Cette section explique comment utiliser le SDK Navigation avec la bibliothèque d'applications Android for Cars pour afficher l'expérience de navigation de votre application sur des unités centrales intégrées. Si le système embarqué d'un utilisateur est compatible avec Android Auto, il lui suffit d'y connecter son téléphone pour pouvoir utiliser votre application directement sur l'écran de sa voiture. Les instructions vocales sont également diffusées sur les haut-parleurs de la voiture.
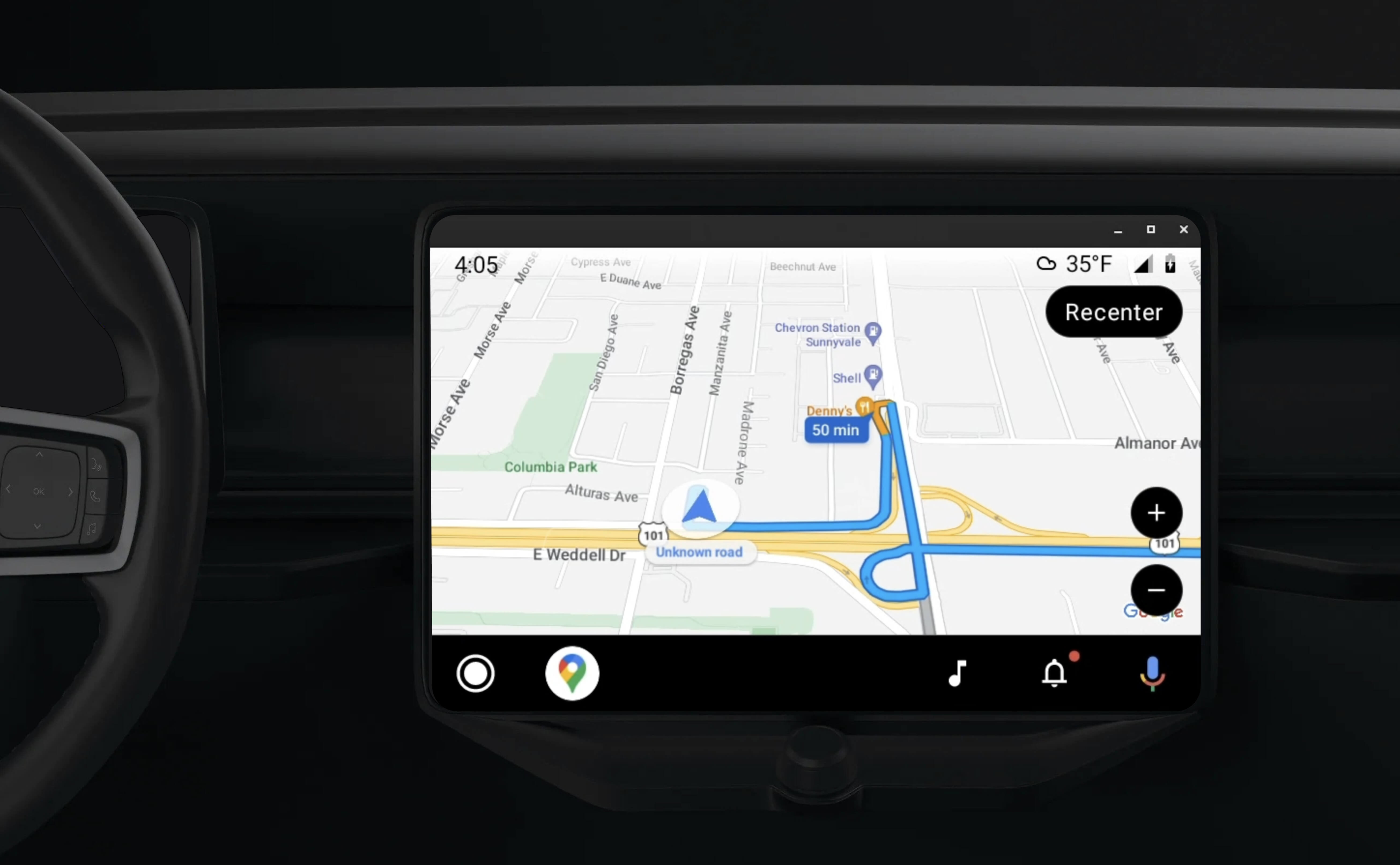
La bibliothèque d'applications Android for Cars permet aux applications Android de s'exécuter sur Android Auto en fournissant un ensemble de modèles visuels approuvés pour la sécurité des conducteurs. Ces modèles limitent volontairement les commandes de l'interface utilisateur du tableau de bord par rapport à celles du téléphone afin de réduire la distraction du conducteur.
