Thành phần Thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm
Thành phần Chi tiết về địa điểm của Places UI Kit cho phép bạn thêm một thành phần giao diện người dùng riêng lẻ để hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm trong ứng dụng. Bạn có thể tuỳ chỉnh thành phần này.
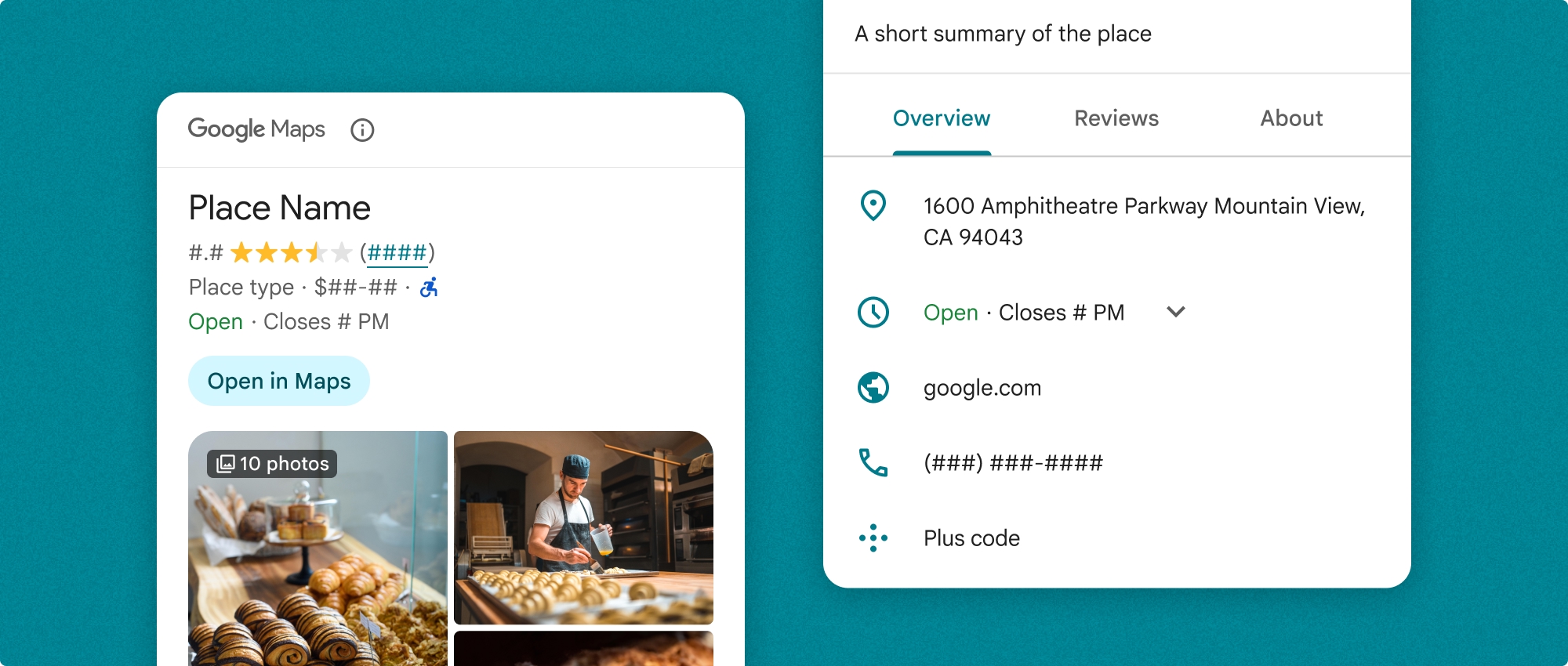
Bạn có thể sử dụng thành phần Thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm một cách độc lập hoặc kết hợp với các API và dịch vụ khác của Google Maps Platform. Thành phần này lấy Place ID, tên tài nguyên hoặc toạ độ vĩ độ/kinh độ và trả về thông tin Chi tiết về địa điểm đã hiển thị.
