การปรับปรุง SEO ด้วยแผนภูมิฟองอากาศของ Search Console
การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลประสิทธิภาพใน Search นั้นเป็นเรื่องที่ท้าทาย แต่จะยิ่งท้าทายขึ้นเมื่อคุณมีคำค้นหาเฉพาะเจาะจงจำนวนมากซึ่งมองเห็นภาพและเข้าใจได้ยาก แผนภูมิฟองอากาศจะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจว่าคำค้นหาใดทำงานได้ดีสำหรับเว็บไซต์และคำค้นหาใดควรปรับปรุง
หากต้องการทดสอบเทคนิคที่กล่าวถึงในที่นี้ คุณเชื่อมต่อข้อมูลกับ Looker Studio และลองเล่นกับการตั้งค่าแผนภูมิได้
หากคุณยังไม่ได้อ่านการเชื่อมต่อ Search Console กับ Looker Studio และการตรวจสอบการเข้าชมจาก Search ด้วย Looker Studio ให้ลองอ่านเพื่อทําความเข้าใจเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสิ่งที่คุณทำได้ด้วย Search Console ใน Looker Studio
การทำความเข้าใจแผนภูมิ
แผนภูมิฟองอากาศเป็นการแสดงภาพที่ยอดเยี่ยมเมื่อคุณมีเมตริกและมิติข้อมูลหลายรายการ เนื่องจากช่วยให้ดูความสัมพันธ์และรูปแบบในข้อมูลได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น ในตัวอย่างที่แสดงที่นี่ คุณจะเห็นอัตราการคลิกผ่าน (CTR), อันดับเฉลี่ย และจำนวนคลิกของคำค้นหาและมิติข้อมูลอุปกรณ์ในมุมมองเดียว
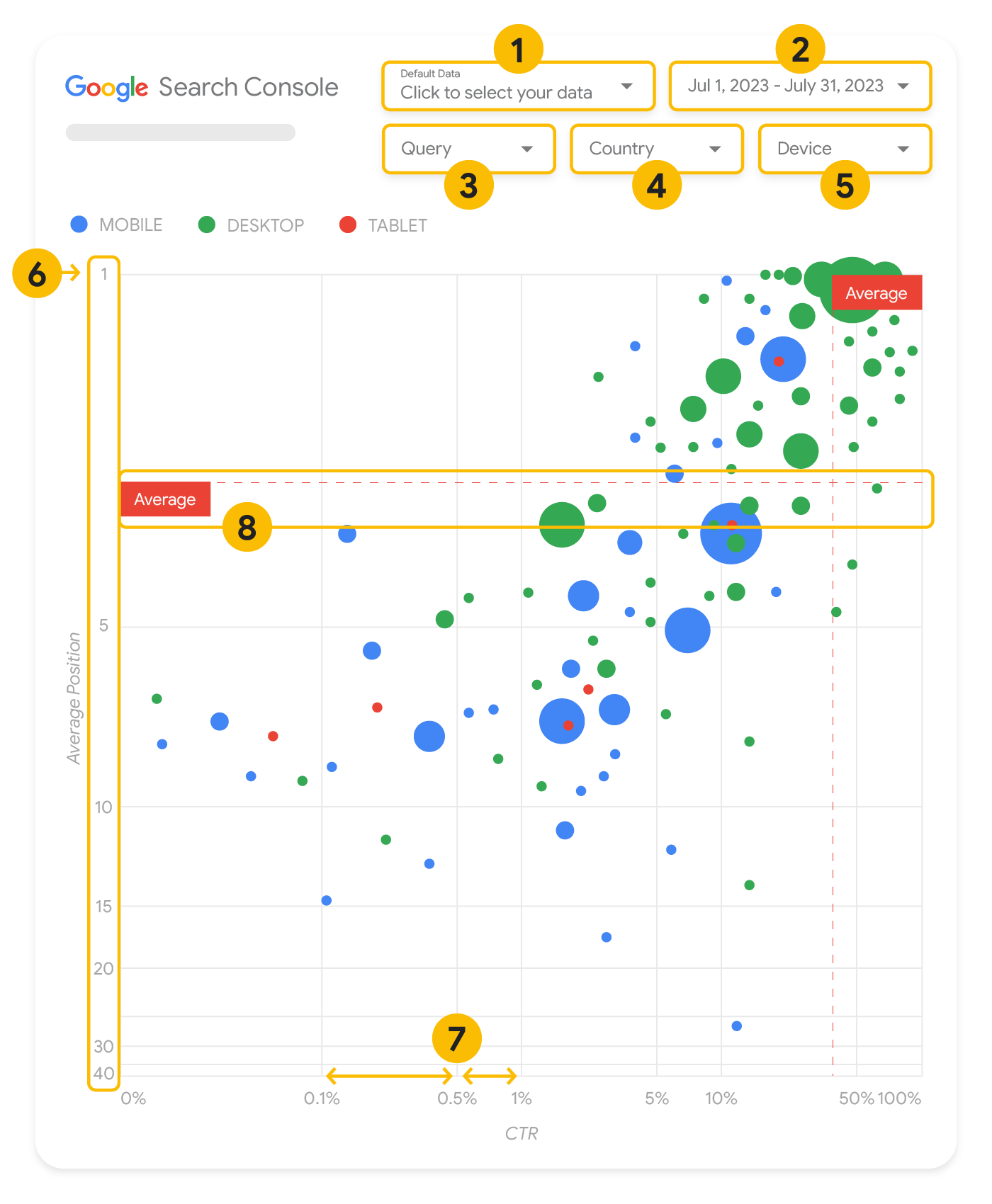
ส่วนนี้จะลงรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับองค์ประกอบบางอย่างของแผนภูมิ เพื่อชี้แจงสิ่งที่แผนภูมิแสดงและสิ่งที่ไม่ได้แสดง
แหล่งข้อมูล
แผนภูมิฟองอากาศที่แสดงในหน้านี้ใช้ตารางการแสดงผลเว็บไซต์ที่มีให้ผ่านแหล่งข้อมูลของ Search Console ซึ่งรวมถึงข้อมูลประสิทธิภาพใน Search ที่รวบรวมแยกตามเว็บไซต์และคำค้นหา
ตัวกรองและการควบคุมข้อมูล
