คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่
คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่ของ Places UI Kit ช่วยให้คุณเพิ่มคอมโพเนนต์ UI แต่ละรายการที่แสดงรายละเอียดสถานที่ในแอปได้ คอมโพเนนต์นี้ปรับแต่งได้
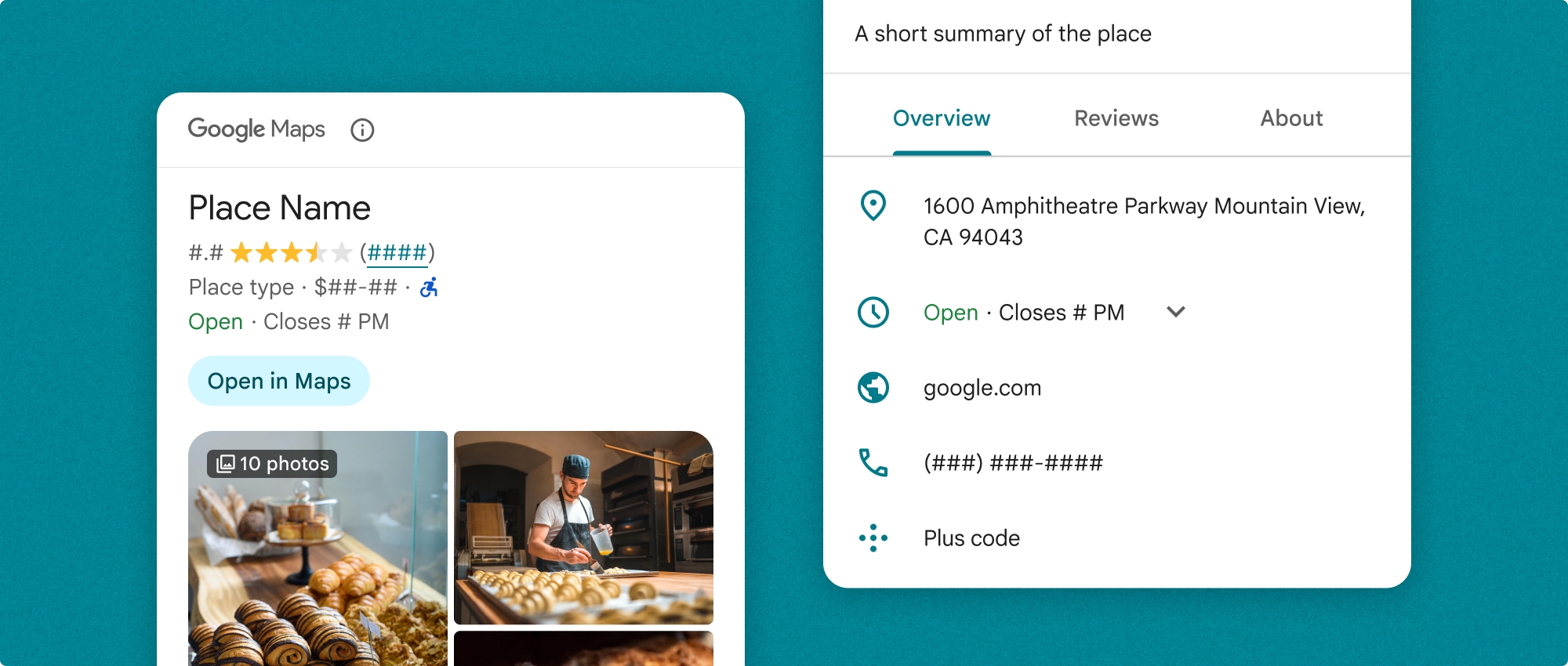
คุณใช้คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่ได้โดยอิสระหรือใช้ร่วมกับ API และบริการอื่นๆ ของ Google Maps Platform คอมโพเนนต์จะใช้รหัสสถานที่ ชื่อทรัพยากร หรือพิกัดละติจูด/ลองจิจูด และแสดงข้อมูลรายละเอียดสถานที่ที่แสดงผล
คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่สามารถปรับแต่งธีมได้อย่างเต็มที่ ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณปรับแต่งแบบอักษร สี และรัศมีมุมให้ตรงกับกรณีการใช้งานและหลักเกณฑ์การใช้แบรนด์แบบภาพได้ คุณปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏของรายละเอียดสถานที่ได้โดยการสร้างธีมที่ขยาย PlacesMaterialTheme และให้การลบล้างแอตทริบิวต์ของธีม นอกจากนี้ คุณยังปรับแต่งช่องรายละเอียดสถานที่ที่จะรวมได้โดยระบุรายการรายการเนื้อหา ซึ่งแต่ละรายการจะสอดคล้องกับข้อมูลที่แสดงเกี่ยวกับสถานที่
รูปแบบเลย์เอาต์
คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่รองรับเลย์เอาต์หลัก 2 รูปแบบ ได้แก่
- กะทัดรัด: เลย์เอาต์สำหรับแสดงตัวอย่างข้อมูลสำคัญ
- เต็ม: เลย์เอาต์ที่ครอบคลุมซึ่งแสดงรายละเอียดสถานที่ทั้งหมดที่พร้อมให้บริการ
เลย์เอาต์แบบกะทัดรัดจะแสดงในแนวตั้งหรือแนวนอนก็ได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณผสานรวมคอมโพเนนต์เข้ากับเลย์เอาต์การออกแบบและขนาดหน้าจอต่างๆ ได้ เลย์เอาต์แบบเต็มจะแสดงได้ในแนวตั้งเท่านั้น
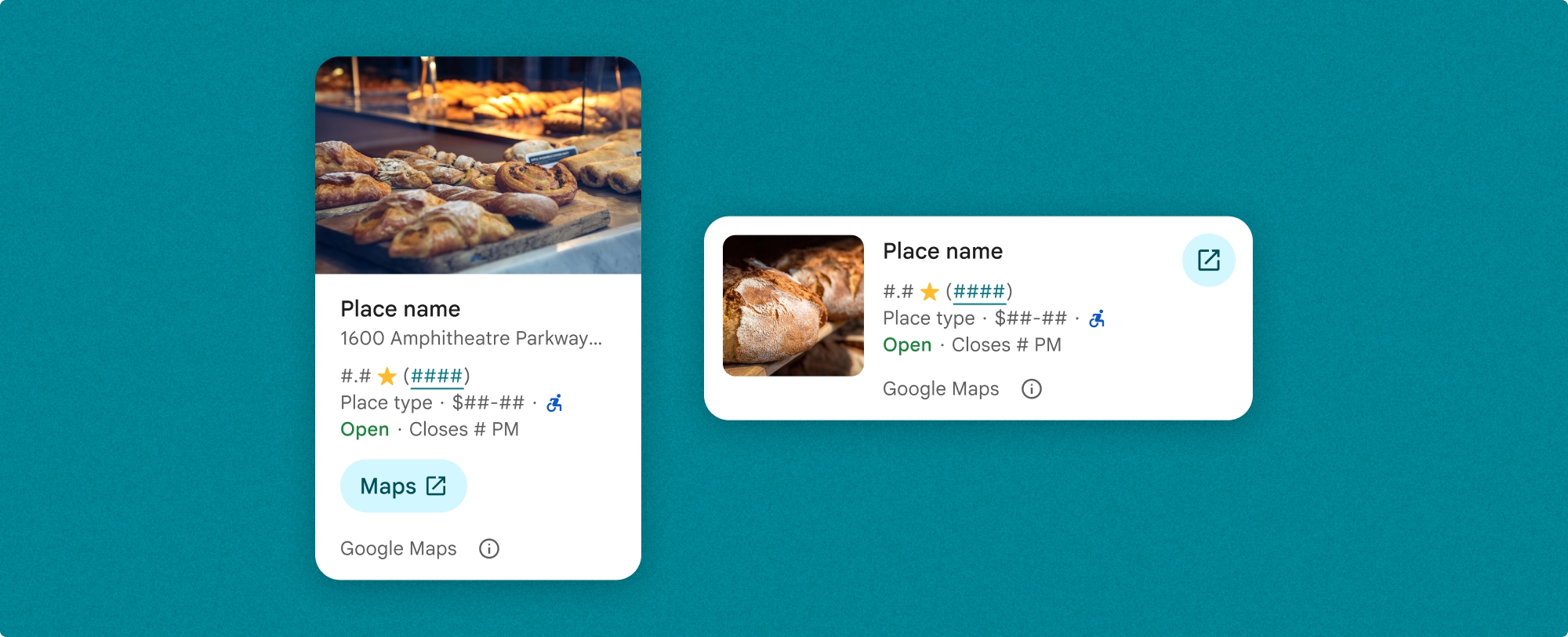
คอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่ช่วยให้คุณควบคุมเนื้อหาที่แสดงในคอมโพเนนต์ได้อย่างละเอียด คุณจะแสดงหรือซ่อนแต่ละองค์ประกอบ (เช่น รูปภาพ รีวิว และข้อมูลติดต่อ) แยกกันได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้ปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏของคอมโพเนนต์และความหนาแน่นของข้อมูลได้อย่างแม่นยำ