Thành phần Chi tiết về địa điểm có thể được tạo giao diện hoàn toàn, cho phép bạn tuỳ chỉnh phông chữ, màu sắc và bán kính góc cho phù hợp với trường hợp sử dụng và nguyên tắc trực quan về thương hiệu của bạn. Bạn có thể tuỳ chỉnh giao diện của thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm bằng cách tạo một giao diện mở rộng PlacesMaterialTheme và cung cấp các chế độ ghi đè cho các thuộc tính giao diện. Bạn cũng có thể tuỳ chỉnh những trường thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm được đưa vào bằng cách chỉ định một danh sách các mục Nội dung, mỗi mục tương ứng với một phần thông tin được hiển thị về địa điểm.
Biến thể bố cục
Thành phần Chi tiết về địa điểm hỗ trợ 2 biến thể bố cục chính:
- Thu gọn: Bố cục để xem trước thông tin chính.
- Đầy đủ: Bố cục toàn diện hiển thị tất cả thông tin chi tiết có sẵn về địa điểm.
Bố cục thu gọn có thể hiển thị theo hướng dọc hoặc hướng ngang. Điều này cho phép bạn tích hợp thành phần này vào nhiều bố cục thiết kế và kích thước màn hình. Bạn chỉ có thể hiển thị bố cục đầy đủ theo chiều dọc.
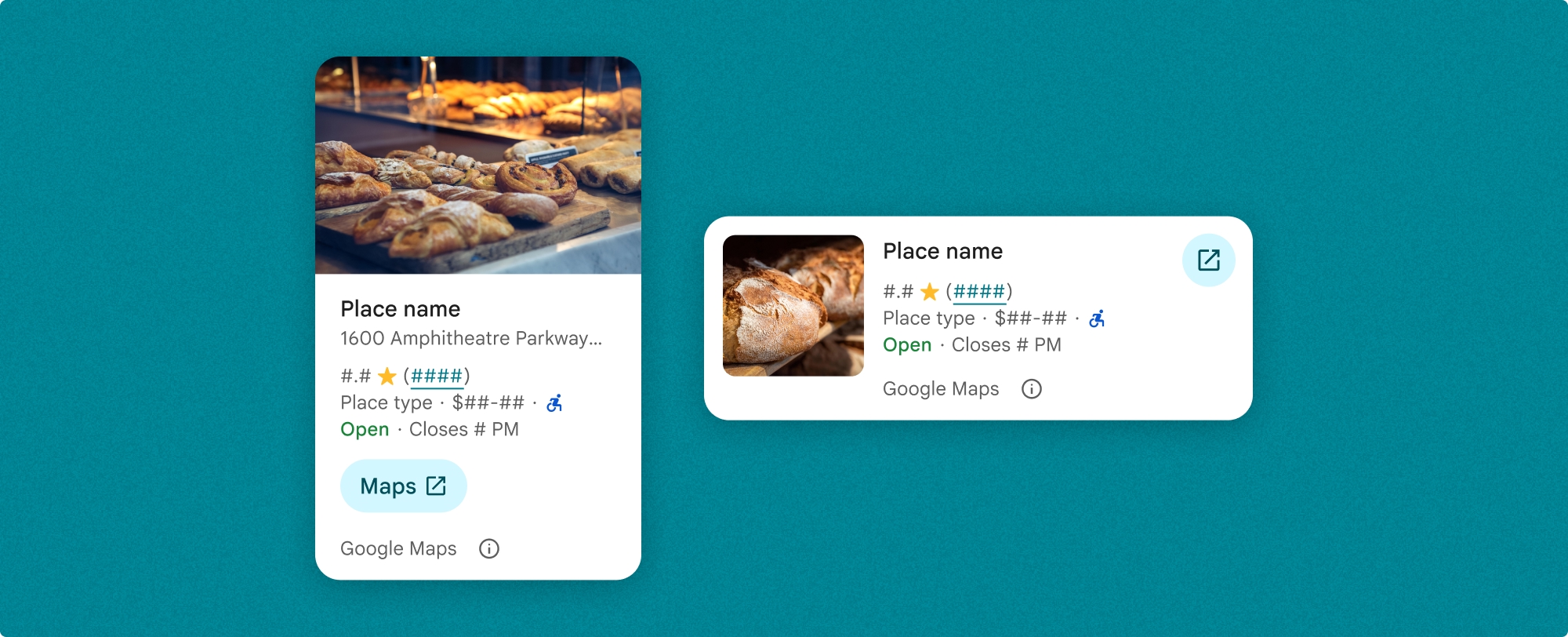
Thành phần Chi tiết về địa điểm cho phép bạn kiểm soát chi tiết nội dung hiển thị trong thành phần này. Bạn có thể hiện hoặc ẩn từng phần tử (chẳng hạn như ảnh, bài đánh giá và thông tin liên hệ), cho phép tuỳ chỉnh chính xác giao diện và mật độ thông tin của các thành phần.