แผนภูมิมีตัวเลือกการปรับแต่ง 5 ตัวเลือกเพื่อช่วยให้คุณควบคุมข้อมูลได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ดังนี้
- การควบคุมข้อมูล: เลือกพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ Search Console ที่ต้องการวิเคราะห์
- ช่วงวันที่: เลือกช่วงวันที่ที่ต้องการดูในรายงาน คุณจะเห็นข้อมูลในช่วง 28 วันที่ผ่านมาโดยค่าเริ่มต้น
- คำค้นหา: รวมหรือยกเว้นคำค้นหาที่ต้องการมุ่งเน้น คุณกรองข้อมูลได้เหมือนกับที่ทำใน Search Console
- ประเทศ: รวมหรือยกเว้นประเทศ
- อุปกรณ์: รวมหรือยกเว้นหมวดหมู่อุปกรณ์
แกน
แกนในแผนภูมิคืออันดับเฉลี่ย (แกน y) และ CTR ของเว็บไซต์ (แกน x) การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่สำคัญในแกนมี 3 ประการดังนี้
- กลับทิศทางของแกน Y: เนื่องจากแกน Y แสดงอันดับเฉลี่ย การกลับทิศทางจึงทำให้เลข 1 อยู่ด้านบน สำหรับแผนภูมิธส่วนใหญ่ ตำแหน่งที่ดีที่สุดจะอยู่ในมุมขวาบน การกลับทิศทางของแกน Y จึงทำให้ดูได้ง่ายขึ้นเมื่อใช้แสดงอันดับเฉลี่ย
- สเกล Log: การใช้สเกลลอการิทึม สำหรับทั้ง 2 แกนช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจคำค้นหาซึ่งอยู่ที่ปลายสุดของแผนภูมิ (CTR หรืออันดับเฉลี่ยที่ต่ำมาก หรือทั้งสองอย่าง) ได้ดีขึ้น
- เส้นอ้างอิง: เส้นอ้างอิงมีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งในการไฮไลต์ค่าที่สูงหรือต่ำกว่าเกณฑ์หนึ่งๆ การดูค่าเฉลี่ย ค่ามัธยฐาน หรือเปอร์เซ็นไทล์หนึ่งๆ จะช่วยให้เห็นค่าที่เบี่ยงเบนไปจากรูปแบบได้ชัดเจน
ฟองอากาศ
ลูกโป่งแต่ละอันในแผนภูมิแสดงถึงคำค้นหาเดียว พร้อมด้วยพร็อพเพอร์ตี้สไตล์ต่อไปนี้
- ขนาด: การแสดงจำนวนคลิกโดยใช้ขนาดฟองอากาศช่วยให้คุณเห็นได้อย่างรวดเร็วว่าคำค้นหาใดกระตุ้นการเข้าชมจำนวนมาก ยิ่งฟองอากาศมีขนาดใหญ่ก็แสดงว่าคำค้นหาสร้างการเข้าชมได้มาก