Lorsque vous activez votre application basée sur le SDK Navigation pour qu'elle fonctionne avec Android Auto, vous fournissez une vue supplémentaire pour l'expérience de navigation.
Cela permet d'afficher deux vues de carte : une pour le téléphone et une pour l'unité principale. Les deux affichages reçoivent des conseils de Navigator.java, qui est un singleton.
Le système intégré au tableau de bord affiche les éléments interactifs approuvés en termes de sécurité afin que l'utilisateur puisse se rendre à destination en toute sécurité, sans être trop distrait. L'utilisateur peut également interagir avec les fonctionnalités spécifiques à votre application, par exemple en acceptant ou en refusant des commandes, ou en affichant la position du client sur une carte. Les mises à jour de l'état des commandes peuvent également s'afficher dans l'unité du tableau de bord.
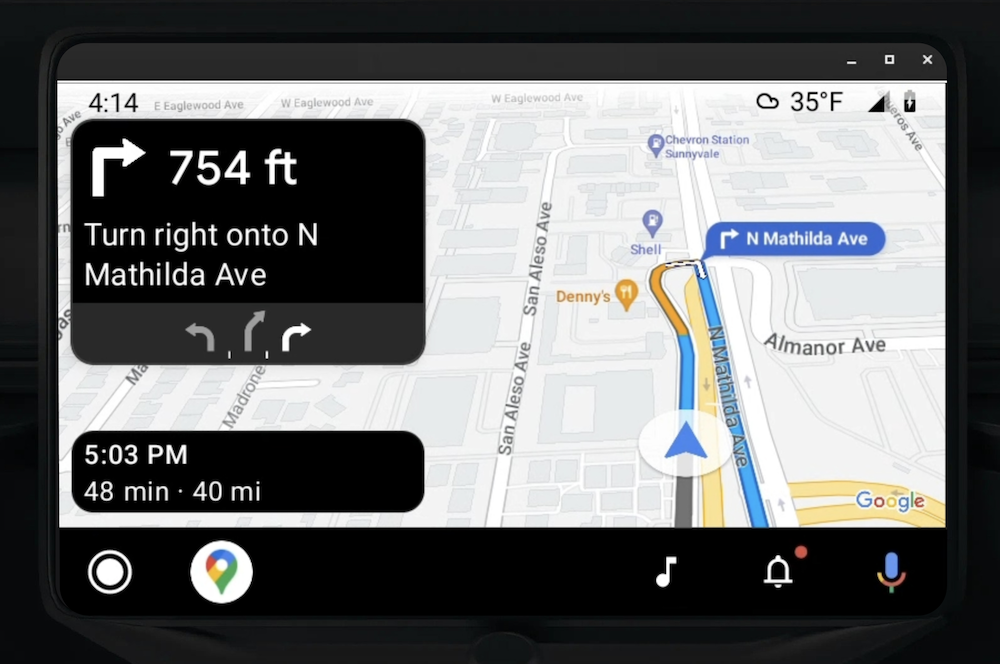
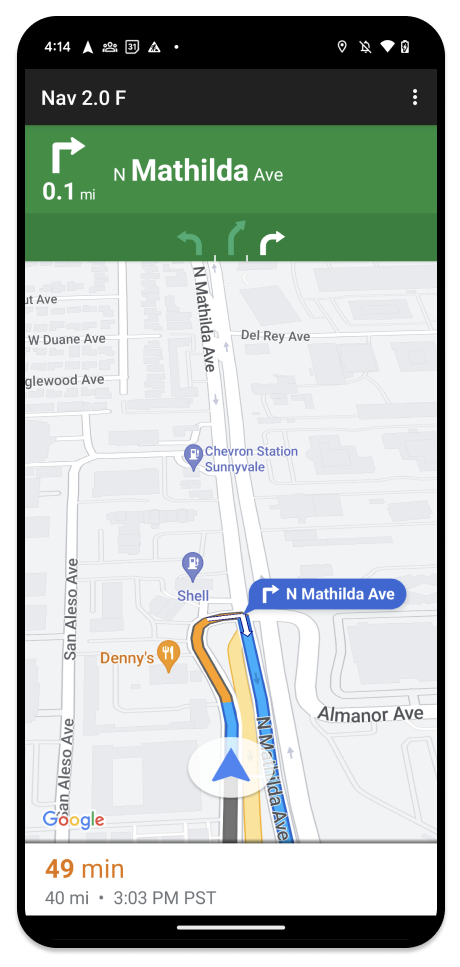
Le téléphone associé peut continuer à afficher l'expérience standard du SDK Navigation ou toute autre vue ou workflow de votre application. Cette fonctionnalité vous permet de continuer à fournir des fonctionnalités personnalisées qui ne fonctionnent pas bien sur un écran de voiture.