Chế độ xem thu gọn của phần Thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm
Mảnh nhỏ gọn Chi tiết về địa điểm (PlaceDetailsCompactFragment) hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về một địa điểm đã chọn bằng cách sử dụng không gian tối thiểu. Điều này có thể hữu ích trong một cửa sổ thông tin làm nổi bật một địa điểm trên bản đồ, trong một trải nghiệm mạng xã hội như chia sẻ vị trí trong cuộc trò chuyện, dưới dạng đề xuất để chọn vị trí hiện tại của bạn hoặc trong một bài viết về nội dung nghe nhìn để tham chiếu địa điểm trên Google Maps.
Chế độ xem đầy đủ về thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm
Chế độ xem đầy đủ thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm (PlaceDetailsFragment) cung cấp một không gian lớn hơn để hiển thị thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm và cho phép bạn hiển thị nhiều loại thông tin hơn.
Các lựa chọn hiển thị nội dung
Bạn có thể chỉ định nội dung cần hiển thị bằng cách sử dụng các enum trong PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.Content hoặc PlaceDetailsFragment.Content.
| Chế độ xem thu gọn | Chế độ xem toàn bộ |
|---|---|
|
|
Thanh toán
Khi sử dụng Place Details UI Kit, bạn sẽ bị tính phí cho mỗi lần gọi phương thức .loadWithPlaceId(), .loadWithResourceName() hoặc loadWithCoordinates(). Nếu tải cùng một địa điểm nhiều lần, bạn sẽ bị tính phí cho mỗi yêu cầu.
Để tránh bị tính phí nhiều lần, đừng thêm trực tiếp .loadWithPlaceId() hoặc .loadWithResourceName() vào các phương thức trong vòng đời Android. Ví dụ: đừng gọi trực tiếp .loadWithPlaceId() hoặc .loadWithResourceName() trong phương thức onResume().
Thêm thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm vào ứng dụng
Bạn có thể thêm thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm vào ứng dụng bằng cách thêm một mảnh vào bố cục. Khi khởi tạo mảnh này, bạn có thể tuỳ chỉnh giao diện của thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm cho phù hợp với nhu cầu và giao diện của ứng dụng. Tìm hiểu thêm về tính năng tuỳ chỉnh.
Bạn có 3 phương thức trong cả Kotlin và Java: một phương thức để tải mảnh bằng mã địa điểm (loadWithPlaceId()), một phương thức để tải mảnh bằng tên tài nguyên (loadWithResourceName()) và một phương thức để tải mảnh bằng toạ độ vĩ độ/kinh độ (loadWithCoordinates()). Bạn có thể chọn bất kỳ phương thức nào hoặc nhiều phương thức.
Vị trí mặc định cho chế độ xem thu gọn là dọc. Nếu bạn muốn bố cục ngang, hãy chỉ định Orientation.HORIZONTAL. Bạn cũng có thể tuỳ ý chỉ định Orientation.VERTICAL để cho rõ ràng. Chế độ xem toàn bộ chỉ có thể hiển thị theo chiều dọc.
Hãy xem ví dụ trong phần Ví dụ về thành phần Thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm.
Tuỳ chỉnh giao diện trực quan
Tạo kiểu tuỳ chỉnh
Bạn có thể tuỳ chỉnh màu sắc, kiểu chữ, khoảng cách, đường viền và góc của thành phần Thông tin chi tiết về địa điểm.
Bộ công cụ giao diện người dùng Places cung cấp một phương pháp tiếp cận hệ thống thiết kế để tuỳ chỉnh hình ảnh dựa trên Material Design (với một số điểm sửa đổi dành riêng cho Google Maps). Xem thông tin tham khảo của Material Design về Màu sắc và Kiểu chữ. Theo mặc định, kiểu này tuân thủ ngôn ngữ thiết kế trực quan của Google Maps.
