เอกสารในส่วนนี้แสดงวิธีสร้างและจัดการการเดินทางโดยใช้บริการการเดินทางแบบออนดีมานด์ของ Google Maps โดยผู้ใช้ควรมีความคุ้นเคยกับสิ่งต่อไปนี้
- Fleet Engine: คุณควรคุ้นเคยกับรายละเอียดการติดตั้งใช้งาน Fleet Engine กลไกคำขอ และความปลอดภัย โปรดดูบริการ Fleet Engine คืออะไรและหัวข้อความปลอดภัยในตั้งค่า Fleet Engine
- ข้อมูลพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับยานพาหนะสำหรับบริการตามความต้องการ ดูข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับยานพาหนะ
- ข้อมูลพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับการเดินทางสำหรับบริการตามความต้องการ ดูการเดินทางตามต้องการ
TripServiceที่คุณจะใช้พร้อมให้บริการสำหรับ gRPC และ REST
เพื่อความสะดวก การอ้างอิงฟิลด์จะเป็นไปตามรูปแบบ gRPC
ใน Fleet Engine สำหรับบริการแบบออนดีมานด์ การเดินทางคือการเดินทางประเภทหนึ่งที่จำลอง
การดำเนินการตามคำขอการนำส่งอาหารหรือคำขอเรียกรถจากผู้บริโภค การเดินทาง
มีสถานะที่คุณรายงานไปยัง Fleet Engine เมื่อการเดินทางเปลี่ยนแปลงไป เช่น
NEW, ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP และอื่นๆ สถานะการเดินทางจะสอดคล้องกับจุดอ้างอิงที่ระบุตำแหน่งทางภูมิศาสตร์
ซึ่งกำหนดให้กับยานพาหนะ และ Fleet Engine จะแก้ไขจุดอ้างอิงของยานพาหนะเหล่านี้
เมื่อคุณอัปเดตการเดินทางแต่ละครั้ง ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเดินทางและความสัมพันธ์กับการเดินทางกับยานพาหนะได้ที่การเดินทางตามคำขอในข้อมูลสำคัญเกี่ยวกับ Fleet Engine
อายุการใช้งานของการเดินทาง
หากต้องการติดตามการเดินทางแต่ละครั้งใน Fleet Engine คุณต้องสร้างเอนทิตี Trip
ก่อน ดูข้อมูลอ้างอิงได้ที่ gRPC หรือ REST
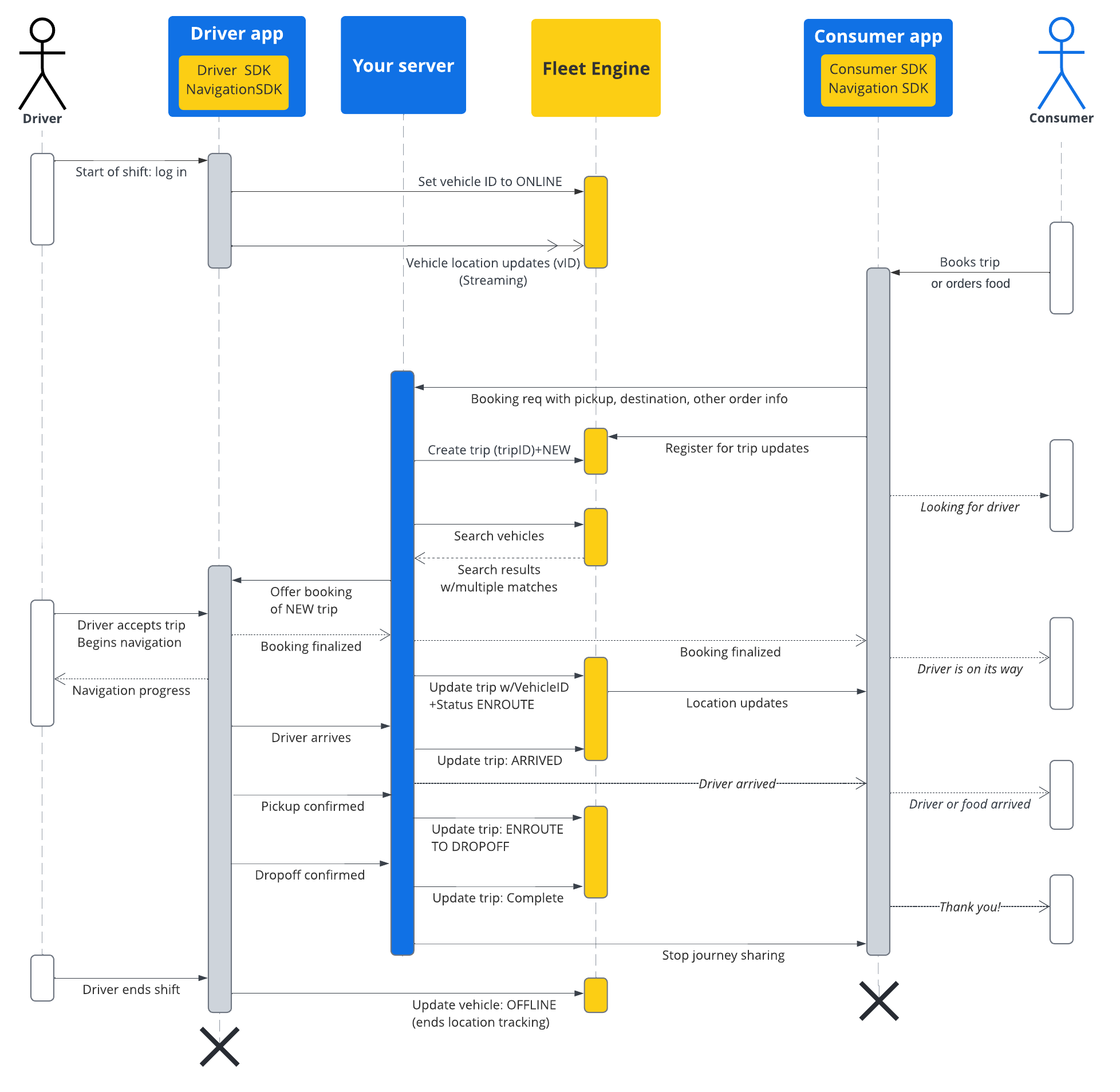
ตารางต่อไปนี้อธิบายตัวอย่างโฟลว์การเดินทางแบบครบวงจรที่สร้างขึ้นใน ระบบของคุณและขั้นตอนวงจรการใช้งานใน Fleet Engine โดยจะถือว่าคุณได้ตั้งค่า Fleet Engine และมีรถที่จะกำหนดให้กับการเดินทาง รวมถึงได้เปิดใช้การอัปเดตตำแหน่ง ในแอปคนขับแล้ว โปรดดู Driver SDK: การเดินทางแบบออนดีมานด์
| 1 | รับคำขอจอง | ก่อนที่การเดินทางของ Fleet Engine จะเริ่มขึ้น ระบบการจองของคุณจะได้รับคำขอการเดินทางหรือการนำส่งจากผู้บริโภคผ่านแอปหรือระบบการจองอื่นๆ ก่อน