มุมมองแบบกะทัดรัดของรายละเอียดสถานที่
Compact Fragment ของรายละเอียดสถานที่ (PlaceDetailsCompactFragment) แสดงรายละเอียดของสถานที่ที่เลือกโดยใช้พื้นที่น้อยที่สุด ซึ่งอาจมีประโยชน์ในหน้าต่างข้อมูลที่ไฮไลต์สถานที่ในแผนที่ ในประสบการณ์การใช้งานโซเชียลมีเดีย เช่น การแชร์ตำแหน่งในแชท เป็นคำแนะนำในการเลือกตำแหน่งปัจจุบัน หรือภายในบทความสื่อเพื่ออ้างอิงสถานที่ใน Google Maps
มุมมองแบบเต็มของรายละเอียดสถานที่
มุมมองแบบเต็มของรายละเอียดสถานที่ (PlaceDetailsFragment) มีพื้นที่ขนาดใหญ่ขึ้นเพื่อแสดงข้อมูลรายละเอียดสถานที่ และช่วยให้คุณแสดงข้อมูลได้หลายประเภทมากขึ้น
ตัวเลือกการแสดงเนื้อหา
คุณระบุเนื้อหาที่จะแสดงได้โดยใช้ Enum ใน PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content หรือ PlaceDetailsFragment.Content
| มุมมองแบบกะทัดรัด | มุมมองเต็ม |
|---|---|
|
|
การเรียกเก็บเงิน
เมื่อใช้ Place Details UI Kit ระบบจะเรียกเก็บเงินทุกครั้งที่มีการเรียกใช้เมธอด .loadWithPlaceId(), .loadWithResourceName() หรือ loadWithCoordinates() หากโหลดสถานที่เดียวกันหลายครั้ง ระบบจะเรียกเก็บเงินสำหรับการขอแต่ละครั้ง
อย่าเพิ่ม .loadWithPlaceId() หรือ .loadWithResourceName() ในวิธีการวงจรของ Android โดยตรงเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการเรียกเก็บเงินหลายครั้ง เช่น อย่าเรียกใช้ .loadWithPlaceId() หรือ .loadWithResourceName() โดยตรงในเมธอด onResume()
เพิ่มรายละเอียดสถานที่ลงในแอป
คุณเพิ่มรายละเอียดสถานที่ลงในแอปได้โดยการเพิ่ม Fragment ลงในเลย์เอาต์ เมื่อสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ Fragment คุณจะปรับแต่งรูปลักษณ์ของข้อมูลรายละเอียดสถานที่ให้เหมาะกับความต้องการและรูปลักษณ์ของแอปได้ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการปรับแต่ง