Places UI Kit cung cấp giao diện tối theo mặc định, vì vậy, bạn có thể cần tuỳ chỉnh cả giao diện tối và giao diện sáng. Để tuỳ chỉnh giao diện tối, hãy thêm một mục cho màu trong values-night/colors.xml.
Hãy xem phần Định kiểu tuỳ chỉnh để biết thêm thông tin về việc định kiểu.
Tuỳ chỉnh chiều rộng và chiều cao
Chế độ xem thu gọn
Chiều rộng đề xuất:
- Hướng dọc: Từ 180 dp đến 300 dp.
- Hướng ngang: Từ 180 dp đến 500 dp.
Những chiều rộng nhỏ hơn 160 dp có thể không hiển thị đúng cách.
Phương pháp hay nhất là không đặt chiều cao cho chế độ xem thu gọn. Thao tác này sẽ cho phép nội dung trong cửa sổ đặt chiều cao, cho phép hiển thị tất cả thông tin.
Lượt xem toàn bộ
Đối với chế độ xem toàn màn hình, chiều rộng đề xuất là từ 250 dp đến 450 dp. Chiều rộng nhỏ hơn 250 dp có thể hiển thị không chính xác.
Bạn có thể đặt chiều cao của thành phần: Chế độ xem Chi tiết về địa điểm theo chiều dọc sẽ cuộn theo chiều dọc trong không gian được phân bổ.
Phương pháp hay nhất là đặt chiều cao cho chế độ xem toàn màn hình. Việc này sẽ giúp nội dung trong cửa sổ cuộn đúng cách.
Ví dụ về thành phần Place Details
Tạo chế độ xem thu gọn hoặc chế độ xem đầy đủ
Kotlin
// We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } }
Java
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( Orientation.HORIZONTAL, Arrays.asList(Content.ADDRESS, Content.TYPE, Content.RATING, Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE_ICON), R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme); fragment.setPlaceLoadListener( new PlaceLoadListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Place place) { ... } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { ... } }); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment) .commitNow(); // Load the fragment with a Place ID. fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId); // Load the fragment with a resource name. fragment.loadWithResourceName(resourceName);
Mẫu mã đầy đủ này xác định hướng của chế độ xem thu gọn theo phương thức lập trình dựa trên cấu hình thiết bị của người dùng.
Kotlin
package com.example.placedetailsuikit import android.Manifest import android.annotation.SuppressLint import android.content.pm.PackageManager import android.content.res.Configuration import android.location.Location import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.view.View import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.activity.viewModels import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import com.example.placedetailsuikit.databinding.ActivityMainBinding import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.PointOfInterest import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceDetailsCompactFragment import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.PlaceLoadListener import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.Orientation private const val TAG = "PlacesUiKit" /** * A simple ViewModel to store UI state that needs to survive configuration changes. * In this case, it holds the ID of the selected place. Using a ViewModel is good practice * as it prevents data loss during events like screen rotation, ensuring a * seamless user experience. */ class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { var selectedPlaceId: String? = null } /** * This activity serves as a basic example of integrating the Place Details UI Kit. * It demonstrates the fundamental steps required: * 1. Setting up a Google Map. * 2. Requesting location permissions to center the map. * 3. Handling clicks on Points of Interest (POIs) to get a Place ID. * 4. Using the Place ID to load and display place details in a [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. */ class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback, GoogleMap.OnPoiClickListener { // ViewBinding provides type-safe access to views defined in the XML layout, // eliminating the need for `findViewById` and preventing null pointer exceptions. private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding private var googleMap: GoogleMap? = null // The FusedLocationProviderClient is the main entry point for interacting with the // fused location provider, which intelligently manages the underlying location technologies. private lateinit var fusedLocationClient: FusedLocationProviderClient // Using registerForActivityResult is the modern, recommended approach for handling // permission requests. It decouples the request from the handling logic, making the // code cleaner and easier to manage compared to the older `onRequestPermissionsResult` callback. private lateinit var requestPermissionLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<Array<String>> // The `by viewModels()` delegate provides a lazy-initialized ViewModel scoped to this Activity. // This ensures that we get the same ViewModel instance across configuration changes. private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels() override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // The ActivityResultLauncher is initialized here. The lambda defines the callback // that will be executed once the user responds to the permission dialog. requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestMultiplePermissions()) { permissions -> // We check if either fine or coarse location permission was granted. if (permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION] == true || permissions[Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION] == true) { Log.d(TAG, "Location permission granted by user.") fetchLastLocation() } else { // If permission is denied, we inform the user and default to a known location. // This ensures the app remains functional even without location access. Log.d(TAG, "Location permission denied by user.") Toast.makeText( this, "Location permission denied. Showing default location.