Search Console のバブルチャートで SEO を改善する
検索パフォーマンス データの分析は常に困難なものですが、視覚化や解釈が難しいロングテール クエリが多い場合には、さらに分析が困難になります。サイトのパフォーマンスが高いクエリや改善の余地があるクエリを把握するのには、バブルチャートが役立ちます。
ここで説明した手法を試す場合には、Looker Studio にデータを接続し、チャートの設定を調節できます。
Search Console と Looker Studio を接続するおよび Looker Studio を使用して検索トラフィックをモニタリングするをご覧になっていない場合は、まずそちらをご確認ください。Looker Studio の Search Console で何ができるのか、理解が深まります。
チャートの見方
バブルチャートは、データの関係性とパターンをより効果的に確認できるため、指標とディメンションが複数ある場合には優れた視覚化方法です。この例では、クエリとデバイスのディメンションに対するクリック率(CTR)、平均掲載順位、クリック数を 1 つのビューで表示しています。
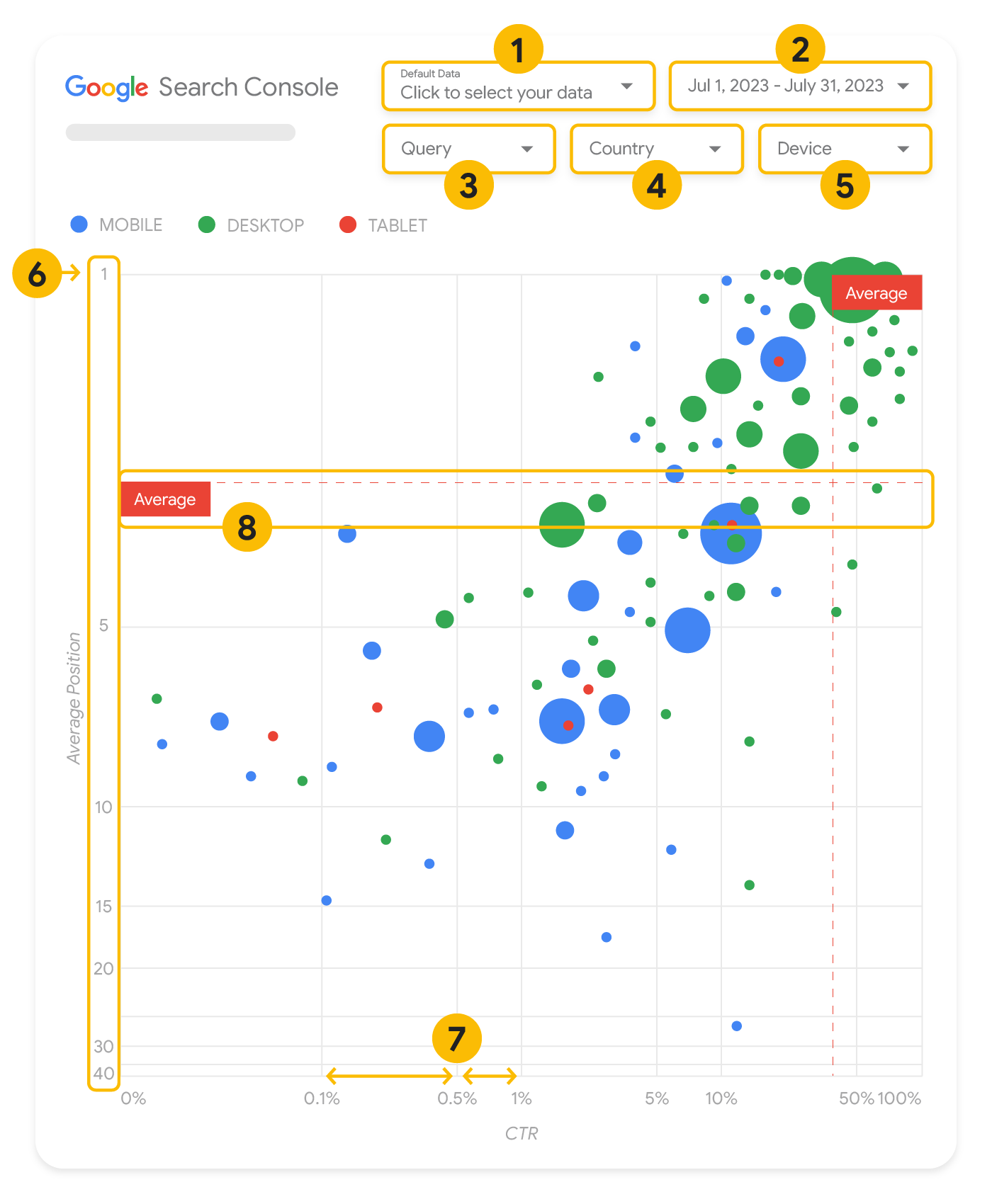
このセクションでは、チャートに表示されるものと表示されないものを明確にするために、チャートの一部の要素を詳しく説明します。
データソース
このページのバブルチャートには、Search Console のデータソースから入手できるサイトのインプレッション テーブルが使用されており、サイトとクエリごとに集計された検索パフォーマンスのデータが含まれています。
フィルタとデータ管理
このチャートには、データを効果的に管理するための 5 つのカスタマイズ オプションがあります。
- データ管理: 分析する Search Console プロパティを選択します。
- 期間: レポートに含める期間を選択します。デフォルトでは過去 28 日間に設定されています。
- クエリ: 注目したいクエリを追加または除外できます。Search Console で行うのと同様にデータをフィルタできます。
- 国: 国を追加または除外できます。
- デバイス: デバイス カテゴリを追加または除外できます。
軸
このチャートで軸となるのは、平均掲載順位(y 軸)とサイトのクリック率(x 軸)です。軸には重要な調整を 3 つ加えています。