- สี: การแสดงหมวดหมู่อุปกรณ์โดยใช้สีฟองอากาศช่วยให้คุณทราบความแตกต่างระหว่างประสิทธิภาพใน Search บนอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่กับเดสก์ท็อป คุณใช้สีแทนมิติข้อมูลใดก็ได้ แต่เมื่อมีหลายค่ามากขึ้น ก็จะทำให้เห็นรูปแบบไม่ชัดเจน
การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล
เป้าหมายของการแสดงภาพนี้คือช่วยให้เห็นโอกาสในการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการค้นหา แผนภูมิประเภทนี้แสดงประสิทธิภาพของคำค้นหา โดยแกน Y แสดงอันดับเฉลี่ย แกน X แสดง CTR ขนาดฟองอากาศแสดงจำนวนการคลิกทั้งหมด และสีฟองอากาศแสดงหมวดหมู่อุปกรณ์
เส้นอ้างอิงที่เป็นเส้นประสีแดงแสดงค่าเฉลี่ยของแต่ละแกน ซึ่งแยกแผนภูมิออกเป็น 4 ส่วนที่แทนประสิทธิภาพ 4 ประเภทของคำค้นหา ส่วนเหล่านี้ในแผนภูมิของคุณอาจดูแตกต่างจากที่แชร์ในโพสต์นี้ เนื่องจากจะขึ้นอยู่กับลักษณะการกระจายการค้นหาของเว็บไซต์
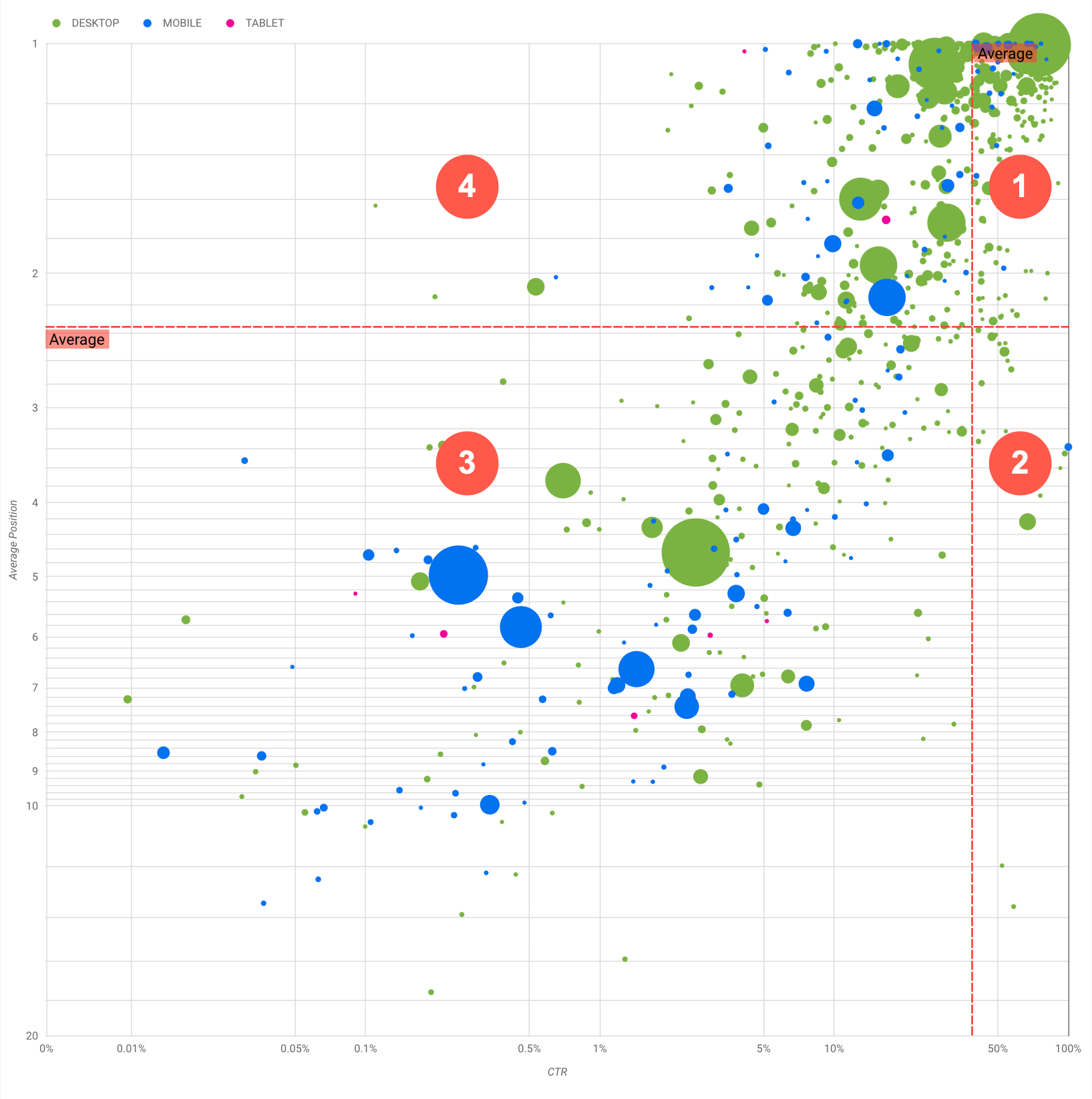
แผนภูมิแสดงกลุ่มการค้นหา 4 กลุ่มซึ่งคุณนำไปวิเคราะห์เพื่อช่วยให้ตัดสินใจได้ว่าควรลงทุนตอนไหนและลงทุนกับส่วนใดในการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของ Google Search
- อันดับสูงสุด, CTR สูง: คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องดำเนินการใดมากนักเนื่องจากประสิทธิภาพดีมากอยู่แล้ว
- อันดับต่ำ, CTR สูง: ดูเหมือนว่าคำค้นหาเกี่ยวข้องกับผู้ใช้ คำค้นหาเหล่านี้ได้รับ CTR สูงแม้ว่าจะอยู่ในอันดับต่ำกว่าคำค้นหาโดยเฉลี่ยในเว็บไซต์ หากอันดับเฉลี่ยของคำค้นหาเพิ่มขึ้น อาจส่งผลกระทบอย่างมากต่อประสิทธิภาพของคุณ โดยให้เน้นที่การปรับปรุง SEO สำหรับการค้นหาเหล่านี้ ตัวอย่างเช่น ข้อความค้นหายอดนิยมในควอแดรนท์ 2 สำหรับเว็บไซต์ด้านการทำสวนอาจเป็น "วิธีสร้างโรงไม้เก็บของ"