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() moveToSydney() } } // enableEdgeToEdge() allows the app to draw behind the system bars for a more immersive experience. enableEdgeToEdge() binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.dismissButton.setOnClickListener { dismissPlaceDetails() } // --- Crucial: Initialize Places SDK --- // It's essential to initialize the Places SDK before making any other Places API calls. // This should ideally be done once, for example, in the Application's `onCreate`. val apiKey = BuildConfig.PLACES_API_KEY if (apiKey.isEmpty() || apiKey == "YOUR_API_KEY") { // A valid API key is required for the Places SDK to function. Log.e(TAG, "No api key") Toast.makeText( this, "Add your own API_KEY in local.properties", Toast.LENGTH_LONG ).show() finish() return } // `initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled` is used to opt-in to the new SDK version. Places.initializeWithNewPlacesApiEnabled(applicationContext, apiKey) fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this) // ------------------------------------ // The SupportMapFragment is the container for the map. `getMapAsync` allows us to // work with the GoogleMap object via a callback once it's fully initialized. val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.map_fragment) as SupportMapFragment? mapFragment?.getMapAsync(this) // This block handles restoration after a configuration change (e.g., screen rotation). // If a place was selected before the rotation, its ID is stored in the ViewModel. // We use this ID to immediately show the details fragment again. if (viewModel.selectedPlaceId != null) { viewModel.selectedPlaceId?.let { placeId -> Log.d(TAG, "Restoring PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } } } /** * This callback is triggered when the GoogleMap object is ready to be used. * All map setup logic should be placed here. */ override fun onMapReady(map: GoogleMap) { Log.d(TAG, "Map is ready") googleMap = map // Setting the OnPoiClickListener allows us to capture user taps on points of interest. googleMap?.setOnPoiClickListener(this) // After the map is ready, we determine the initial camera position based on location permissions. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fetchLastLocation() } else { requestLocationPermissions() } } /** * A helper function to centralize the check for location permissions. */ private fun isLocationPermissionGranted(): Boolean { return ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED || ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission( this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED } /** * This function triggers the permission request flow. The result is handled by the * ActivityResultLauncher defined in `onCreate`. */ private fun requestLocationPermissions() { Log.d(TAG, "Requesting location permissions.") requestPermissionLauncher.launch( arrayOf( Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ) ) } /** * Fetches the device's last known location. This is a fast and battery-efficient way * to get a location fix. It should only be called after verifying permissions. */ @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private fun fetchLastLocation() { // Double-checking permissions here is a good practice, although the call sites are already guarded. if (isLocationPermissionGranted()) { fusedLocationClient.lastLocation .addOnSuccessListener { location: Location? -> if (location != null) { val userLocation = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(userLocation, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to user's last known location.") } else { // `lastLocation` can be null if the location has never been recorded. // In this case, we fall back to a default location. Log.d(TAG, "Last known location is null. Falling back to Sydney.") moveToSydney() } } .addOnFailureListener { // This listener handles errors in the location fetching process. Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get location.", it) moveToSydney() } } } /** * Moves the map camera to a default, hardcoded location (Sydney). * This serves as a reliable fallback. */ private fun moveToSydney() { val sydney = LatLng(-33.8688, 151.2093) googleMap?.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(sydney, 13f)) Log.d(TAG, "Moved to Sydney") } /** * This is the callback for the `OnPoiClickListener`. It's triggered when a user * taps a POI on the map. */ override fun onPoiClick(poi: PointOfInterest) { val placeId = poi.placeId Log.d(TAG, "Place ID: $placeId") // We save the selected place ID to the ViewModel. This is critical for surviving // configuration changes. If the user rotates the screen now, the `onCreate` // method will be able to restore the place details view. