Komponen Place Details
Komponen Place Details dari Places UI Kit memungkinkan Anda menambahkan komponen UI individual yang menampilkan detail tempat di aplikasi. Komponen ini dapat disesuaikan.
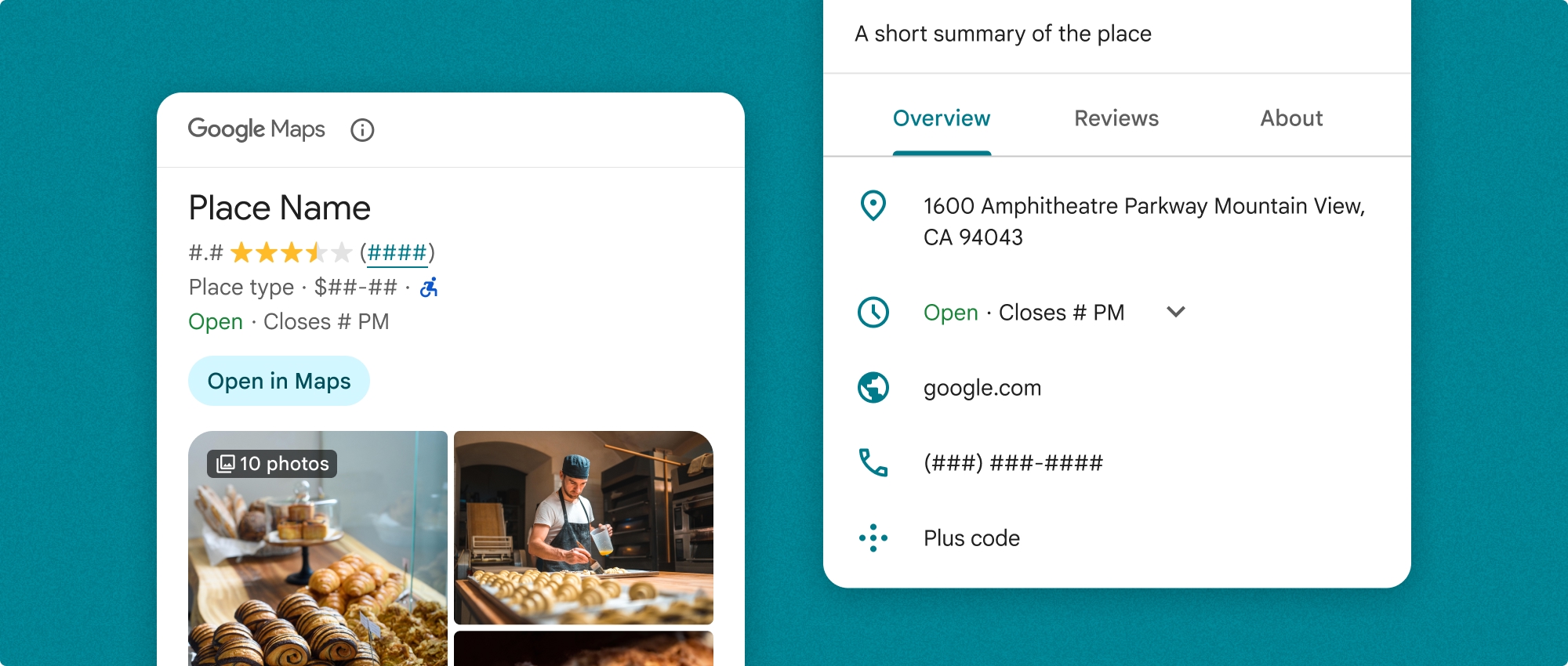
Komponen Detail Tempat dapat digunakan secara terpisah atau bersama dengan API dan layanan Google Maps Platform lainnya. Komponen ini mengambil ID Tempat, nama resource, atau koordinat garis lintang/bujur, lalu menampilkan informasi Detail Tempat yang dirender.
Komponen Place Details sepenuhnya dapat diberi tema, sehingga Anda dapat menyesuaikan font, warna, dan radius sudut agar sesuai dengan kasus penggunaan dan pedoman merek visual Anda. Anda dapat menyesuaikan tampilan detail tempat dengan membuat tema yang memperluas PlacesMaterialTheme dan memberikan penggantian untuk atribut tema. Anda juga dapat menyesuaikan kolom detail tempat yang disertakan dengan menentukan daftar entri Konten, yang masing-masing sesuai dengan informasi yang ditampilkan tentang tempat tersebut.