คุณมี 3 วิธีที่ใช้ได้ทั้งใน Kotlin และ Java ได้แก่ วิธีโหลด Fragment ด้วยรหัสสถานที่ (loadWithPlaceId()) วิธีโหลด Fragment ด้วยชื่อทรัพยากร (loadWithResourceName()) และวิธีโหลด Fragment ด้วยพิกัดละติจูด/ลองจิจูด (loadWithCoordinates()) คุณเลือกวิธีใดก็ได้หรือจะเลือกหลายวิธีก็ได้
ตําแหน่งเริ่มต้นสําหรับมุมมองแบบกะทัดรัดคือแนวตั้ง หากต้องการเลย์เอาต์แนวนอน ให้ระบุ Orientation.HORIZONTAL นอกจากนี้ คุณยังระบุ Orientation.VERTICAL เพื่อให้ชัดเจนได้ด้วย โดยจะแสดงมุมมองแบบเต็มได้ในแนวตั้งเท่านั้น
ดูตัวอย่างได้ในส่วนตัวอย่างคอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่
ปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏ
การจัดรูปแบบที่กำหนดเอง
คุณปรับแต่งสี การพิมพ์ ระยะห่าง เส้นขอบ และมุมของคอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่ได้
ชุดเครื่องมือ UI ของ Places มีแนวทางระบบการออกแบบสำหรับการปรับแต่งภาพโดยอิงตาม Material Design โดยประมาณ (มีการแก้ไขบางอย่างที่เฉพาะเจาะจงสำหรับ Google Maps) ดูข้อมูลอ้างอิงของ Material Design สำหรับสีและการพิมพ์ โดยค่าเริ่มต้น สไตล์จะเป็นไปตามภาษาการออกแบบภาพของ Google Maps
UI Kit ของ Places มีธีมมืดเป็นค่าเริ่มต้น คุณจึงอาจต้องปรับแต่งทั้งธีมมืดและธีมสว่าง หากต้องการปรับแต่งธีมมืด ให้เพิ่มรายการสำหรับสีใน values-night/colors.xml
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการจัดรูปแบบได้ที่ส่วนการจัดรูปแบบที่กำหนดเอง
การปรับแต่งความกว้างและความสูง
มุมมองแบบกะทัดรัด
ความกว้างที่แนะนำ
- การวางแนวตั้ง: ระหว่าง 180dp ถึง 300dp
- การวางแนวนอน: ระหว่าง 180dp ถึง 500dp
ความกว้างที่ต่ำกว่า 160dp อาจแสดงผลไม่ถูกต้อง
แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำคือไม่ควรกำหนดความสูงสำหรับมุมมองแบบกะทัดรัด ซึ่งจะช่วยให้เนื้อหาในหน้าต่างกำหนดความสูงได้ ทำให้แสดงข้อมูลทั้งหมดได้
มุมมองแบบเต็ม
