
تُعدّ واجهة برمجة التطبيقات ML Kit Pose Detection API حلاً خفيفًا ومتعدد الاستخدامات يتيح لمطوّري التطبيقات اكتشاف وضعية جسم الشخص في الوقت الفعلي من فيديو متواصل أو صورة ثابتة. تصف الوضعية وضع الجسم في لحظة من الوقت مع مجموعة من نقاط المعالم الهيكلية. تتجاوب المعالم مع أجزاء مختلفة من الجسم مثل الكتفين والورك. يمكن استخدام المواضع النسبية للمعالم لتمييز وضعية عن الأخرى.
تنتج أداة ML Kit Pose Detection مطابقة الهيكل العظمي لكامل الجسم من 33 نقطة وتشمل معالم الوجه (الأذنين والعينين والفم والأنف) ونقاط على اليدين والقدمين. يوضح الشكل 1 أدناه المعالم التي تنظر عبر الكاميرا إلى المستخدم، لذا فهي صورة معكوسة. يظهر الجانب الأيمن للمستخدم على يمين الصورة:
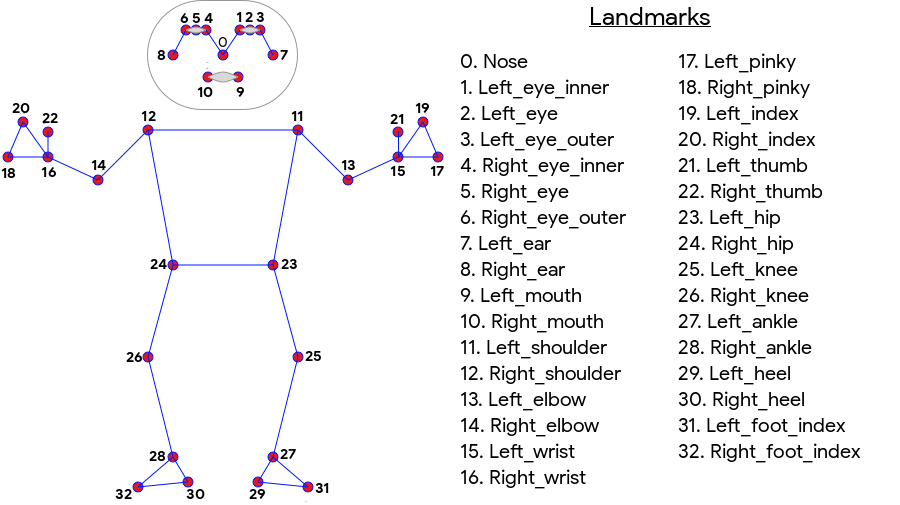
إنّ ميزة "رصد وضعية حزمة تعلُّم الآلة" لا تتطلّب معدّات متخصّصة أو خبرة في تعلُّم الآلة من أجل تحقيق نتائج رائعة. باستخدام هذه التكنولوجيا، يمكن للمطورين إنشاء تجارب فريدة من نوعها لمستخدميهم باستخدام بضعة أسطر من التعليمات البرمجية فقط.
يجب أن يكون وجه المستخدم موجودًا لاكتشاف وضعية ما. تعمل ميزة "رصد الوضعية" بشكل أفضل عندما يظهر جسم الجسم بأكمله في الإطار، وترصد أيضًا وضعية جزئية من الجسم. في هذه الحالة، يتم تعيين إحداثيات خارج الصورة للمعالم التي لا يتم التعرف عليها.
الإمكانات الرئيسية
- دعم من عدّة منصات يمكنك التمتع بالتجربة نفسها على كل من Android وiOS.
- تتبُّع الجسم بالكامل يعرض النموذج 33 نقطة رئيسية للمعلَم السيني، بما في ذلك مواضع اليدين والقدمين.
- درجة InFrame LikeliITY: لكل معلَم، هو مقياس يشير إلى احتمالية أن يكون المَعلم ضمن إطار الصورة. تتراوح النتيجة بين 0.0 و1.0، حيث يشير 1.0 إلى درجة عالية من الثقة.