Configurer
Pour que votre application fonctionne avec Android Auto, vous devez d'abord configurer un service automobile avec Android Auto, puis activer la bibliothèque TurnByTurn dans votre application Navigation SDK.
Premiers pas avec Android Auto
Avant de commencer à utiliser les fonctionnalités du SDK Navigation conçues pour fonctionner avec Android Auto, vous devez configurer un service automobile pour votre application afin qu'Android Auto puisse le détecter.
Suivez ces étapes, que vous trouverez toutes dans la documentation pour les développeurs Android for Cars :
- Familiarisez-vous avec les fonctionnalités de base d'Android Auto.
- Installez la bibliothèque d'applications Android for Cars.
- Configurez le fichier manifeste de votre application pour inclure Android Auto.
- Déclarez un niveau d'application automobile minimal de 1 dans votre fichier manifeste.
- Créez votre
CarAppServiceet votre session.
Configurer le SDK Navigation
Une fois que vous avez établi votre service d'application automobile, vous êtes prêt à utiliser le SDK Navigation.
- Configurez votre projet si vous n'avez pas encore intégré le SDK Navigation à votre application.
- Activez le flux de guidage TurnbyTurn pour votre application.
- Facultatif. Utilisez les icônes générées à partir du SDK Navigation.
- Dessinez la carte à l'aide de la classe
NavigationViewForAutosur la surface Android Auto fournie dans la classeScreen. - Remplissez le modèle de navigation Android Auto avec les données de la bibliothèque TurnbyTurn.
Maintenant que vous avez enregistré un service pour fournir des informations de navigation à votre application et que votre application peut se connecter à Android Auto, vous êtes prêt à créer le reste des éléments de navigation nécessaires au bon fonctionnement de votre application avec Android Auto :
- Dessiner l'UI de la carte et de la navigation
- Activer l'interaction avec la carte
- Afficher un itinéraire de navigation
- S'assurer que les types de manœuvre sont corrects
Dessiner l'UI de la carte et de la navigation
La classe NavigationViewForAuto affiche une carte et une UI de navigation sur les écrans Android Auto. Il offre les mêmes fonctionnalités que NavigationView pour les téléphones, mais avec une interactivité limitée. Utilisez NavigationViewForAuto pour dessiner sur la Surface fournie par Android Auto :
private boolean isSurfaceReady(SurfaceContainer surfaceContainer) {
return surfaceContainer.getSurface() != null
&& surfaceContainer.getDpi() != 0
&& surfaceContainer.getHeight() != 0
&& surfaceContainer.getWidth() != 0;
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceAvailable(@NonNull SurfaceContainer surfaceContainer) {
if (!isSurfaceReady(surfaceContainer)) {
return;
}
virtualDisplay =
getCarContext()
.getSystemService(DisplayManager.class)
.createVirtualDisplay(
VIRTUAL_DISPLAY_NAME,
surfaceContainer.getWidth(),
surfaceContainer.getHeight(),
surfaceContainer.getDpi(),
surfaceContainer.getSurface(),
DisplayManager.VIRTUAL_DISPLAY_FLAG_OWN_CONTENT_ONLY);
presentation = new Presentation(getCarContext(), virtualDisplay.getDisplay());
navigationView = new NavigationViewForAuto(getCarContext());
navigationView.onCreate(null);
navigationView.onStart();
navigationView.onResume();
presentation.setContentView(navigationView);
presentation.show();
navigationView.getMapAsync(googleMap -> this.googleMap = googleMap);
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceDestroyed(@NonNull SurfaceContainer surfaceContainer) {
navigationView.onPause();
navigationView.onStop();
navigationView.onDestroy();
presentation.dismiss();
virtualDisplay.release();
}
Activer l'interaction avec la carte
Pour la sécurité du conducteur, Android Auto limite l'interaction avec la surface de l'écran à une série de méthodes SurfaceCallback. Utilisez ces rappels pour permettre une interaction limitée du conducteur avec la carte sur un écran intégré. Par exemple, onClick et onScale correspondent aux gestes appuyer et pincer de l'utilisateur. Les rappels d'interactivité doivent utiliser la bande d'actions de la carte comme suit :
Pour recevoir des rappels d'interactivité sur la carte, votre application doit utiliser un bouton Action.PAN.