- y 軸を反転する: y 軸は平均掲載順位を示すため、反転することで 1 が上になります。ほとんどのチャートでは最も良好な状態が右上に来るため、平均掲載順位を表示する場合は y 軸を反転したほうが理解しやすくなります。
- 対数目盛: 両軸で対数目盛を使用すると、チャートの端に位置するクエリ(クリック率と平均掲載順位のどちらかが、または両方が非常に低い)が把握しやすくなります。
- 基準線: 基準線は、特定のしきい値を上回る値、または下回る値を目立たせるのに役立ちます。平均、中央値、または特定のパーセンタイルを確認することで、パターンからの逸脱に注目できます。
バブル
チャートの各バブルは、次のスタイル プロパティに基づいて 1 つのクエリを表しています。
- サイズ: クリック数をバブルのサイズとして使用することで、大量のトラフィックの発生源となっているクエリを一目で確認できます。バブルが大きいほど、クエリで生成されるトラフィックが多くなります。
- 色: デバイス カテゴリによってバブルの色を変えることで、モバイルとパソコンにおける検索のパフォーマンスの違いを把握しやすくなります。どのディメンションにも色を設定できますが、値の数が増えると、パターンを認識するのが難しくなります。
データの分析
こういった可視化を行う目的は、クエリを最適化するためのチャンスを見つけることにあります。チャートはクエリのパフォーマンスを示しています。y 軸は平均掲載順位、x 軸はクリック率、バブルのサイズはクリック数の合計、バブルの色はデバイス カテゴリを表しています。
赤い破線で示した「平均」基準線は各軸の平均値を示しています。これによりチャートが 4 つの領域に分割され、4 種類のクエリのパフォーマンスが示されます。実際の 4 つの領域は、サイトクエリの分布によって異なるため、この投稿で紹介しているものと同じように分割されるとは限りません。
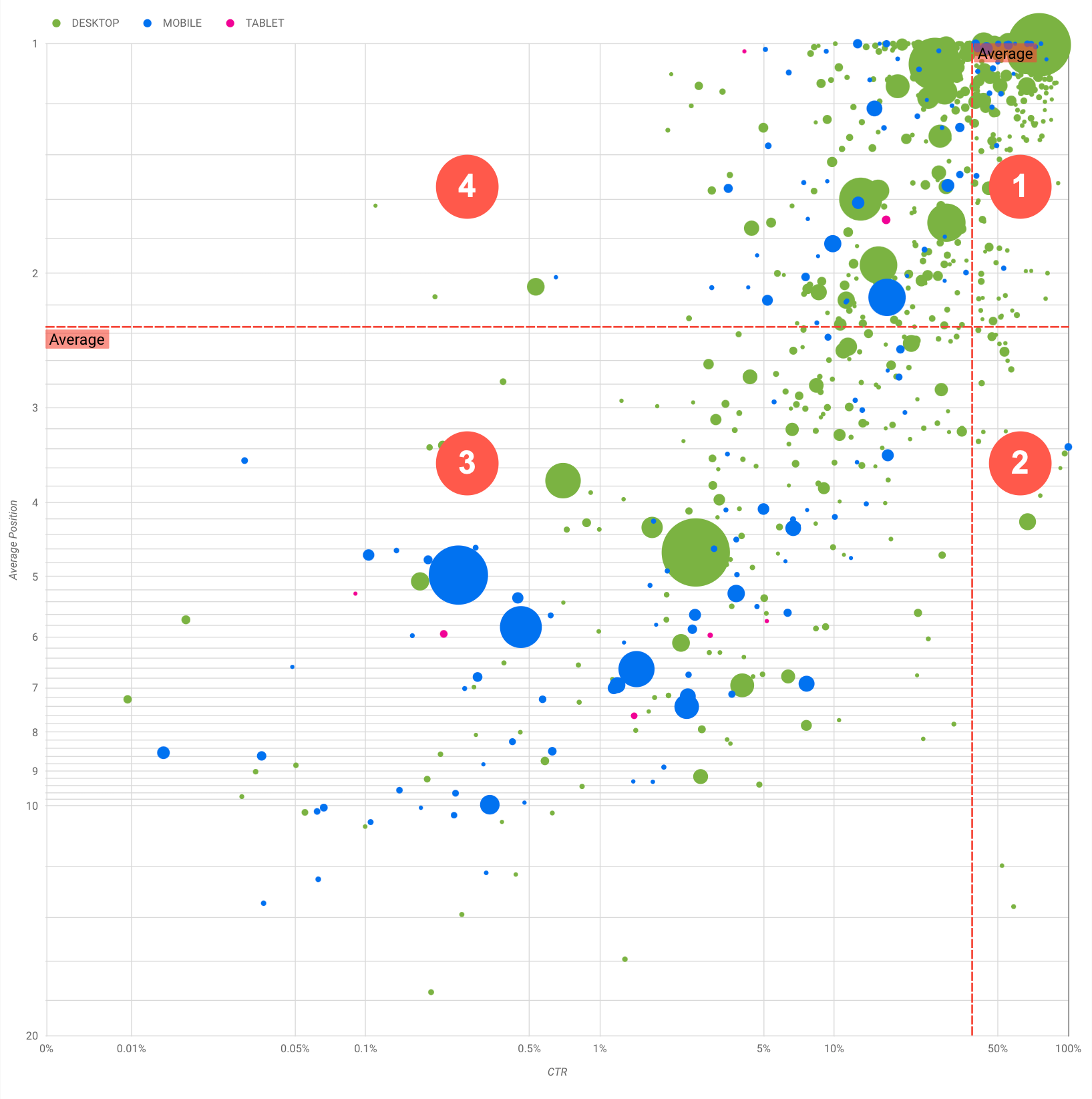
このチャートには 4 つのクエリグループが示されており、これを分析することで、Google 検索のパフォーマンスを最適化する際にどこに重点を置くべきか判断できます。
- 掲載順位とクリック率の両方が高い: すでにパフォーマンスは良好です。必要な作業は特にありません。
