In diesem Dokument erhalten Sie einen allgemeinen Überblick über die Google Tag Manager API.
Einführung
Die Google Tag Manager API bietet autorisierten Nutzern Zugriff auf Google Tag Manager-Konfigurationsdaten. Mit dieser API können Sie Folgendes verwalten:
- Konten
- Container
- Ziele
- Arbeitsbereiche
- Google-Tag-Konfiguration
- Tags
- Trigger
- Ordner
- Integrierte Variablen
- Kunden
- Variablen
- Containerversionen
- Containerversionsheader
- Nutzerberechtigungen
- Umgebungen
Erste Schritte
Möchten Sie gleich beginnen? Lesen Sie das Entwicklerhandbuch. Jede Anwendung, die die API verwendet, muss einige Schritte ausführen, um den Nutzer zu registrieren, zu autorisieren und mit der API zu arbeiten. Der Entwicklerleitfaden führt Sie durch die einzelnen Schritte. Am Ende haben Sie eine funktionierende Anwendung, die Sie anpassen können.
Konzeptübersicht
Die API stellt mehrere Google Tag Manager-Konfigurationsentitäten bereit, die hierarchisch organisiert sind. Das Konto jedes Nutzers kann einen oder mehrere Container haben, von denen jeder einen oder mehrere Arbeitsbereiche haben kann. Ein Arbeitsbereich ermöglicht mehrere gleichzeitige Änderungen an den Variablen, integrierten Variablen, Triggern, Ordnern und Tags eines Containers. Nachdem Sie die gewünschten Änderungen am Arbeitsbereich vorgenommen haben, können Sie eine Version erstellen, in der Vorschau anzeigen und veröffentlichen. Mit einer Ressource vom Typ „Permission“ können Sie Nutzerberechtigungen auf Kontoebene verwalten. Das folgende Diagramm zeigt die hierarchischen Beziehungen zwischen den Entitäten:
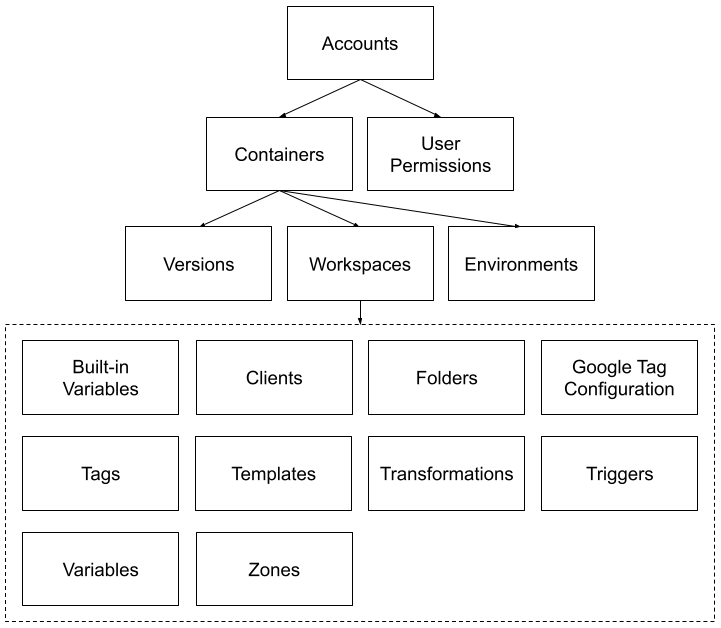
Die Google Tag Manager API stellt jede der Entitäten als Ressource bereit. Eine Liste von Ressourcen einer bestimmten Art bildet eine Sammlung. Die API stellt jede Sammlung in einem URI bereit, der abgefragt werden kann, um die Liste der darin enthaltenen Entitäten zurückzugeben.
Eine detaillierte Beschreibung der Methoden in der API und der zurückgegebenen Daten finden Sie in der Tag Manager API-Referenz.
Kontingentrichtlinien
Über die Google Tag Manager API werden Millionen von Vorgängen ausgeführt. Um zu verhindern, dass das System mehr Vorgänge erhält, als es verarbeiten kann, und um eine gleichmäßige Verteilung der Systemressourcen zu gewährleisten, ist ein Kontingentsystem erforderlich. Informationen zu spezifischen Limits finden Sie im Leitfaden zu Limits und Kontingenten.
Nächste Schritte
Ressourcen mit weiteren Informationen zur API:
- Informationen zur Verwendung der API finden Sie im Entwicklerhandbuch.
- Sehen Sie sich die Tag Manager API-Referenz an, um sich mit Tag Manager-Ressourcen und verfügbaren Vorgängen vertraut zu machen.