Pour prendre en charge d'autres actions utilisateur, ajoutez des boutons à la bande d'actions de la carte.
Activer les rappels de surface
@NonNull
@Override
public Template onGetTemplate() {
return new NavigationTemplate.Builder()
.setActionStrip(new ActionStrip.Builder().build())
.setMapActionStrip(new ActionStrip.Builder().addAction(Action.PAN).build())
.build();
}
Zoomer en pinçant
@Override
public void onScale(float focusX, float focusY, float scaleFactor) {
CameraUpdate update =
CameraUpdateFactory.zoomBy((scaleFactor - 1),
new Point((int) focusX, (int) focusY));
googleMap.animateCamera(update); // map is set in onSurfaceAvailable.
}
Panoramique
@Override
public void onScroll(float distanceX, float distanceY) {
googleMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.scrollBy(distanceX, distanceY));
}
Afficher l'itinéraire de navigation
Cette section explique comment configurer un observateur pour les posts de navigation et comment remplir les instructions de navigation dans le modèle de carte de direction.
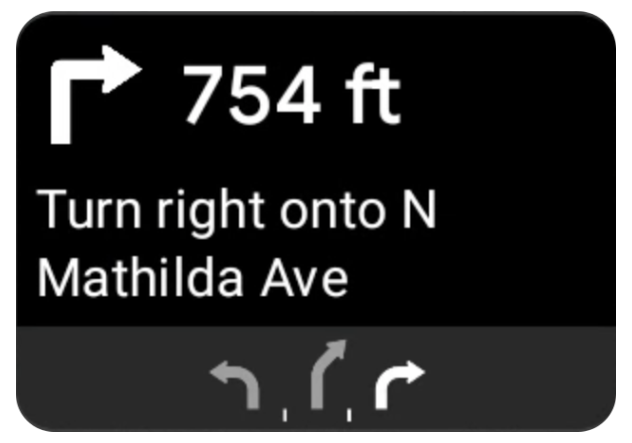
Le modèle de navigation Android Auto fournit une carte d'itinéraire qui affiche des informations de navigation liées au trajet en cours. La bibliothèque TurnByTurn du SDK Navigation fournit ces informations de navigation, que votre code utilise pour remplir le modèle de navigation Android Auto.
Configurer un observateur
Dans l'exemple suivant, SampleApplication est une classe d'application personnalisée qui gère un objet MutableLiveData<NavInfo>. Lorsque l'observateur reçoit une mise à jour de l'objet navigateur, il publie cet objet NavInfo dans le NavInfoMutableLiveData géré par la classe SampleApplication.
L'exemple suivant enregistre un observateur pour cet objet dans son implémentation de l'écran Android Auto.
public SampleAndroidAutoNavigationScreen(@NonNull CarContext carContext,
SampleApplication application) {
super(carContext);
getCarContext().getCarService(AppManager.class).setSurfaceCallback(this);
application.getNavInfoMutableLiveData().observe(this, this::processNextStep);
}
Renseigner les informations de navigation
L'extrait de code suivant montre comment remplir le modèle Android Auto avec les informations de routage actuelles, y compris les étapes, les distances et les icônes. Pour en savoir plus sur ces éléments d'affichage, consultez Remplir l'affichage du flux.
