تحسين محركات البحث باستخدام رسم بياني فقاعي على Search Console
يُعدّ تحليل بيانات الأداء على "بحث Google" عملية صعبة، وتزداد صعوبة عندما يكون هناك العديد من طلبات البحث الأقل تكرارًا أو استخدامًا والتي يصعب عرضها بشكل مرئي وفهمها. وبالتالي، بإمكان الرسم البياني الفقاعي مساعدتك في التعرّف على طلبات البحث التي تحقق أداءً جيدًا بالنسبة إلى موقعك الإلكتروني وتلك التي يمكن تحسين أدائها.
إذا أردت اختبار الأساليب الموضّحة هنا، يمكنك ربط بياناتك بـ Looker Studio وإجراء أي تعديلات تريدها على الإعدادات.
ننصحك بقراءة المحتوى الذي نوفره حول ربط خدمة Search Console بأداة Looker Studio وتتبُّع عدد الزيارات الواردة من محرّك بحث Google باستخدام أداة Looker Studio إذا لم يسبق لك قراءته، لأنّ ذلك يتيح لك معرفة المزيد حول الإجراءات التي يمكنك تنفيذها في Search Console باستخدام أداة Looker Studio.
فهم الرسم البياني
يشكّل الرسم البياني الفقاعي طريقة رائعة لعرض البيانات بشكل مرئي إذا كانت لديك عدة مقاييس وسمات، لأنّه يتيح لك الاطّلاع على العلاقات والأنماط في بياناتك على نحو أكثر فعالية. في المثال المعروض هنا، يمكنك رؤية نسبة النقر إلى الظهور (CTR) ومتوسط موضع الظهور وعدد النقرات الخاصة بِسمتَي طلب البحث والجهاز في الوقت نفسه.
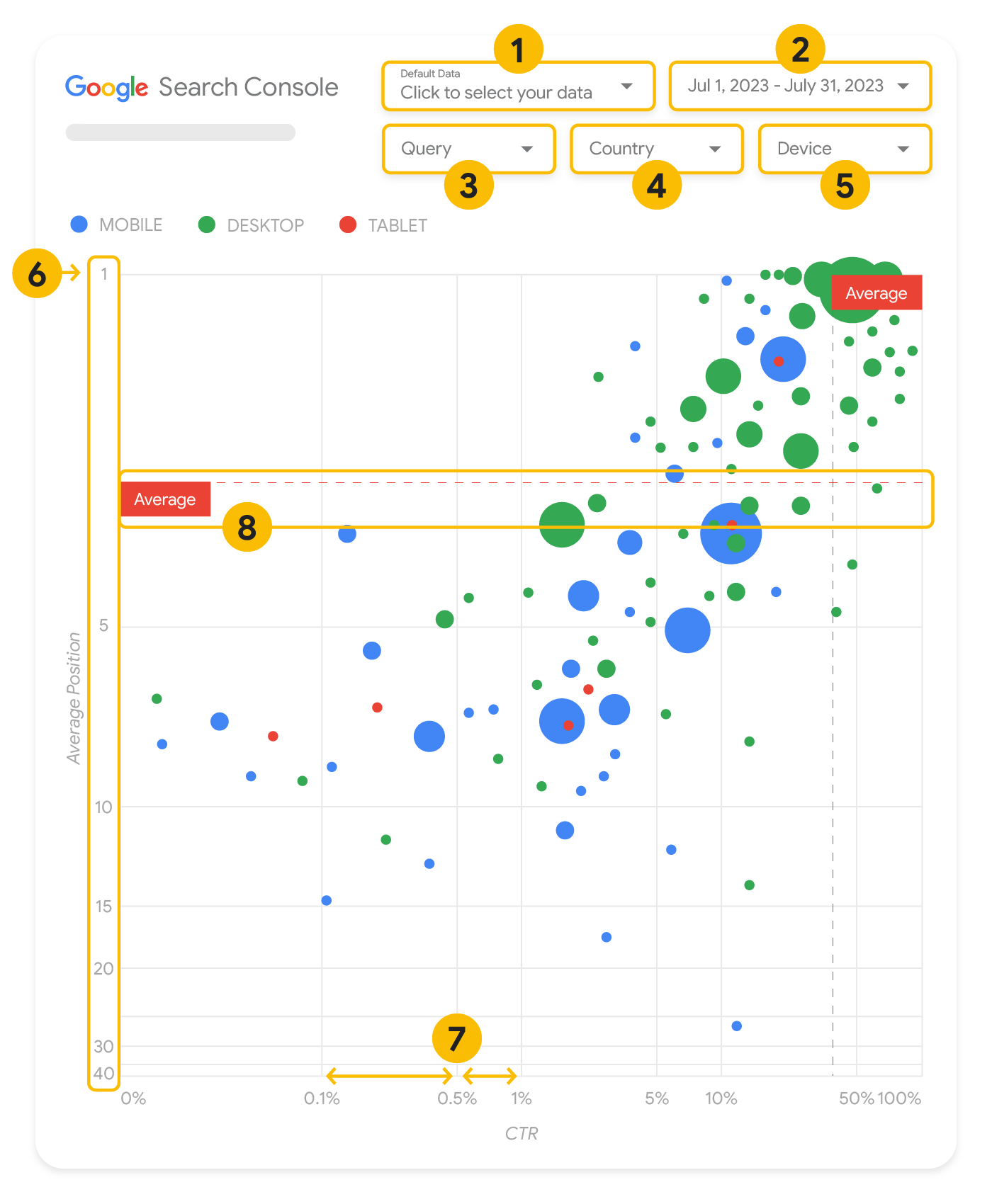
تتناول هذه الفقرة بالتفصيل بعض عناصر الرسم البياني لتوضيح البيانات التي تظهر فيه وتلك التي لا تظهر.