- حزمتا SDK محسَّنتان يتم تشغيل حزمة SDK الأساسية في الوقت الفعلي على الهواتف الحديثة مثل Pixel 4 وiPhone X. وهو يعرض النتائج بمعدل 30 و45 لقطة في الثانية تقريبًا على التوالي. ومع ذلك، قد تختلف دقة إحداثيات المعالم. تعرض حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) الدقيقة النتائج بمعدل عرض إطارات أبطأ، غير أنها تُنتج قيم إحداثيات أكثر دقة.
- تخطيط Z لتحليل متعمق يمكن أن تساعد هذه القيمة في تحديد ما إذا كانت أجزاء من جسم المستخدم في مقدمة أو خلف أودي المستخدمين. لمزيد من المعلومات، راجع قسم إدارة Z أدناه.
تشبه واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Pose Detection واجهة برمجة التطبيقات للتعرف على الوجوه من حيث أنها تعرض مجموعة من المَعالم وموقعها. ومع ذلك، تحاول ميزة "التعرّف على الوجه" أيضًا التعرّف على سمات مثل الفم المبتسم أو العيون المفتوحة، إلا أنّ هذه الميزة لا تضيف أي معنى إلى العلامات الأرضية في الوضعية أو الوضعية نفسها. يمكنك إنشاء الخوارزميات الخاصة بك لتفسير وضعية. راجع نصائح تصنيف الوضع للحصول على بعض الأمثلة.
يمكن لميزة "رصد الوضعية" رصد شخص واحد فقط في الصورة. إذا ظهر شخصان في الصورة، سيحدد النموذج معالم للشخص الذي تم اكتشافه بأعلى درجة من الثقة.
إحداثيات Z
إحداثيات Z هي قيمة تجريبية يتم حسابها لكل معلم. وتُقاس بـ "بكسل الصور" مثل الإحداثي X وY، لكنها ليست قيمة ثلاثية الأبعاد صحيحة. المحور Z عمودي تجاه الكاميرا ويمر بين وركي الشخص. يقع أصل المحور Z تقريبًا بين نقطة المركز بين الوركين (اليسار/اليمين والأمام/الخلف بالنسبة إلى الكاميرا). القيم السالبة Z تتجه نحو الكاميرا؛ والقيم الموجبة بعيدة عنها. ليس للإحداثي Z حد أعلى أو أدنى.