ตรวจสอบว่าคุณมีหน้าเว็บเกี่ยวกับเรื่องนี้แล้วหรือไม่ และดำเนินการด้วย 2 วิธีดังนี้
- หากคุณไม่มีหน้าเว็บ ให้พิจารณาสร้างหน้าเพื่อรวมข้อมูลทั้งหมดที่มีในเว็บไซต์เกี่ยวกับหัวข้อนั้นไว้ในที่เดียว
- หากคุณมีหน้าเว็บอยู่แล้ว ให้พิจารณาเพิ่มเนื้อหาเพื่อให้รองรับความต้องการของผู้ใช้ได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
- อันดับต่ำ CTR ต่ำ: เมื่อดูคำค้นหาที่มี CTR ต่ำ (ทั้งที่มีอันดับต่ำและอยู่ในตำแหน่งบนสุด) คุณควรดูที่ขนาดของฟองอากาศเพื่อให้ทราบว่าคำค้นหาใดมี CTR ต่ำแต่ยังคงกระตุ้นการเข้าชมที่สำคัญอยู่ แม้ว่าคำค้นหาในส่วนนี้อาจดูเหมือนจะไม่คุ้มกับความพยายามเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ แต่ก็แบ่งออกได้เป็น 2 กลุ่มหลักๆ ได้แก่
- คำค้นหาที่เกี่ยวข้อง: หากคำค้นหานี้สำคัญกับคุณ การปรากฏใน Search อยู่แล้วเป็นจุดเริ่มต้นที่ดี จัดลําดับความสำคัญของคำค้นหาเหล่านี้ก่อนคำค้นหาที่ไม่ปรากฏในผลการค้นหาเลย เนื่องจากจะเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพได้ง่ายกว่า
- คำค้นหาที่ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง: หากเว็บไซต์ไม่ครอบคลุมเนื้อหาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคำค้นหานี้ ก็อาจเป็นโอกาสดีที่จะปรับแต่งเนื้อหาหรือมุ่งเน้นที่คำค้นหาที่จะนำการเข้าชมที่เกี่ยวข้องมาให้
- อันดับสูงสุด, CTR ต่ำ: คำค้นหานี้อาจมี CTR ต่ำด้วยเหตุผลหลายประการ ตรวจสอบฟองอากาศที่ใหญ่ที่สุดเพื่อหาสัญญาณของสิ่งต่อไปนี้
