Araçları doğrudan sisteminizde gezilere atayabilir ve atamayı Fleet Engine'e bildirebilirsiniz. Alternatif olarak, Search Vehicle hizmetini kullanarak araç arayabilir, yolculuğu tamamlamak için en uygun aracı bulmak üzere hem geziye hem de araç özelliklerine göre filtreleme yapabilirsiniz. Arama yarıçapınızdaki tüm online araçlar, Driver SDK'sı tarafından sağlanan konum güncellemeleri aracılığıyla yakınlıklarını bildirir.
|
| 3 | Gezinizi güncelleyin. | Sürücü yolculuğu kabul edip yolcu alma konumuna gitmek için navigasyonu başlattığında sisteminiz yolculuk durumunu NEW'dan ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP'ye günceller. Uygulamadan arka uçunuza doğrudan bağlantı kurarak veya Driver SDK'sından sürekli olarak araç konumu güncellemeleri alan Fleet Engine'i yoklayarak yolculuk boyunca araç konumunu yoklamaya devam edersiniz. Sisteminiz daha sonra yolculuğun her aşamasını Fleet Engine'e bildirir. Fleet Engine de aracın yol noktası listesini buna göre günceller.
|
| 4 | Yolculuğu tüketiciyle paylaşın. | Fleet Engine, gezi ayrıntılarını ve araç konumunu Consumer SDK'da kullanılabilir hale getirir. Consumer SDK, gezi güncellemelerini almak ve bunları tüketici uygulamasında göstermek için bir dinleyici kullanır. Fleet Engine, tahmini varış zamanını, kalan mesafeyi, rotaları ve kalan araç yol noktalarını otomatik olarak günceller. Daha fazla bilgi için Talep üzerine yolculuklarda yolculukları paylaşma başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin. |
| 5 | Yolculuğu tamamlayın. | Araç, yolculuğun hedef ara noktasına ulaştığında ve sürücünüz yolculuğun başarılı olduğunu belirttiğinde sisteminiz, Fleet Engine'de TripStatus durumunu COMPLETE olarak ayarlar. Araçlar gibi, gezi öğelerinin de durumdan bağımsız olarak 7 gün boyunca Fleet Engine'de etkin kalacağını ve bu sürenin sonunda kaldırılacağını unutmayın. |
Seyahat sırası akışı
Aşağıdaki şemada bu akışın daha ayrıntılı bir görünümü gösterilmektedir.