จากนั้นระบบจะสร้างเอนทิตีการเดินทางโดยใช้
CreateTrip พร้อมฟิลด์ที่จำเป็น เช่น สถานที่รับ
นอกจากนี้ ยังตั้งค่าฟิลด์อื่นๆ ได้ในตอนนี้ เช่น ผู้โดยสารและ
สถานที่ส่ง หรือรอจนกว่าจะมีการกำหนดรถ ดูหัวข้อ
สร้างการเดินทางแบบมีจุดหมายเดียว |
| 2 | มอบหมายยานพาหนะ | คุณจะกำหนดรถให้กับการเดินทางโดยตรงภายในระบบ และรายงานการกำหนดไปยัง Fleet Engine หรือจะใช้บริการค้นหารถ เพื่อค้นหารถ โดยกรองตามทั้งการเดินทางและรถ เพื่อค้นหารถที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับการเดินทางก็ได้ ยานพาหนะออนไลน์ ที่อยู่ภายในรัศมีการค้นหาจะแจ้งให้ทราบถึงระยะใกล้ผ่าน การอัปเดตตำแหน่งที่ได้รับจาก Driver SDK เมื่อ |
| 3 | อัปเดตการเดินทาง | เมื่อคนขับยอมรับการเดินทางและเริ่มนำทางไปยัง
จุดรับ ระบบจะอัปเดตสถานะการเดินทางจาก NEW
เป็น ENROUTE_TO_PICKUP คุณจะยังคงสำรวจตำแหน่งของยานพาหนะตลอดการเดินทาง ไม่ว่าจะผ่านการเชื่อมต่อโดยตรงจากแอปไปยังแบ็กเอนด์ หรือโดยการสำรวจ Fleet Engine ซึ่งจะได้รับสตรีมการอัปเดตตำแหน่งของยานพาหนะอย่างต่อเนื่องจาก Driver SDK จากนั้น
ระบบจะรายงานเหตุการณ์สำคัญของแต่ละการเดินทางไปยัง Fleet Engine ซึ่งจะอัปเดต
รายการจุดแวะพักของยานพาหนะตามนั้น
|
| 4 | แชร์เส้นทางกับผู้บริโภค | Fleet Engine จะทำให้รายละเอียดการเดินทางและตำแหน่งของยานพาหนะพร้อมใช้งานใน Consumer SDK ซึ่งใช้ Listener เพื่อรับการอัปเดตการเดินทางและแสดงการอัปเดต ในแอปสำหรับผู้บริโภค Fleet Engine จะอัปเดตเวลาถึงโดยประมาณ ระยะทางที่เหลือ เส้นทาง และจุดแวะพักที่เหลือของยานพาหนะโดยอัตโนมัติ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่แชร์การเดินทางสำหรับการเดินทางแบบออนดีมานด์ |
| 5 | การเดินทางเสร็จสมบูรณ์ | เมื่อยานพาหนะถึงจุดอ้างอิงปลายทางของการเดินทางและคนขับระบุว่าการเดินทางสำเร็จ ระบบจะตั้งค่า TripStatus เป็น COMPLETE ใน Fleet Engine โปรดทราบว่าเอนทิตีการเดินทางจะยังคงใช้งานได้ภายใน Fleet Engine เป็นเวลา 7 วันไม่ว่าสถานะจะเป็นอย่างไร จากนั้นระบบจะนำเอนทิตีออก |
ขั้นตอนการเดินทาง
แผนภาพต่อไปนี้แสดงมุมมองที่ละเอียดยิ่งขึ้นของโฟลว์นี้