مثال على النتائج
يوضح الجدول التالي الإحداثيات وInFrame LikeliITY لبعض المعالم الرئيسية في الوضعية على اليمين. لاحظ أن الإحداثيات Z لليد اليسرى للمستخدم سلبية، نظرًا لأنها أمام مركز الوركين للشخص واتجاه الكاميرا.
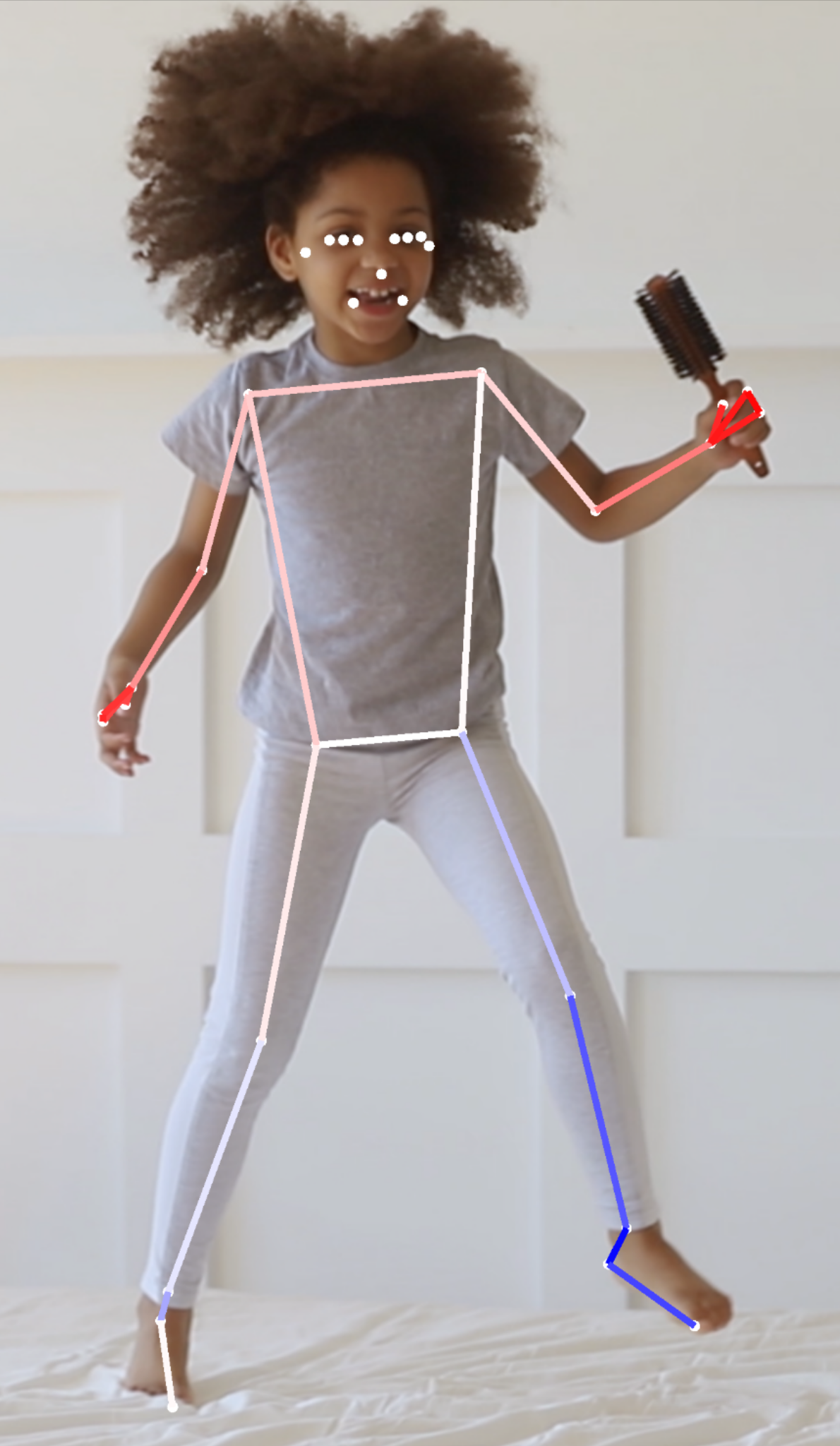

| مَعلم | Type | الموضع | InFrameLikelihood |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | LEFT_SHOULDER | (734.9671، 550.7924، -118.11934) | 0.9999038 |
| 12 | RIGHT_SHOULDER | (391.27032، 583.2485، -321.15836) | 0.9999894 |
| 13 | LEFT_ELBOW | (903.83704، 754.676، -219.67009) | 0.9836427 |
| 14 | RIGHT_ELBOW | (322.18152، 842.5973، -179.28519) | 0.99970156 |
| 15 | LEFT_WRIST | (1073.8956، 654.9725، -820.93463) | 0.9737737 |
| 16 | RIGHT_WRIST | (218.27956، 1015.70435، -683.6567) | 0.995568 |
| 17 | LEFT_PINKY | (1146.1635، 609.6432، -956.9976) | 0.95273364 |
| 18 | RIGHT_PINKY | (176.17755، 1065.838، -776.5006) | 0.9785348 |
الخيارات المتقدمة
للحصول على مزيد من تفاصيل التنفيذ حول نماذج تعلُّم الآلة الأساسية لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه، يُرجى الاطّلاع على مشاركة مدونة Google AI.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول ممارسات العدالة في تعلُّم الآلة وكيفية تدريب النماذج، اطّلِع على بطاقة النموذج.