Varian tata letak
Komponen Detail Tempat mendukung dua varian tata letak utama:
- Ringkas: Tata letak untuk melihat pratinjau informasi penting.
- Penuh: Tata letak komprehensif yang menampilkan semua detail tempat yang tersedia.
Tata letak ringkas dapat ditampilkan dalam orientasi vertikal atau horizontal. Dengan begitu, Anda dapat mengintegrasikan komponen ke dalam berbagai tata letak desain dan ukuran layar. Tata letak lengkap hanya dapat ditampilkan secara vertikal.
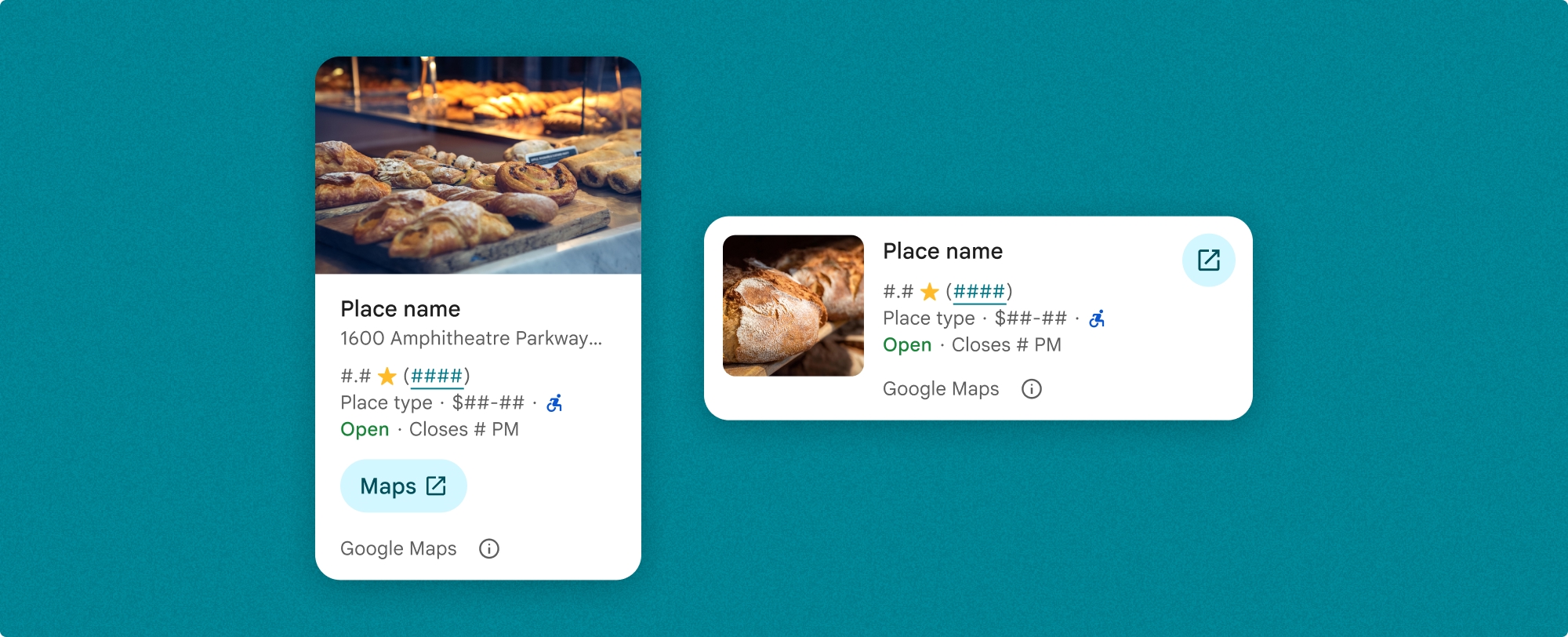
Komponen Detail Tempat memberi Anda kontrol terperinci atas konten yang ditampilkan dalam komponen. Setiap elemen (seperti foto, ulasan, dan informasi kontak) dapat ditampilkan atau disembunyikan satu per satu, sehingga memungkinkan penyesuaian yang tepat terhadap tampilan komponen dan kepadatan informasi.