مصدر البيانات
يستخدِم الرسم البياني الفقاعي المعروض في هذه الصفحة جدول "عدد مرات ظهور الموقع الإلكتروني" المتاح من خلال مصدر البيانات في Search Console، وهو يتضمن بيانات الأداء على "بحث Google" التي تم تجميعها حسب الموقع الإلكتروني وطلبات البحث.
الفلاتر وعناصر التحكم في البيانات
تتوفر خمسة خيارات تخصيص في الرسم البياني لمساعدتك في التحكم بالبيانات بشكلٍ فعّال:
- التحكّم بالبيانات: يتيح لك اختيار الموقع الإلكتروني على Search Console الذي تريد تحليل بياناته.
- النطاق الزمني: يتيح لك تحديد النطاق الزمني الذي تريد عرضه في التقرير. حسب الإعدادات التلقائية، يتم عرض آخر 28 يومًا.
- طلب البحث: يتيح لك تضمين أو استبعاد طلبات بحث معيّنة بهدف التركيز عليها. يمكنك فلترة بياناتك بشكل مشابه للطريقة التي تتّبعها في Search Console.
- البلد: يتيح لك تضمين بلدان محددة أو استبعادها.
- الجهاز: يتيح لك تضمين فئات أجهزة محددة أو استبعادها.
المحوران في الرسم البياني
يتضمن الرسم البياني محورَين، هما متوسط موضع الظهور (المحور الصادي) ونسبة النقر إلى الظهور الخاصة بالموقع الإلكتروني (المحور السيني). وقد أجرينا ثلاثة تغييرات مهمة فيهما:
- الاتجاه العكسي للمحور الصادي: بما أنّ المحور الصادي يعرض متوسط موضع الظهور، سيؤدي عكسه إلى أن يصبح الرقم 1 في الأعلى. في معظم الرسومات البيانية، يكون الموضع الأفضل في الزاوية العليا اليمنى، لذا من الأسهل أن يتم عكس المحور الصادي عند استخدامه لعرض متوسط موضع الظهور.
- المقياس اللوغاريتمي: يتيح لك استخدام المقياس اللوغاريتمي على كِلا المحورَين إمكانية التعرّف بشكل أفضل على طلبات البحث الظاهرة في طرفَي الرسم البياني (التي تكون فيها قيمة نسبة النقر إلى الظهور أو قيمة متوسط موضع الإعلان منخفضة جدًا أو تكون كلتا القيمتين منخفضتَين).
- الخطوط المرجعية: يساعدك الخط المرجعي في إبراز القيم الواقعة فوق حدّ معيّن أو أدنى منه. وعند الاطّلاع على المعدّل أو المتوسّط أو قيمة مئوية محددة، قد تظهر الانحرافات عن النمط بشكل واضح.
الفقاعات التفسيرية
تمثّل كل فقاعة تفسيرية في الرسم البياني طلب بحث واحدًا يشمل سمتَين للنمط:
- الحجم: إنّ استخدام عدد النقرات لتمثيل حجم الفقاعة التفسيرية يساعدك في الاطّلاع سريعًا على طلبات البحث التي تحقق العدد الأكبر من الزيارات، إذ كلما كبر حجم الفقاعة، ازداد عدد الزيارات الناتجة عن طلب البحث.
- اللون: إنّ استخدام فئة الجهاز لتمثيل لون الفقاعة التفسيرية يمكن أن يساعدك في معرفة الاختلافات بين أداء الموقع الإلكتروني على "بحث Google" لكلّ من أجهزة الكمبيوتر المكتبي والأجهزة الجوّالة. يمكنك استخدام أي سمة لتمثيل اللون، ولكن عندما يزداد عدد القيم، يصبح التعرّف على الأنماط أكثر صعوبة.