Développez pour voir l'exemple de code.
private RoutingInfo currentRoutingInfo; @NonNull @Override public Template onGetTemplate() { NavigationTemplate.Builder navigationTemplateBuilder = new NavigationTemplate.Builder() .setActionStrip(...) .setMapActionStrip(...) if (currentRoutingInfo != null) { navigationTemplateBuilder.setNavigationInfo(currentRoutingInfo); } return navigationTemplateBuilder.build(); } private void processNextStep(NavInfo navInfo) { if (navInfo == null || navinfo.getCurrentStep() == null) { return; } /** * Converts data received from the Navigation data feed * into Android-Auto compatible data structures. For more information * see the "Ensure correct maneuver types" below. */ Step currentStep = buildStepFromStepInfo(navInfo.getCurrentStep()); Distance distanceToStep = buildDistanceFromMeters(navInfo.getDistanceToCurrentStepMeters()); currentRoutingInfo = new RoutingInfo.Builder().setCurrentStep(currentStep, distanceToStep).build(); // Invalidate the current template which leads to another onGetTemplate call. invalidate(); } private Step buildStepFromStepInfo(StepInfo stepInfo) { IconCompat maneuverIcon = IconCompat.createWithBitmap(stepInfo.getManeuverBitmap()); Maneuver.Builder maneuverBuilder = newManeuver.Builder( ManeuverConverter .getAndroidAutoManeuverType(stepInfo.getManeuver())); CarIcon maneuverCarIcon = new CarIcon.Builder(maneuverIcon).build(); maneuverBuilder.setIcon(maneuverCarIcon); Step.Builder stepBuilder = new Step.Builder() .setRoad(stepInfo.getFullRoadName()) .setCue(stepInfo.getFullInstructionText()) .setManeuver(maneuverBuilder.build()); if (stepInfo.getLanes() != null && stepInfo.getLanesBitmap() != null) { for (Lane lane : buildAndroidAutoLanesFromStep(stepInfo)) { stepBuilder.addLane(lane); } IconCompat lanesIcon = IconCompat.createWithBitmap(stepInfo.getLanesBitmap()); CarIcon lanesImage = new CarIcon.Builder(lanesIcon).build(); stepBuilder.setLanesImage(lanesImage); } return stepBuilder.build(); } /* * Constructs a {@code Distance} object in imperial measurement units. * In a real world scenario, units would be based on locale. */ private Distance buildDistanceFromMeters(int distanceMeters) { // Distance can be negative so set the min distance to 0. int remainingFeet = (int) max(0, distanceMeters * DistanceConstants.FEET_PER_METER); double remainingMiles = ((double) remainingFeet) / DistanceConstants.FEET_PER_MILE; // Only use the tenths place digit if distance is less than 10 miles and show // feet if distance is less than 0.25 miles. if (remainingMiles >= DistanceConstants.MIN_MILES_TO_SHOW_INTEGER) { return Distance.create((int) round(remainingMiles), Distance.UNIT_MILES); } else if (remainingMiles >= 0.25) { return Distance.create((int) remainingMiles, Distance.UNIT_MILES); } else { return Distance.create(remainingFeet, Distance.UNIT_FEET); } }
Vérifier que les types de manœuvre sont corrects
Les types de manœuvres utilisés dans la bibliothèque Android Auto Car correspondent exactement à ceux fournis par la bibliothèque TurnByTurn. Toutefois, vous devez convertir les manœuvres du SDK Navigation en une déclaration valide dans la bibliothèque Android Auto Car. Le tableau suivant indique la correspondance pour quelques champs. Vous trouverez également un exemple d'utilitaire de conversion pour vous aider.
| Manœuvre de la bibliothèque de navigation détaillée | Android Auto Maneuver |
|---|---|
DEPART |
TYPE_DEPART |
DESTINATION |
TYPE_DESTINATION |
DESTINATION_LEFT |
TYPE_DESTINATION_LEFT |
DESTINATION_RIGHT |
TYPE_DESTINATION_RIGHT |
TURN_U_TURN_CLOCKWISE |
TYPE_U_TURN_RIGHT |
ON_RAMP_LEFT |
TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_LEFT |
ON_RAMP_RIGHT |
TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT |
ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT |
TYPE_ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT |
FORK_RIGHT |
TYPE_FORK_RIGHT |
Développez pour voir l'exemple de code.