- 掲載順位が低くクリック率が高い: ユーザーとの関連性が高いクエリであると考えられます。ウェブサイトの平均的なクエリより掲載順位が低くても、高いクリック率が得られます。クエリの平均掲載順位が上がるとパフォーマンスに大きく影響する可能性があるため、SEO の改善に注力してください。たとえば、ガーデニングについてのウェブサイトの第 2 領域で「木造小屋の作り方」が最上位のクエリだったとします。これに関するページがすでに存在するかどうかを確認し、次のように進めてください。
- ページが存在しない場合は、そのテーマに関するウェブサイト内の情報をすべて集約し、新たなページを作成することを検討してください。
- ページが存在する場合は、より柔軟にユーザーのニーズに対応できるよう、コンテンツを追加することを検討してください。
- 掲載順位とクリック率の両方が低い: クリック率が低いクエリ(掲載順位の高低にかかわらず)を調べる場合、バブルのサイズを見て、クリック率が低いにもかかわらず大量のトラフィックの発生源となっているクエリに注目してください。この領域に分布するクエリに労力を割くのは無駄のように思えるかもしれませんが、このクエリは 2 つのグループに分けることができます。
- 関連クエリ: 問題のクエリがサイトにとって重要である場合、そのクエリがすでに検索結果に表示されているのは有利です。検索結果にまったく表示されないクエリと比べて最適化は容易なので、これらのクエリの最適化を優先しましょう。
- 無関係なクエリ: サイトがクエリに関連するコンテンツを掲載していない場合、コンテンツを微調整したり、関連性の高いトラフィックをもたらすクエリに焦点を当てたりするチャンスかもしれません。
- 掲載順位が高くクリック率が低い: この手のクエリのクリック率が低くなる理由はさまざまです。特にサイズが大きなバブルを確認し、以下の傾向がないかを調べます。
- 競合相手のサイトが構造化データのマークアップやリッチリザルトの表示を取り入れて、よりユーザーを引き付けてクリックを促すものになっている可能性があります。Google 検索の視覚要素を最も一般的なものに最適化することを検討してください。
- サイトに関心のないユーザーのクエリに対して最適化してしまったか、「意図せずに」順位が上がった可能性があります。必ずしもサイトにとって問題があるわけではないので、このようなクエリは無視することもできます。このようなクエリで検索されることを望まない場合(不適切なワードが含まれているなど)は、コンテンツを微調整し、トラフィックをもたらすクエリの類義語や関連クエリと見なされる表現を削除してみてください。