تحليل البيانات
الهدف من هذا التمثيل المرئي هو مساعدتك في التعرّف على أي فرص متاحة لتحسين أداء طلبات البحث. يعرض الرسم البياني أداء طلبات البحث، حيث يمثّل المحور الصادي متوسط موضع الظهور ويمثّل المحور السيني نسبة النقر إلى الظهور، في حين يمثّل حجم الفقاعة إجمالي عدد النقرات، ويمثّل لونها فئة الجهاز.
يعرض الخطّان المرجعيان المتقطعان المرسومان باللون الأحمر (باسم Average) القيمة المتوسطة لكل محور، ويقسّمان الرسم البياني إلى أربعة أقسام تعرض أربعة أنواع من الأداء الخاص بطلبات البحث. من المرجّح أن تبدو الأقسام الأربعة في الرسم البياني الخاص بك بشكل مختلف عن الأقسام المعروضة في هذه المشاركة، إذ إنّها تستند إلى كيفية توزيع طلبات البحث الخاصة بموقعك الإلكتروني.

يعرض الرسم البياني أربع مجموعات من طلبات البحث، ويمكنك تحليلها لتساعدك في تحديد الجانب الذي من المجدي تخصيص الوقت له عند تحسين أداء موقعك الإلكتروني على "بحث Google".
- موضع مرتفع ونسبة نقر إلى ظهور مرتفعة: ما مِن حاجة إلى بذل الكثير من الجهد، لأنّ الأداء جيّد.
- موضع منخفض ونسبة نقر إلى ظهور مرتفعة: يبدو أنّ طلبات البحث هذه ذات صلة باهتمامات المستخدمين، لأنّها تحصل على نسبة نقر إلى ظهور مرتفعة
حتى عندما يكون موضع الظهور أدنى
من متوسّط طلبات البحث على موقعك الإلكتروني. إذا ارتفع متوسط موضع الظهور الخاص بطلبات البحث هذه، قد يكون لذلك
تأثير مهم على أداء موقعك الإلكتروني، لذا ركِّز على تحسين محركات البحث استجابةً لطلبات البحث هذه. على سبيل المثال،
أحد طلبات البحث الأكثر رواجًا في القسم 2 من الرسم البياني بالنسبة إلى موقع إلكتروني مخصص للعناية بالحدائق هو "كيفية بناء كوخ خشبي".
تحقَّق ممّا إذا كان موقعك الإلكتروني يتضمّن صفحة تعرض معلومات ذات صلة بطلب البحث هذا، ثم تابِع العمل بإحدى هاتين الطريقتين:
- إذا لم تتوفّر لديك صفحة مماثلة، ننصحك بإنشاء صفحة تجمع في مكان مركزي كل المعلومات المتاحة على موقعك الإلكتروني حول هذا الموضوع.
- إذا كان موقعك الإلكتروني يضم صفحة مماثلة، ننصحك بإضافة محتوى إليها بهدف تلبية احتياجات المستخدمين بشكل أفضل.
- موضع منخفض ونسبة نقر إلى ظهور منخفضة: عند عرض طلبات البحث التي لديها نسبة نقر إلى ظهور منخفضة (سواء كان موضع الظهور منخفضًا أو مرتفعًا)، من المهم ملاحظة حجم الفقاعات التفسيرية لمعرفة طلبات البحث
التي لديها نسبة نقر إلى ظهور منخفضة ولكنّها تجذب عددًا كبيرًا من الزيارات. قد يبدو أنّ طلبات البحث الظاهرة في هذا
القسم لا تستحق بذل أي مجهود لتحسينها، ولكن يمكن تقسيمها إلى مجموعتَين:
- طلبات البحث ذات الصلة: إذا كان طلب البحث المعني مهمًا بالنسبة إليك، يمكنك اعتبار ظهوره في "بحث Google" إشارة جيدة للبدء. امنح أولوية أكبر لطلبات البحث هذه مقارنةً بطلبات البحث التي لا تظهر في "بحث Google" إطلاقًا، لأنّه من الأسهل تحسين طلبات البحث الظاهرة.
- طلبات البحث غير المرتبطة بموقعك الإلكتروني: إذا لم يكُن موقعك الإلكتروني يعرض محتوى ذا صلة بطلب البحث هذا، ننصحك بتحسين المحتوى الذي تعرضه والتركيز على طلبات البحث التي من شأنها جذب زيارات ذات صلة بذلك المحتوى.