import com.google.android.libraries.mapsplatform.turnbyturn.model.Maneuver; import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap; import javax.annotation.Nullable; /** Converter that converts between turn-by-turn and Android Auto Maneuvers. */ public final class ManeuverConverter { private ManeuverConverter() {} // Map from turn-by-turn Maneuver to Android Auto Maneuver.Type. private static final ImmutableMap<Integer, Integer> MANEUVER_TO_ANDROID_AUTO_MANEUVER_TYPE = ImmutableMap.<Integer, Integer>builder() .put(Maneuver.DEPART, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_DEPART) .put(Maneuver.DESTINATION, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_DESTINATION) .put( Maneuver.DESTINATION_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_DESTINATION_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.DESTINATION_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_DESTINATION_RIGHT) .put(Maneuver.STRAIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_STRAIGHT) .put(Maneuver.TURN_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_TURN_NORMAL_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_TURN_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put(Maneuver.TURN_KEEP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_KEEP_LEFT) .put(Maneuver.TURN_KEEP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_KEEP_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_SLIGHT_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_TURN_SLIGHT_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_SLIGHT_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_TURN_SLIGHT_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_SHARP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_TURN_SHARP_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_SHARP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_SHARP_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_U_TURN_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_U_TURN_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.TURN_U_TURN_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_U_TURN_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.MERGE_UNSPECIFIED, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_MERGE_SIDE_UNSPECIFIED) .put(Maneuver.MERGE_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_MERGE_LEFT) .put(Maneuver.MERGE_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_MERGE_RIGHT) .put(Maneuver.FORK_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_FORK_LEFT) .put(Maneuver.FORK_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_FORK_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_UNSPECIFIED, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_KEEP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_KEEP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_SLIGHT_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_SHARP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_SHARP_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_SHARP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_SHARP_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_U_TURN_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_U_TURN_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ON_RAMP_U_TURN_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ON_RAMP_U_TURN_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_NORMAL_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_KEEP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_KEEP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_SLIGHT_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_SHARP_LEFT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_NORMAL_LEFT) .put( Maneuver.OFF_RAMP_SHARP_RIGHT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_OFF_RAMP_NORMAL_RIGHT) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_STRAIGHT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_CW) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_STRAIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_CCW) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_LEFT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_LEFT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_LEFT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_U_TURN_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_U_TURN_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver .TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_ENTER_AND_EXIT_CCW_WITH_ANGLE) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_EXIT_CLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_EXIT_CW) .put( Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_EXIT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_ROUNDABOUT_EXIT_CCW) .put(Maneuver.FERRY_BOAT, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_FERRY_BOAT) .put(Maneuver.FERRY_TRAIN, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_FERRY_TRAIN) .put(Maneuver.NAME_CHANGE, androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.TYPE_NAME_CHANGE) .buildOrThrow(); /** Represents the roundabout turn angle for a slight turn in either right or left directions. */ private static final int ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_SLIGHT = 10; /** Represents the roundabout turn angle for a normal turn in either right or left directions. */ private static final int ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_NORMAL = 45; /** Represents the roundabout turn angle for a sharp turn in either right or left directions. */ private static final int ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_SHARP = 135; /** Represents the roundabout turn angle for a u-turn in either right or left directions. */ private static final int ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_U_TURN = 180; /** * Returns the corresponding {@link androidx.car.app.navigation.model.Maneuver.Type} for the given * direction {@link Maneuver} * * @throws {@link IllegalArgumentException} if the given maneuver does not have a corresponding * Android Auto Maneuver type. */ public static int getAndroidAutoManeuverType(@Maneuver int maneuver) { if (MANEUVER_TO_ANDROID_AUTO_MANEUVER_TYPE.containsKey(maneuver)) { return MANEUVER_TO_ANDROID_AUTO_MANEUVER_TYPE.get(maneuver); } throw new IllegalArgumentException( String.format( "Given turn-by-turn Maneuver %d cannot be converted to an Android Auto equivalent.", maneuver)); } /** * Returns the corresponding Android Auto roundabout angle for the given turn {@link Maneuver}. * Returns {@code null} if given maneuver does not involve a roundabout with a turn. */ @Nullable public static Integer getAndroidAutoRoundaboutAngle(@Maneuver int maneuver) { if (maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_LEFT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE) { return ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_NORMAL; } if (maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_LEFT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SHARP_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE) { return ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_SHARP; } if (maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_LEFT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_RIGHT_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_LEFT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_SLIGHT_RIGHT_COUNTERCLOCKWISE) { return ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_SLIGHT; } if (maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_U_TURN_CLOCKWISE || maneuver == Maneuver.ROUNDABOUT_U_TURN_COUNTERCLOCKWISE) { return ROUNDABOUT_ANGLE_U_TURN; } return null; } }
Documentation associée
- Activer le flux de guidage vocal : intégrez d'abord la fonctionnalité de guidage vocal pour que votre application puisse fonctionner avec Android Auto.
- Renseignez l'affichage du flux : accédez aux champs de données pour obtenir des informations et utilisez des icônes.