สำหรับมุมมองแบบเต็ม ความกว้างที่แนะนำคือระหว่าง 250dp ถึง 450dp ความกว้างที่ต่ำกว่า 250dp อาจแสดงผลไม่ถูกต้อง
คุณกำหนดความสูงของคอมโพเนนต์ได้ โดยมุมมองรายละเอียดสถานที่แนวตั้งจะเลื่อนในแนวตั้งภายในพื้นที่ที่จัดสรรไว้
แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำคือการตั้งค่าความสูงสำหรับการดูแบบเต็ม ซึ่งจะช่วยให้เนื้อหาในหน้าต่างเลื่อนได้อย่างถูกต้อง
ตัวอย่างคอมโพเนนต์รายละเอียดสถานที่
สร้างมุมมองแบบย่อหรือแบบเต็ม
Kotlin
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
Java
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
ตัวอย่างโค้ดแบบเต็มนี้จะกำหนดการวางแนวของมุมมองขนาดกะทัดรัดโดยอัตโนมัติตามการกำหนดค่าของอุปกรณ์ผู้ใช้
Kotlin
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
สร้างธีม
เมื่อสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ Fragment คุณจะระบุธีมที่ลบล้างแอตทริบิวต์รูปแบบเริ่มต้นได้ แอตทริบิวต์ธีมที่ไม่ได้ลบล้างจะใช้รูปแบบเริ่มต้น หากต้องการรองรับธีมมืด คุณสามารถเพิ่มรายการสำหรับสีใน values-night/colors.xml ได้
UI Kit ของ Places มีธีมมืดเป็นค่าเริ่มต้น คุณจึงอาจต้องปรับแต่งทั้งธีมมืดและธีมสว่าง หากต้องการปรับแต่งธีมมืด ให้เพิ่มรายการสำหรับสีใน values-night/colors.xml
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
ใช้เนื้อหามาตรฐาน
ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้เนื้อหามาตรฐาน
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)ปรับแต่งเนื้อหาที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
ตัวอย่างนี้จะเลือกเฉพาะที่อยู่ ทางเข้าที่เข้าถึงได้ และContentตัวเลือกสื่อCustomizedPlaceDetailsThemeเพื่อมุมมองแบบกะทัดรัด และแสดงผลด้วย CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)ใช้เนื้อหาทั้งหมด
ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ตัวเลือก Content ทั้งหมดของมุมมองขนาดกะทัดรัด
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)