- موضع مرتفع ونسبة نقر إلى الظهور منخفضة: قد تكون نسبة النقر إلى الظهور الخاصة بطلبات البحث هذه منخفضة لعدة أسباب. تحقَّق من
الفقاعات التفسيرية الأكبر حجمًا للعثور على إشارات ذات صلة بما يلي:
- قد يكون منافسوك يستخدمون ترميز البيانات المنظّمة ويعرضون المحتوى ضمن النتائج الغنية بصريًا، ما قد يجذب المستخدمين إلى النقر على تلك النتائج بدلاً من النتائج الذي يعرضها موقعك الإلكتروني. ننصحك بتحسين المحتوى الذي تعرضه ليتوافق مع العناصر المرئية الأكثر شيوعًا في "بحث Google".
- قد تكون أجريت تحسينات أو حصلت على ترتيب عن طريق "الخطأ" لطلب بحث لا يهم المستخدمين في ما يتعلّق بموقعك الإلكتروني. قد لا يكون في ذلك أي مشكلة بالنسبة إليك، وفي تلك الحالة، يمكنك تجاهل طلبات البحث هذه. أما إذا كنت تفضّل ألّا يعثر عليك المستخدمون من خلال طلبات البحث هذه (لأنّها تتضمّن كلمات مسيئة على سبيل المثال)، حاوِل إجراء تعديلات على المحتوى الخاص بك لإزالة أي عبارات قد يتم تصنيفها على أنّها مرادفة لطلبات البحث التي تجذب هذه الزيارات أو ذات صلة بها.
- قد يكون المستخدمون سبق أن عثروا على المعلومات التي يحتاجون إليها، مثل ساعات العمل في شركتك أو عنوانها أو رقم الهاتف الخاص بها. اطّلِع على عبارات البحث التي تم استخدامها وعناوين URL التي تضمّنت المعلومات المطلوبة. إذا كان أحد أهداف موقعك الإلكتروني هو جذب المستخدمين إلى متاجرك، يعني ذلك أنّك على الطريق الصحيح. أما إذا كنت تفضّل أن ينتقل المستخدمون إلى موقعك الإلكتروني للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات، فننصحك بالإشارة إلى ذلك بوضوح من خلال تحسين العناوين والأوصاف في موقعك. لمزيد من التفاصيل، انتقِل إلى الفقرة التالية.
لم نذكر فئات الأجهزة لأنّها قد تُستخدَم كإشارات إضافية بخصوص أداء طلبات البحث. على سبيل المثال، قد تكون بعض طلبات البحث أكثر صلة بالمستخدمين الذين يتنقلون في الشارع محاولين العثور على موقع جغرافي محدّد. وفي تلك الحالة، قد يكون أداء طلب البحث عاليًا على الأجهزة الجوّالة ومنخفضًا على أجهزة الكمبيوتر المكتبي.
تحسين محركات البحث استجابةً لطلبات بحث محدّدة
بعد العثور على طلبات البحث التي تستحق بذل الوقت والمجهود، احرص على تحسين صفحاتك بما يتوافق معها أو إنشاء صفحات ذات صلة بها.
بعد العثور على طلبات البحث المناسبة باستخدام العرض المرئي الظاهر في هذه الصفحة، يمكنك إنشاء فلتر طلب بحث خاص بطلبات بحث محدَّدة باستخدام واجهة المستخدم في Search Console، أو إنشاء جدول محوري باستخدام أداة Looker Studio، وتتيح لك كلتا الطريقتين الاطّلاع على جميع الصفحات التي تتلقّى زيارات استجابةً لطلب بحث محدَّد. بعد تحديد طلبات البحث التي تريد تحسينها وعناوين URL ذات الصلة بها، استخدِم دليل تحسين نتائج محرّكات البحث للمبتدئين بهدف تحسين المحتوى الذي تعرضه. إليك بعض النصائح:
- احرص على أن تكون عناصر العناوين والعلامات الوصفية وسمات النص البديل وصفية ومحددة ودقيقة.
- استخدِم عناصر العناوين لتسليط الضوء على النص المهم والمساعدة في إنشاء بنية هرمية للمحتوى، ما يسهّل على المستخدمين ومحرّكات البحث إمكانية التنقّل بين أقسام المستند.
- ننصحك بالتفكير في كلمات إضافية قد يبحث عنها المستخدم للعثور على محتوى معروض على موقعك الإلكتروني، على سبيل المثال، المرادفات وطلبات البحث ذات الصلة بالمحتوى. يمكنك استخدام أداة تخطيط الكلمات الرئيسية المقدَّمة من "إعلانات Google" لمساعدتك في التعرّف على صيغ جديدة من الكلمات الرئيسية والاطّلاع على حجم البحث التقريبي لكل كلمة رئيسية. يمكنك أيضًا استخدام مؤشرات Google للاطّلاع على أفكار جديدة من خلال المواضيع والطلبات الرائجة ذات الصلة بموقعك الإلكتروني.