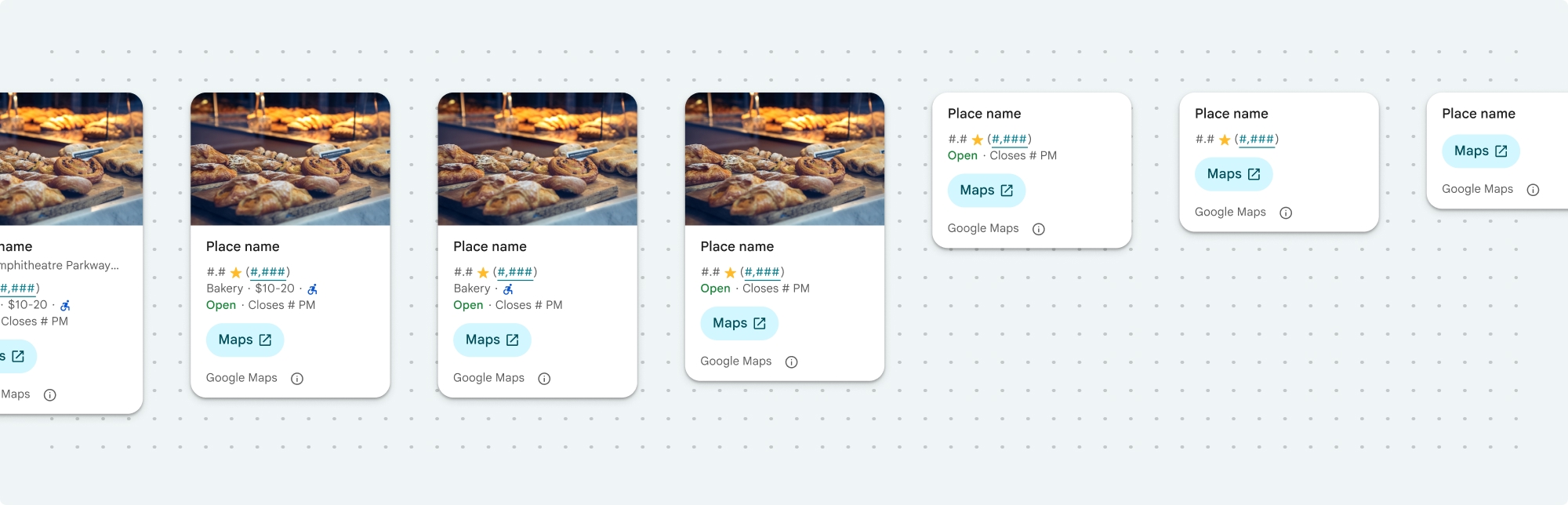
Tampilan ringkas Place Details
Fragmen ringkas Place Details (PlaceDetailsCompactFragment) merender detail untuk tempat yang dipilih menggunakan ruang minimal. Hal ini dapat berguna di jendela info yang menandai tempat di peta, dalam pengalaman media sosial seperti membagikan lokasi dalam chat, sebagai saran untuk memilih lokasi Anda saat ini, atau dalam artikel media untuk merujuk ke tempat di Google Maps.
Tampilan penuh Place Details
Tampilan lengkap detail tempat (PlaceDetailsFragment) menawarkan area yang lebih besar untuk menampilkan informasi detail tempat, dan memungkinkan Anda menampilkan lebih banyak jenis informasi.
Opsi tampilan konten
Anda dapat menentukan konten yang akan ditampilkan menggunakan enum di PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content atau PlaceDetailsFragment.Content.
| Tampilan ringkas | Tampilan lengkap |
|---|---|
|
|
Penagihan
Saat menggunakan Kit UI Place Details, Anda akan ditagih setiap kali metode .loadWithPlaceId(), .loadWithResourceName(), atau loadWithCoordinates() dipanggil. Jika Anda memuat tempat yang sama beberapa kali, Anda akan ditagih untuk setiap permintaan.
Untuk menghindari penagihan beberapa kali, jangan langsung menambahkan .loadWithPlaceId() atau .loadWithResourceName()dalam metode siklus proses Android. Misalnya, jangan langsung memanggil .loadWithPlaceId() atau .loadWithResourceName() dalam metode onResume().