- ユーザーが、会社の営業時間、住所、電話番号など必要な情報をすでに入手していたことが考えられます。使用されていたクエリ、情報が含まれている URL を確認してください。ウェブサイトの目的の一つが集客であるのなら狙いどおりに機能していることになりますが、その他の情報提供に力を入れたい場合は、タイトルや説明を最適化して目的を明確にしましょう。詳しくは、次のセクションをご覧ください。
デバイスのカテゴリについては、クエリ パフォーマンスの付加的な傾向として使用されることがあるため、言及してきませんでした。たとえば、移動中の人が路上で場所を検索する際に関連性の深いクエリがあるとします。そのような場合、モバイル デバイスでは高いパフォーマンスを発揮するクエリでも、パソコンではパフォーマンスが下がることがあります。
特定のクエリに対する SEO を改善する
時間と労力をかけるのに値するクエリを見つけたら、そのクエリに関連するページを最適化するか作成してください。
このページに掲載した可視化手法を使用してクエリを見つけたら、Search Console のユーザー インターフェースを使用して特定のクエリに対するクエリフィルタを作成できます。または、Looker Studio を使用してピボット テーブルを作成することもできます。どちらの方法でも、特定のクエリに対するトラフィックを獲得しているすべてのページを確認することが可能です。最適化の対象となるクエリと関連 URL を確認したら、SEO スターター ガイドを使用してコンテンツを最適化します。以下にいくつかのヒントをご紹介します。
- title 要素、description メタタグ、および alt 属性が、わかりやすく具体的で正確であることを確認してください。
- 見出し要素を使用して重要なテキストを強調し、コンテンツの階層構造を作成すると、ユーザーと検索エンジンがドキュメント内を移動しやすくなります。
- ユーザーがコンテンツを探すときに、他にも検索しそうなキーワード(類義語や関連クエリなど)がないか考えてみましょう。Google 広告が提供しているキーワード プランナーを使用すると、新しいキーワードのバリエーションを見つけたり、各キーワードのおおよその検索ボリュームを確認したりできます。Google トレンドを使用して、急上昇のトピックやウェブサイトに関連するクエリからアイデアを見つけることもできます。