- คู่แข่งอาจมีมาร์กอัป Structured Data ซึ่งแสดงพร้อมกับผลการค้นหาที่เป็นริชมีเดีย ซึ่งอาจดึงดูดให้ผู้ใช้คลิกผลการค้นหานั้นแทนที่จะเป็นผลการค้นหาของคุณ ลองเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพให้องค์ประกอบภาพทั่วไปใน Google Search
- คุณอาจได้เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพหรือมีการจัดอันดับ "โดยไม่ตั้งใจ" สำหรับคำค้นหาที่ผู้ใช้ไม่สนใจซึ่งเกี่ยวข้องกับเว็บไซต์ของคุณ กรณีนี้อาจไม่เป็นปัญหาสำหรับคุณ ซึ่งคุณไม่จำเป็นต้องสนใจคำค้นหาเหล่านั้น หากไม่ต้องการให้ผู้ใช้ค้นพบคุณผ่านคำค้นหาเหล่านั้น (เช่น การค้นหาที่มีคำที่ไม่เหมาะสม) ให้ลองปรับแต่งเนื้อหาของคุณเพื่อนำการพูดถึงที่อาจมองว่าเป็นคำพ้องความหมายหรือคำค้นหาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคำที่นำการเข้าชมมาออกไป
- ผู้ใช้อาจพบข้อมูลที่ต้องการแล้ว เช่น เวลาทำการ ที่อยู่ หรือหมายเลขโทรศัพท์ของบริษัท ตรวจสอบการค้นหาที่ใช้และ URL ที่มีข้อมูล หากเป้าหมายหนึ่งของเว็บไซต์คือการกระตุ้นให้ผู้คนไปที่ร้านค้า ก็จะเป็นการทำงานได้ตามที่ตั้งใจไว้ หากคุณเชื่อว่าผู้คนควรเข้าชมเว็บไซต์ของคุณเพื่อดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ให้ลองเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพชื่อและคำอธิบายให้ชัดเจน ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ที่หัวข้อถัดไป
เรายังไม่ได้พูดถึงหมวดหมู่อุปกรณ์ เนื่องจากสามารถใช้เป็นสัญญาณเพิ่มเติมของประสิทธิภาพการค้นหาได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น สมมติว่าการค้นหาบางรายการมีความเกี่ยวข้องมากขึ้นเมื่อผู้ใช้ใช้การกำลังนำทางบนถนน พยายามหาตำแหน่ง ในกรณีนั้น คำค้นหาอาจมีประสิทธิภาพสูงในอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่ แต่ประสิทธิภาพต่ำในเดสก์ท็อป