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = placeId showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId) } /** * This function is the core of the integration. It creates, configures, and displays * the [PlaceDetailsCompactFragment]. * @param placeId The unique identifier for the place to be displayed. */ private fun showPlaceDetailsFragment(placeId: String) { Log.d(TAG, "Showing PlaceDetailsFragment for place ID: $placeId") // We manage the visibility of UI elements to provide feedback to the user. // The wrapper is shown, and a loading indicator is displayed while the data is fetched. binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.GONE binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.VISIBLE // The Place Details widget can be displayed vertically or horizontally. // We dynamically choose the orientation based on the device's current configuration. val orientation = if (resources.configuration.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) { Orientation.HORIZONTAL } else { Orientation.VERTICAL } // We create a new instance of the fragment using its factory method. // We can specify which content to show, the orientation, and a custom theme. val fragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance( PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT, // Show all available content. orientation, R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme, ).apply { // The PlaceLoadListener provides callbacks for when the place data is successfully // loaded or when an error occurs. This is where we update our UI state. setPlaceLoadListener(object : PlaceLoadListener { override fun onSuccess(place: Place) { Log.d(TAG, "Place loaded: ${place.id}") // Once the data is loaded, we hide the loading indicator and show the fragment. binding.loadingIndicatorMain.visibility = View.GONE binding.placeDetailsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE binding.dismissButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE } override fun onFailure(e: Exception) { Log.e(TAG, "Place failed to load", e) // On failure, we hide the UI and notify the user. dismissPlaceDetails() Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Failed to load place details.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } }) } // We add the fragment to our layout's container view. // `commitNow()` is used to ensure the fragment is immediately added and available, // which is important because we need to call a method on it right after. supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(binding.placeDetailsContainer.id, fragment) .commitNow() // **This is the key step**: After adding the fragment, we call `loadWithPlaceId` // to trigger the data loading process for the selected place. // We use `post` to ensure this runs after the layout has been measured, // which can prevent potential timing issues. binding.root.post { fragment.loadWithPlaceId(placeId) } } /** * Hides the place details view and clears the selected place ID from the ViewModel. */ private fun dismissPlaceDetails() { binding.placeDetailsWrapper.visibility = View.GONE // Clearing the ID in the ViewModel is important so that if the user rotates the // screen after dismissing, the details view doesn't reappear. viewModel.selectedPlaceId = null } override fun onDestroy() { super.onDestroy() // It's a good practice to nullify references to objects that have a lifecycle // tied to the activity, like the GoogleMap object, to prevent potential memory leaks. googleMap = null } }
Tạo một giao diện
Khi tạo một mảnh, bạn có thể chỉ định một giao diện ghi đè bất kỳ thuộc tính kiểu mặc định nào. Mọi thuộc tính giao diện không bị ghi đè sẽ sử dụng kiểu mặc định. Nếu muốn hỗ trợ giao diện tối, bạn có thể thêm một mục cho màu trong values-night/colors.xml.
Places UI Kit cung cấp giao diện tối theo mặc định, vì vậy, bạn có thể cần tuỳ chỉnh cả giao diện tối và giao diện sáng. Để tuỳ chỉnh giao diện tối, hãy thêm một mục cho màu trong values-night/colors.xml.
<style name="CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme" parent="PlacesMaterialTheme"> <item name="placesColorPrimary">@color/app_primary_color</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurface">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesColorOnSurfaceVariant">@color/app_color_on_surface</item> <item name="placesTextAppearanceBodySmall">@style/app_text_appearence_small</item> <item name="placesCornerRadius">20dp</item> </style>
Sử dụng nội dung chuẩn
Mẫu này sử dụng nội dung tiêu chuẩn.
val fragmentStandardContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.STANDARD_CONTENT,
orientation,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)Tuỳ chỉnh nội dung cụ thể
Mẫu này chỉ chọn địa chỉ, lối vào cho người khuyết tật và các lựa chọn về phương tiện Content cho chế độ xem thu gọn, đồng thời hiển thị các lựa chọn đó bằng CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme.
val placeDetailsFragment = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
listOf(
Content.ADDRESS,
Content.ACCESSIBLE_ENTRANCE,
Content.MEDIA
),
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)Sử dụng tất cả nội dung
Mẫu này sử dụng tất cả các lựa chọn Content của chế độ xem thu gọn.
val fragmentAllContent = PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.newInstance(
orientation,
PlaceDetailsCompactFragment.ALL_CONTENT,
R.style.CustomizedPlaceDetailsTheme
)