Menambahkan detail tempat ke aplikasi Anda
Anda dapat menambahkan detail tempat ke aplikasi dengan menambahkan fragmen ke tata letak. Saat membuat instance fragmen, Anda dapat menyesuaikan tampilan dan nuansa informasi detail tempat agar sesuai dengan kebutuhan dan tampilan aplikasi Anda. Pelajari penyesuaian lebih lanjut.
Anda memiliki tiga metode yang tersedia di Kotlin dan Java: satu untuk memuat fragmen dengan ID Tempat (loadWithPlaceId()), satu untuk memuat fragmen dengan nama resource (loadWithResourceName()), dan satu untuk memuat fragmen dengan koordinat lintang/bujur (loadWithCoordinates()). Anda dapat memilih satu atau beberapa metode.
Posisi default untuk tampilan ringkas adalah vertikal. Jika Anda menginginkan tata letak horizontal, tentukan Orientation.HORIZONTAL. Anda juga dapat menentukan Orientation.VERTICAL untuk memperjelas. Tampilan penuh hanya dapat ditampilkan secara vertikal.
Lihat contoh di bagian Contoh komponen Detail Tempat.
Menyesuaikan tampilan visual
Gaya visual kustom
Anda dapat menyesuaikan warna, tipografi, jarak, batas, dan sudut komponen Detail Tempat.
Kit UI Places menawarkan pendekatan sistem desain untuk penyesuaian visual yang kurang lebih didasarkan pada Desain Material (dengan beberapa modifikasi khusus Google Maps). Lihat referensi Desain Material untuk Warna dan Tipografi. Secara default, gaya ini mematuhi bahasa desain visual Google Maps.
UI Kit Places menyediakan tema gelap secara default, jadi Anda mungkin perlu menyesuaikan tema gelap dan terang. Untuk menyesuaikan tema gelap, tambahkan entri untuk warna di values-night/colors.xml.
Lihat bagian Gaya kustom untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang gaya.
Penyesuaian lebar dan tinggi
Tampilan ringkas
Lebar yang direkomendasikan:
- Orientasi vertikal: Antara 180 dp dan 300 dp.
- Orientasi horizontal: Antara 180 dp dan 500 dp.
Lebar yang lebih kecil dari 160 dp mungkin tidak ditampilkan dengan benar.
Praktik terbaiknya adalah tidak menetapkan tinggi untuk tampilan ringkas. Tindakan ini akan memungkinkan konten di jendela menyetel tinggi, sehingga semua informasi dapat ditampilkan.
Tampilan penuh
Untuk tampilan penuh, lebar yang direkomendasikan adalah antara 250 dp dan 450 dp. Lebar yang lebih kecil dari 250 dp mungkin tidak ditampilkan dengan benar.
Anda dapat menetapkan tinggi komponen: tampilan Detail Tempat vertikal akan men-scroll secara vertikal dalam ruang yang dialokasikan.
Praktik terbaik adalah menetapkan tinggi untuk tampilan penuh. Dengan begitu, konten di jendela dapat di-scroll dengan benar.
Contoh komponen Place Details
Membuat tampilan ringkas atau penuh
Kotlin
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
Java
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
Contoh kode lengkap ini menentukan orientasi tampilan ringkas secara terprogram berdasarkan konfigurasi perangkat pengguna.
Kotlin
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
Membuat tema
Saat membuat instance fragmen, Anda dapat menentukan tema yang menggantikan atribut gaya default. Atribut tema yang tidak diganti akan menggunakan gaya default. Jika ingin mendukung tema gelap, Anda dapat menambahkan entri untuk warna di values-night/colors.xml.
UI Kit Places menyediakan tema gelap secara default, jadi Anda mungkin perlu menyesuaikan tema gelap dan terang. Untuk menyesuaikan tema gelap, tambahkan entri untuk warna di values-night/colors.xml.
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
Menggunakan konten standar
Contoh ini menggunakan konten standar.
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)Menyesuaikan konten tertentu
Contoh ini hanya memilih opsi alamat, pintu masuk yang dapat diakses, dan media Content untuk tampilan ringkas, lalu merendernya dengan CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme.
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)Menggunakan semua konten
Contoh ini menggunakan semua opsi Content tampilan ringkas.
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)