การปรับปรุง SEO สำหรับคำค้นหาที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
เมื่อคุณพบข้อความค้นหาที่คุ้มค่ากับเวลาและความพยายามแล้ว ให้เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพหรือสร้างหน้าเว็บที่เกี่ยวข้องกับข้อความค้นหาเหล่านั้น
หลังจากพบการค้นหาโดยใช้การแสดงภาพที่แสดงในหน้านี้แล้ว คุณจะสร้างตัวกรองการค้นหาสำหรับคำค้นหาที่เจาะจงโดยใช้อินเทอร์เฟซผู้ใช้ของ Search Console หรือสร้างตาราง Pivot ได้ โดยใช้ Looker Studio จากทั้ง 2 วิธี คุณสามารถตรวจสอบหน้าเว็บทุกหน้าที่ได้รับการเข้าชมสำหรับข้อความค้นหาหนึ่งๆ หลังจากทราบคำค้นหาที่ต้องการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและ URL ที่เกี่ยวข้องแล้ว ให้ใช้คู่มือ SEO สำหรับมือใหม่เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเนื้อหา มาดูเคล็ดลับบางส่วนกัน
- ตรวจสอบว่าองค์ประกอบชื่อ เมตาแท็กคำอธิบาย และแอตทริบิวต์ Alt นั้นสื่อความหมาย มีความเจาะจง และถูกต้อง
- ใช้องค์ประกอบส่วนหัวเพื่อเน้นข้อความสำคัญและช่วยให้เนื้อหามีโครงสร้างตามลำดับชั้น เพื่อให้ผู้ใช้และเครื่องมือค้นหาไปยังส่วนต่างๆ ในเอกสารได้ง่ายขึ้น
- ลองนึกถึงคำอื่นๆ ที่ผู้ใช้อาจใช้ค้นหาเนื้อหาของคุณ เช่น คำพ้องความหมายและคำค้นหาที่เกี่ยวข้อง ขอแนะนำให้ใช้เครื่องมือวางแผนคีย์เวิร์ดของ Google Ads เพื่อช่วยค้นหาคีย์เวิร์ดรูปแบบใหม่ๆ และดูปริมาณการค้นหาโดยประมาณของคีย์เวิร์ดแต่ละรายการ คุณยังใช้ Google เทรนด์เพื่อหาไอเดียจากหัวข้อที่กําลังเป็นที่นิยมและคำค้นหาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับเว็บไซต์ของคุณได้อีกด้วย
